并发编程之Phaser类多阶段任务(以遗传算法TSP问题为例)
目录
一、认识Phaser类
1、Phaser类特征
2、任务注册与注销
3、同步阶段变更
二、遗传算法
1、DataLoader类:加载数据
2、Individual类:问题所有可能解
3、GeneticOperators类:GA算法核心
三、GA应用:Phaser类解决旅行商问题(TSP)
2、GeneticPhaser类:Java并发Phaser类实现
3、ConcurrentGeneticTask类:GA算法阶段任务执行
4、ConcurrentGeneticAlgorithm类:GA算法并发实现
5、主类main
四、实验结果
五、分析总结
一、认识Phaser类
学习Java并发有一段时间了,从基础开始,认识了许多同步机制API,这次学习了Phaser类这个同步机制,刷新了以前的认识,再添一项新知识。
下面先认识一下Phaser是什么,然后结合实际应用,通过遗传算法经典应用的旅行商问题(TSP)的案例,更好地学习一下Phaser类同步机制的使用方法。
1、Phaser类特征
Java7的并发API引入了Phaser类,提供了强大的同步机制——分段器,它将任务划分为多个阶段执行,处理过程定义了明确的步骤,完成每个阶段任务需要遵循先后顺序。
主要特点:
- 分段器必须知道要控制的任务数量,Java中成为参与者(任务)的注册机制。
- 任务完成一个阶段后告知分段器。完成此阶段之前,分段器使该任务处于休眠状态。
- 分段器保存了一个整数值,存储已经进行的阶段变更数目。
- 当分段器做出阶段变更时候,可以执行定制的代码。
- 控制phaser的终止。
- 可以通过方法获取参与者的数目和状态。
2、任务注册与注销
这里根据上面说到的第1个特点,介绍注册参与者的方法。注册可以在执行任务开始时,也可以随时注册。
Phaser对象创建,常用的2个构造函数:
- Phaser():创建一个有0个参与者的分段器。
- Phaser(int parties):创建一个给定数目参与者的分段器。
显式创建方法:
- bulkRegisterl(int parties) :注册给定数目的参与者。
- register():注册一个参与者。
分段器控制的任务完成之后必须注销,否则分段器会处于一直等待状态。
注销方法:
arriveAndDeRegister():告知分段器该任务已完成当前阶段,而且不参与下一阶段。
3、同步阶段变更
分段器的主要目的是使那些可以分割为多阶段算法,以并发方式执行。任务只有完成当前阶段,才能进入下一个阶段。
Phaser类中有arrive,arriveAndDeRegister,arriveAndwaitAdvance三个方法来告知当前阶段已经完成,但是当一个任务完成阶段后未调用其中之一的方法,分段器可能对其余任务或阶段进行阻塞。
因此,进入下一阶段调用以下方法:
- arriveAndwaitAdvance():告知分段器当前阶段已经完成,进入下一阶段。phaser阻塞该任务,直到所有参与的任务调用了其中一种同步方法。
- awaitAdvance(int phaser):告知分段器,若参数等于实际阶段数,则等待当前阶段结束;不等则返回。
二、遗传算法
上面其实都是一些理论知识,对Phaser有一定的了解之后,开始在实际案例中学习,更进一步理解,遗传算法就是一个很好的例子。
遗传算法耳熟能详,是基于自然选择原理的一种自适应启发式搜索算法,用于最优化问题和在搜索问题中寻找更好地方案。换言之,“优胜劣汰,适者生存”。这也是从生物学引申而来的有类似原理的算法,所以也使用了生物学的一些术语。
一些在遗传算法中使用的特定术语:
- 适应度函数:是主要目标,能够使函数最大化或者最小化的解决方案,来确定方案的优劣。
- 种群:问题的所有可能方案的集合。初始集合可以随机生成或使用启发函数获取初始解决方案。
初始种群之后,启动包含3个阶段的迭代过程:
- 选择:在种群中选择更好地个体,个体在适应度函数中有着较好的值。
- 交叉:上一步选择优质个体后进行交叉,生成新一代个体。具体操作:parent1 X parent2 ——>> child1 + child2 ,主要依赖于待解决问题。
- 突变:可以应用突变运算符更改某个体的值,只对极少个体执行此操作。
结束标准:
- 固定代数
- 适应度函数设定的阈值
- 找到满足预定标准的方案
- 时间限制
- 手动停止
将遗传算法应用于TSP问题,目标找到一条最优路线,经过每个城市有且仅有一次,同时旅行总距离最短。
数据有两份,包括15个城市和57个城市。二维矩阵中每个值表示城市之间的距离。
1、DataLoader类:加载数据
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class DataLoader {
/**
* @param path
* @return int[][]
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 10:46
*
* 加载文件,转化为二维数组
*/
public static int[][] load(Path path) throws IOException {
InputStream in = Files.newInputStream(path);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String line = null;
String[] row = null;
int[][] a;
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
int rowNum = 0, colNum = 0, i = 0, j = 0;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
arrayList.add(line);
colNum = line.split(",").length;
}
rowNum = arrayList.size();
a = new int[rowNum][colNum];
int count = 0;
for (String str : arrayList) {
row = str.split(",");
for (i = 0; i < colNum; i++) {
a[count][i] = Integer.parseInt(row[i]);
}
count++;
}
return a;
}
/**
* @param args
* @return void
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 10:45
*
* 类内测试,加载文件
*/
// public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// Path file = Paths.get("data/kn57_dist.txt");
// int[][] a;
// a = DataLoader.load(file);
// for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
// for (int j = 0; j < a[0].length; j++) {
// System.out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
// }
}
2、Individual类:问题所有可能解
/**
* 存放访问不同城市的顺序,TSP问题的所有可能解
*
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 10:53
*/
public class Individual implements Comparable {
private Integer[] chromosomes;
private int value;
public Integer[] getChromosomes() {
return chromosomes;
}
public void setChromosomes(Integer[] chromosomes) {
this.chromosomes = chromosomes;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public Individual(int size) {
chromosomes = new Integer[size];
}
public Individual(Individual other) {
chromosomes = other.getChromosomes().clone();
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Individual o) {
return Integer.compare(this.getValue(), o.getValue());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String ret = "";
for (Integer number : chromosomes)
ret += number + ",";
return ret;
}
}
3、GeneticOperators类:GA算法核心
遗传算法核心内部逻辑实现:选择、交叉、个体和种群评估,详见代码注释
import java.util.*;
/**
* 实现遗传算法内部逻辑
*
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 11:21
*
*/
public class GeneticOperators {
/**
* @param selected
* @param numberOfIndividual
* @param size
* @return GeneticAlgorithm.Individual[]
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 11:29
*
* 接收被选中的个体,交叉操作生成下一代种群
*/
public static Individual[] crossover(Individual[] selected,int numberOfIndividual,int size){
Individual population[] =new Individual[numberOfIndividual];
Random random=new Random(System.nanoTime());
for (int i=0;i individual1 , individual2
*/
public static void crossover(final Individual parent1,final Individual parent2,final Individual individual1,final Individual individual2){
List p1= Arrays.asList(parent1.getChromosomes());
List p2= Arrays.asList(parent2.getChromosomes());
List ch1=new ArrayList(p1.size());
List ch2=new ArrayList(p2.size());//p1 ? p2
int size=p1.size();
Random random=new Random();
int number1=random.nextInt(size-1);
int number2;
//1,14,6,2,3,5,7,0,12,4,11,13,9,8,10,
do {
number2=random.nextInt(size);
}while (number1==number2);
int start=Math.min(number1,number2);
int end=Math.max(number1,number2);
ch1.addAll(p1.subList(start,end));
ch2.addAll(p2.subList(start,end));
int currentCity=0;
int currentCityParent1=0;
int currentCityParent2=0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
currentCity=(end+i)%size;
currentCityParent1=p1.get(currentCity);
currentCityParent2=p2.get(currentCity);
if (!ch1.contains(currentCityParent2))
ch1.add(currentCityParent2);
if (!ch2.contains(currentCityParent1))
ch2.add(currentCityParent1);
}
Collections.rotate(ch1,start);
Collections.rotate(ch2,start);
individual1.setChromosomes(ch1.toArray(individual1.getChromosomes()));
individual2.setChromosomes(ch2.toArray(individual2.getChromosomes()));
}
/**
* @param population
* @return GeneticAlgorithm.Individual[]
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 11:23
*
* 获取种群的最优个体,返回种群一半的个体,可使用最适合函数选择
*/
public static Individual[] selection(Individual[] population){
Individual selected[] =new Individual[population.length/2];
for (int i = 0; i < selected.length; i++) {
selected[i]=new Individual(population[i]);
}
return selected;
}
/**
* @param numberOfIndividual
* @param size
* @return GeneticAlgorithm.Individual[]
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 11:24
*
* 创建一个群,城市数目size
*/
public static Individual[] initialize(int numberOfIndividual,int size){
Individual population[] =new Individual[numberOfIndividual];
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfIndividual; i++) {
population[i]=new Individual(size);
initialize(population[i].getChromosomes());
}
return population;
}
/**
* @param chromosomes
* @return void
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 11:25
*
* 随机初始化某一个体的染色体,生成合法的个体(即每个城市只访问一次)
*/
public static void initialize(Integer[] chromosomes){
int size=chromosomes.length;
List values=new ArrayList(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
values.add(i);
}
Collections.shuffle(values,new Random(System.nanoTime()));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
chromosomes[i]=values.get(i);
}
}
/**
* @param population
* @param distanceMatrix
* @return void
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 11:33
*
* 接收距离矩阵,将适应函数应用到全部个体,对种群排序
*/
public static void evaluate(Individual[] population,int[][] distanceMatrix){
for (Individual individual:population) {
evaluate(individual,distanceMatrix);
}
Arrays.sort(population);
}
/**
* @param individual
* @param distanceMatrix
* @return void
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 11:36
*
* 接将适应函数应用到一个个体,结果加入到个体集合,以供对种群所有进行排序
*/
public static void evaluate(Individual individual,int[][] distanceMatrix){
Integer chromosomes[]=individual.getChromosomes();
int totalDistance=0;
int source,destination;
for (int i = 0; i < chromosomes.length-1; i++) {
source=chromosomes[i];
destination=chromosomes[i+1];
totalDistance+=distanceMatrix[source][destination];
}
source=chromosomes[chromosomes.length-1];
destination=chromosomes[0];
totalDistance+=distanceMatrix[source][destination];
individual.setValue(totalDistance);
}
}
三、GA应用:Phaser类解决旅行商问题(TSP)
1、SharedData类:共享对象
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* 存放任务之间共享的对象
*
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 15:16
*
*/
public class SharedData {
private Individual[] population;
private Individual[] selected;
private AtomicInteger index;
private Individual best;
private int[][] distanceMatrix;
public SharedData() {
index=new AtomicInteger();
}
public Individual[] getPopulation() {
return population;
}
public void setPopulation(Individual[] population) {
this.population = population;
}
public Individual[] getSelected() {
return selected;
}
public void setSelected(Individual[] selected) {
this.selected = selected;
}
public AtomicInteger getIndex() {
return index;
}
public void setIndex(AtomicInteger index) {
this.index = index;
}
public Individual getBest() {
return best;
}
public void setBest(Individual best) {
this.best = best;
}
public int[][] getDistanceMatrix() {
return distanceMatrix;
}
public void setDistanceMatrix(int[][] distanceMatrix) {
this.distanceMatrix = distanceMatrix;
}
}
2、GeneticPhaser类:Java并发Phaser类实现
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.concurrent.Phaser;
public class GeneticPhaser extends Phaser {
private SharedData data;
public GeneticPhaser(int parties, SharedData data) {
super(parties);
this.data=data;
}
/**
* @param phase
* @param registeredParties
* @return boolean
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 15:20
*
* 重载onAdvance方法,使所有任务完成第一阶段之后执行代码
*/
@Override
protected boolean onAdvance(int phase, int registeredParties) {
int realPhase=phase%3;
if (registeredParties>0) {
switch (realPhase) {
case 0:
case 1:
data.getIndex().set(0);
break;
case 2:
Arrays.sort(data.getPopulation());
if (data.getPopulation()[0].getValue() < data.getBest().getValue()) {
data.setBest(data.getPopulation()[0]);
}
break;
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
public SharedData getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(SharedData data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
3、ConcurrentGeneticTask类:GA算法阶段任务执行
import JavaConcurrencyProgramming.chapter06.GeneticAlgorithm.GeneticOperators;
import JavaConcurrencyProgramming.chapter06.GeneticAlgorithm.Individual;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 执行遗传算法各个阶段的任务
*
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 15:28
*
*/
public class ConcurrentGeneticTask implements Runnable {
private GeneticPhaser phaser;
private SharedData data;
private int numberOfGenerations;
private boolean main;
public ConcurrentGeneticTask(GeneticPhaser phaser, int numberOfGenerations,
boolean main) {
this.phaser = phaser;
this.numberOfGenerations = numberOfGenerations;
this.main = main;
this.data = phaser.getData();
}
@Override
public void run() {
Random random = new Random((System.nanoTime()));
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfGenerations; i++) {
if (main)
data.setSelected(GeneticOperators.selection(data.getPopulation()));
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
//交叉操作
int individualIndex;
do {
individualIndex = data.getIndex().getAndAdd(2);
if (individualIndex < data.getPopulation().length) {
int secondIndividual = individualIndex++;
int p1Index = random.nextInt(data.getSelected().length);
int p2Index;
do {
p2Index = random.nextInt(data.getSelected().length);
} while (p1Index == p2Index);
Individual parent1 = data.getSelected()[p1Index];
Individual parent2 = data.getSelected()[p2Index];
Individual individual1 = data.getPopulation()[individualIndex];
Individual individual2 = data.getPopulation()[secondIndividual];
GeneticOperators.crossover(parent1, parent2, individual1, individual2);
}
} while (individualIndex < data.getPopulation().length);
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
do {
individualIndex = data.getIndex().getAndIncrement();
if (individualIndex < data.getPopulation().length) {
GeneticOperators.evaluate(data.getPopulation()[individualIndex], data.getDistanceMatrix());
}
} while (individualIndex < data.getPopulation().length);
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
}
phaser.arriveAndDeregister();
}
}
4、ConcurrentGeneticAlgorithm类:GA算法并发实现
/**
* 遗传算法并发算法
* @author Charzous
* @date 2021/2/5 15:30
*
*/
public class ConcurrentGeneticAlgorithm {
private int numberOfGenerations;
private int numberOfIndividuals;
private int[][] distanceMatrix;
private int size;
public ConcurrentGeneticAlgorithm(int[][] distanceMatrix, int numberOfGenerations, int numberOfIndividuals) {
this.distanceMatrix = distanceMatrix;
this.numberOfGenerations = numberOfGenerations;
this.numberOfIndividuals = numberOfIndividuals;
size = distanceMatrix.length;
}
public Individual calculate() {
Individual[] population = GeneticOperators.initialize(numberOfIndividuals, size);
GeneticOperators.evaluate(population, distanceMatrix);
SharedData data = new SharedData();
data.setPopulation(population);
data.setDistanceMatrix(distanceMatrix);
data.setBest(population[0]);
int numTasks = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
GeneticPhaser phaser = new GeneticPhaser(numTasks, data);
ConcurrentGeneticTask[] tasks = new ConcurrentGeneticTask[numTasks];
Thread[] threads = new Thread[numTasks];
tasks[0] = new ConcurrentGeneticTask(phaser, numberOfGenerations, true);
for (int i = 1; i < numTasks; i++) {
tasks[i] = new ConcurrentGeneticTask(phaser, numberOfGenerations, false);
}
for (int i = 0; i < numTasks; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(tasks[i]);
threads[i].start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < numTasks; i++) {
try {
threads[i].join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return data.getBest();
}
}
5、主类main
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class ConcurrentMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long start, end;
int generations = 1000;
int individuals = 1000;
String[] names={"kn57_dist"};//"lau15_dist" ,
for (String name:names) {
int[][] distanceMatrix = DataLoader.load(Paths.get("data", name + ".txt"));
ConcurrentGeneticAlgorithm concurrentGeneticAlgorithm = new ConcurrentGeneticAlgorithm(distanceMatrix, generations,
individuals);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Individual result = concurrentGeneticAlgorithm.calculate();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("=======================================");
System.out.println("Example:"+name);
System.out.println("Generations: " + generations);
System.out.println("Population: " + individuals);
System.out.println("Execution Time: " + (end - start)+"ms");
System.out.println("Best Individual: " + result);
System.out.println("Total Distance: " + result.getValue());
System.out.println("=======================================");
}
}
}
四、实验结果
数据和实验参数设置:
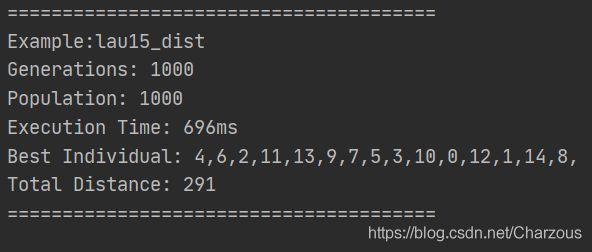
generations = 1000; individuals = 1000; 数据:lau15_dist.txt(15个城市)
测试执行10次,平均执行时间为500ms左右。
当然,种群数和代数可以设置其他值,数据集使用可以更换,进行实验。
为了比较并发版本执行表现的提升,简单实现了单线程版本,只需要将ConcurrentGeneticAlgorithm类里面的并发部分修改为单线程方法,结果如下:
测试执行10次,平均执行时间为690ms左右,对比之下可看出并发的性能提升。
五、总结
这篇记录Phaser类同步机制的原理和实践理解,学习Java并发有一段时间了,从基础开始,认识了许多同步机制API,这次学习了Phaser类这个同步机制,刷新了以前的认识,再添一项新知识。先认识一下Phaser是什么,然后结合实际应用,通过遗传算法经典应用的旅行商问题(TSP)的案例,更好地学习一下Phaser类同步机制的使用方法。对Phaser一些理论知识有一定的了解之后,开始在实际案例中学习,更进一步理解,遗传算法就是一个很好的例子,掌握了分段器在并发编程中的基础使用,也希望在之后的学习应用能够有所帮助。
如果觉得不错欢迎“一键三连”哦,点赞收藏关注,有问题直接评论,交流学习!
Java并发编程系列文章:
- 原创 Java并发API案例分析之并发设计原理[https://blog.csdn.net/Charzous/article/details/112603639]
- 原创 Java并发(Runnable+Thread)实现硬盘文件搜索[https://blog.csdn.net/Charzous/article/details/112853937]
- 原创 并发编程之Callable/Future接口(以单词最佳匹配算法为例)[https://blog.csdn.net/Charzous/article/details/113338669]
- 并发编程之Phaser类多阶段任务(以遗传算法TSP问题为例)[https://blog.csdn.net/Charzous/article/details/113698041]
我的CSDN博客:https://blog.csdn.net/Charzous/article/details/113698041