Leetcode-1631 最小体力消耗路径 - 并查集
题目描述
你准备参加一场远足活动。给你一个二维 rows x columns 的地图 heights ,其中 heights[row][col] 表示格子 (row, col) 的高度。一开始你在最左上角的格子 (0, 0) ,且你希望去最右下角的格子 (rows-1, columns-1) (注意下标从 0 开始编号)。你每次可以往 上,下,左,右 四个方向之一移动,你想要找到耗费 体力 最小的一条路径。
一条路径耗费的 体力值 是路径上相邻格子之间 高度差绝对值 的 最大值 决定的。
请你返回从左上角走到右下角的最小 体力消耗值 。
示例 1:
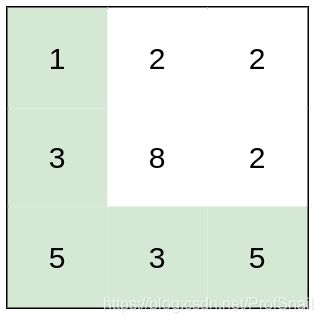
输入:heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]]
输出:2
解释:路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 连续格子的差值绝对值最大为 2 。
这条路径比路径 [1,2,2,2,5] 更优,因为另一条路径差值最大值为 3 。
示例 2:
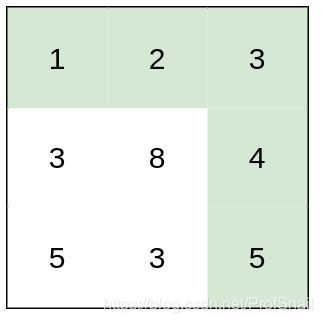
输入:heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]]
输出:1
解释:路径 [1,2,3,4,5] 的相邻格子差值绝对值最大为 1 ,比路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 更优。
示例 3:
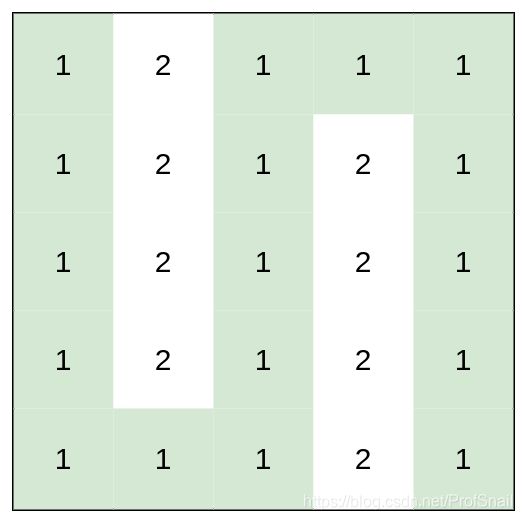
输入:heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]]
输出:0
解释:上图所示路径不需要消耗任何体力。
提示:
rows == heights.length
columns == heights[i].length
1 <= rows, columns <= 100
1 <= heights[i][j] <= 106
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-with-minimum-effort
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路
与一般的并查集是用来记录图中连通分量个数不同,这道题使用并查集的思路是逐渐添加边,直到起点和终点处于同一个连通分量(即存在一条路径使得起点和终点相连),插边的过程结束。
- 先把这张图存起来:边为所有上下左右相邻的顶点构成,边权是相邻顶点之间的高度差。
- 策略是什么呢?
- 假设整张图m*n个节点最开始都是孤立点,需要添加一条条的边,使得各个顶点相连,直到起点和终点在同一个集合中,路径就结束了。
- 由于题设中的整个体力消耗值,是路径上所有相邻节点的高度差中的最大值。那么我们一直不停的向整张图中添加权值最小的边,就算添加进来的这条边,在最后的路径中用不到,他也不会让当前图中的路径体力消耗值变得更多。
- 一直添加边,如同上文说到的,直到加上某条边时候,起点和终点处于同一个集合下,那么路径就找到了。又因为咱们是从最小高度差的边一个个添加进来的,所以最后加进来的这条边的权值就是题目要的最小消耗的体力值。返回他就可以了。
- 妙啊~

代码
class Union{
public:
int n;
vector<int> f;
Union(int _n): n(_n), f(_n){
for(int i = 0; i < _n; i++){
f[i] = i;
}
}
int findf(int x){
int root = x, z;
while(root!=f[root])root=f[root];
while(f[x]!=root){
z = f[x];
f[x] = root;
x = z;
}
return root;
}
int merge(int a, int b){
int fa = findf(a);
int fb = findf(b);
if(fa!=fb){
f[max(fa, fb)] = min(fa, fb);
}
return 0;
}
};
struct Edge{
int u, v, cost;
Edge(int _u, int _v, int _cost){
u = _u;
v = _v;
cost = _cost;
}
bool operator < (const Edge e) const{
return cost < e.cost;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
int m = heights.size();
int n = heights[0].size();
Union un = Union(m*n);
vector<Edge> edges;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(i>0){
edges.push_back(Edge((i-1)*n+j, i*n+j, abs(heights[i-1][j]-heights[i][j])));
}
if(j>0){
edges.push_back(Edge(i*n+j-1, i*n+j, abs(heights[i][j-1]-heights[i][j])));
}
}
}
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end());
int s = 0, e = m*n-1, ans;
for(auto& edge: edges){
un.merge(edge.u, edge.v);
if(un.findf(s)==un.findf(e)){
return edge.cost;
}
}
return 0;
}
};