JDBC学习笔记02【ResultSet类详解、JDBC登录案例练习、PreparedStatement类详解】
- 黑马程序员-JDBC文档(腾讯微云)JDBC笔记.pdf:https://share.weiyun.com/Kxy7LmRm
- JDBC学习笔记01【JDBC快速入门、JDBC各个类详解、JDBC之CRUD练习】
- JDBC学习笔记02【ResultSet类详解、JDBC登录案例练习、PreparedStatement类详解】
- JDBC学习笔记03【JDBC事务管理、数据库连接池、JDBCTemplate】
目录
04 ResultSet类详解
JDBC各个类详解_ResultSet_基本使用
JDBC各个类详解_ResultSet_遍历
05 JDBC登录案例练习
JDBC练习_select语句
Emp.java // 封装Emp表数据的JavaBean
JDBCDemo8.java
JDBC工具类
JDBC练习_登录案例
06 PreparedStatement类详解
JDBC各个类详解_PreparedStatement
登录案例——解决sql注入问题
04 ResultSet类详解
JDBC各个类详解_ResultSet_基本使用
4. ResultSet:结果集对象,封装查询结果
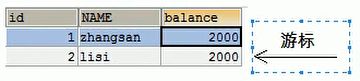
* boolean next():游标向下移动一行,判断当前行是否是最后一行末尾(是否有数据);如果是,则返回false,如果不是则返回true。
* getXxx(参数):获取数据
* Xxx:代表数据类型 如:int getInt()、String getString()
* 参数:
1. int:代表列的编号,从1开始,如: getString(1)
2. String:代表列名称,如: getDouble("balance")
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 执行DDL语句
*/
public class JDBCDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from account";
//4.获取执行sql对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.处理结果
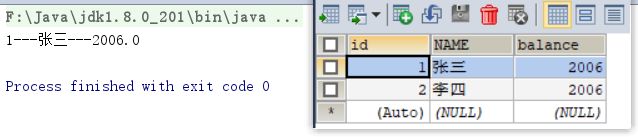
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
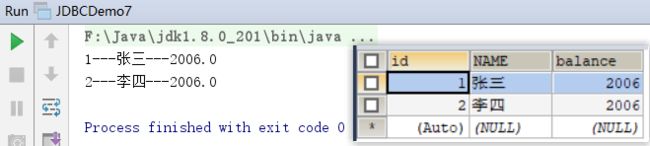
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//7.释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}JDBC各个类详解_ResultSet_遍历
4. ResultSet:结果集对象,封装查询结果
* boolean next(): 游标向下移动一行,判断当前行是否是最后一行末尾(是否有数据);如果是,则返回false;如果不是则返回true。
* getXxx(参数):获取数据
* Xxx:代表数据类型,如:int getInt(),String getString()
* 参数:
1. int:代表列的编号,从1开始,如: getString(1)
2. String:代表列名称。如: getDouble("balance")
* 注意:
* 使用步骤:
1. 游标向下移动一行
2. 判断是否有数据
3. 获取数据//6.1 循环判断游标是否是最后一行末尾。
while(rs.next()){
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
报错的代码:
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 执行DDL语句
*/
public class JDBCDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from account";
//4.获取执行sql对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.处理结果
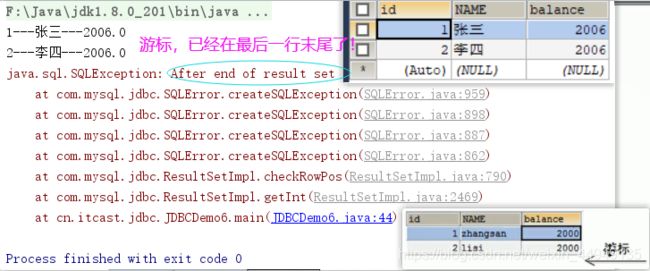
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id2 = rs.getInt(1);
String name2 = rs.getString("name");
double balance2 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id2 + "---" + name2 + "---" + balance2);
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id3 = rs.getInt(1);
String name3 = rs.getString("name");
double balance3 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id3 + "---" + name3 + "---" + balance3);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//7.释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 执行DDL语句
*/
public class JDBCDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from account";
//4.获取执行sql对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.处理结果
//6.1 循环判断游标是否是最后一行末尾。
while (rs.next()) {
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
/* //6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
if(rs.next()){
//判断是否有数据
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}*/
/* //6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id2 = rs.getInt(1);
String name2 = rs.getString("name");
double balance2 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id2 + "---" + name2 + "---" + balance2);
//6.1 让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2 获取数据
int id3 = rs.getInt(1);
String name3 = rs.getString("name");
double balance3 = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id3 + "---" + name3 + "---" + balance3);*/
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//7.释放资源
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}05 JDBC登录案例练习
JDBC练习_select语句
4. ResultSet:结果集对象,封装查询结果
* boolean next(): 游标向下移动一行,判断当前行是否是最后一行末尾(是否有数据);如果是,则返回false;如果不是则返回true。
* getXxx(参数):获取数据
* Xxx:代表数据类型,如:int getInt(),String getString()
* 参数:
1. int:代表列的编号,从1开始,如: getString(1)
2. String:代表列名称。如: getDouble("balance")
* 注意:
* 使用步骤:
1. 游标向下移动一行
2. 判断是否有数据
3. 获取数据//6.1 循环判断游标是否是最后一行末尾。
while(rs.next()){
//6.2 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
double balance = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id + "---" + name + "---" + balance);
}* 练习:
* 定义一个方法,查询emp表的数据将其封装为对象,然后装载集合,返回。
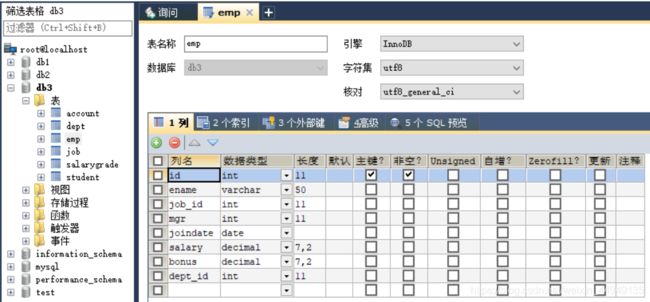
1. 定义Emp类
2. 定义方法 public ListfindAll() {}
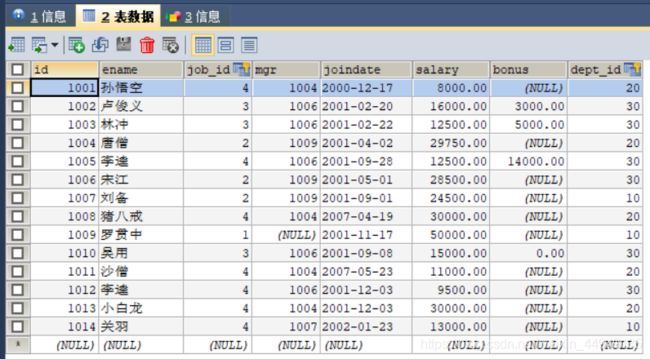
3. 实现方法 select * from emp;
Emp.java // 封装Emp表数据的JavaBean
package cn.itcast.domain;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 封装Emp表数据的JavaBean
*/
public class Emp {
private int id;
private String ename;
private int job_id;
private int mgr;
private Date joindate;
private double salary;
private double bonus;
private int dept_id;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getEname() {
return ename;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public int getJob_id() {
return job_id;
}
public void setJob_id(int job_id) {
this.job_id = job_id;
}
public int getMgr() {
return mgr;
}
public void setMgr(int mgr) {
this.mgr = mgr;
}
public Date getJoindate() {
return joindate;
}
public void setJoindate(Date joindate) {
this.joindate = joindate;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getDept_id() {
return dept_id;
}
public void setDept_id(int dept_id) {
this.dept_id = dept_id;
}
public double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", ename='" + ename + '\'' +
", job_id=" + job_id +
", mgr=" + mgr +
", joindate=" + joindate +
", salary=" + salary +
", bonus=" + bonus +
", dept_id=" + dept_id +
'}';
}
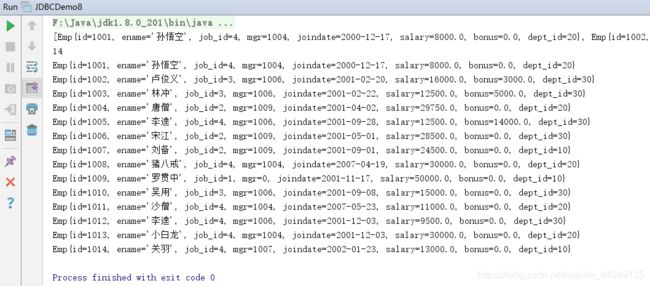
}JDBCDemo8.java
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import cn.itcast.domain.Emp;
import cn.itcast.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* * 定义一个方法,查询emp表的数据将其封装为对象,然后装载集合,返回。
*/
public class JDBCDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new JDBCDemo8().findAll();
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.size());
for (Emp x : list) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
/**
* 查询所有emp对象
*
* @return
*/
public List findAll() {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List list = null;
try {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db3", "root", "root");
//3.定义sql
String sql = "select * from emp";
//4.获取执行sql的对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.遍历结果集,封装对象,装载集合
Emp emp = null;
list = new ArrayList();
while (rs.next()) {
//获取数据
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String ename = rs.getString("ename");
int job_id = rs.getInt("job_id");
int mgr = rs.getInt("mgr");
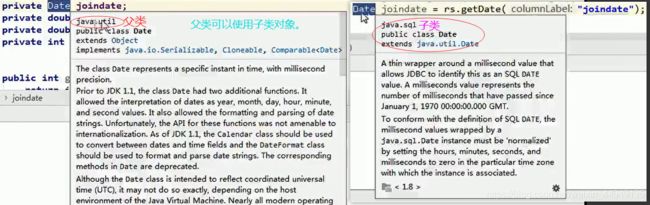
Date joindate = rs.getDate("joindate");
double salary = rs.getDouble("salary");
double bonus = rs.getDouble("bonus");
int dept_id = rs.getInt("dept_id");
// 创建emp对象,并赋值
emp = new Emp();
emp.setId(id);
emp.setEname(ename);
emp.setJob_id(job_id);
emp.setMgr(mgr);
emp.setJoindate(joindate);
emp.setSalary(salary);
emp.setBonus(bonus);
emp.setDept_id(dept_id);
//装载集合
list.add(emp);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return list;
}
} JDBC工具类
抽取JDBC工具类 : JDBCUtils
* 目的:简化书写
* 分析:
1. 注册驱动也抽取
2. 抽取一个方法获取连接对象
* 需求:不想传递参数(麻烦),还得保证工具类的通用性。
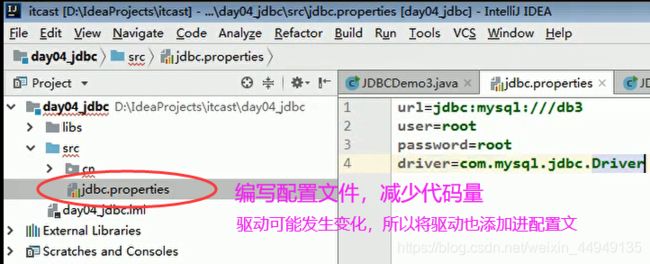
* 解决:配置文件
jdbc.properties
url=...
user=...
password=...3. 抽取一个方法释放资源
* 代码实现:...
Java19-day10【标准输入输出流、字节字符打印流、对象序列化-反序列化流、serialVersionUID&transient、Properties】
Properties介绍
- 是一个Map体系的集合类。
- Properties可以保存到流中或从流中加载。
- 属性列表中的每个键及其对应的值都是一个字符串。
package cn.itcast.util;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* JDBC工具类
*/
public class JDBCUtils {
private static String url;
private static String user;
private static String password;
private static String driver;
/**
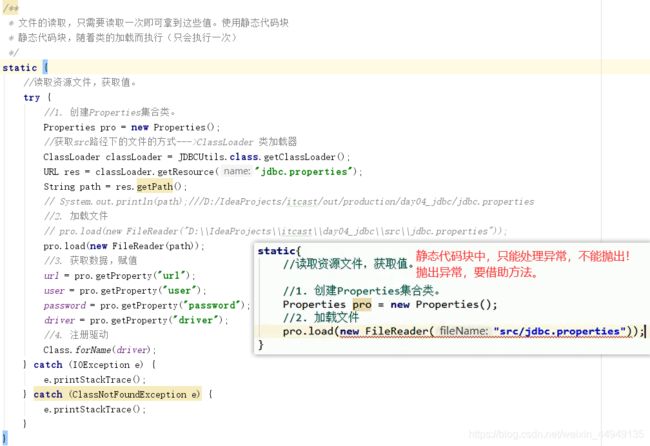
* 文件的读取,只需要读取一次即可拿到这些值。使用静态代码块
* 静态代码块,随着类的加载而执行(只会执行一次)
*/
static {
//读取资源文件,获取值。
try {
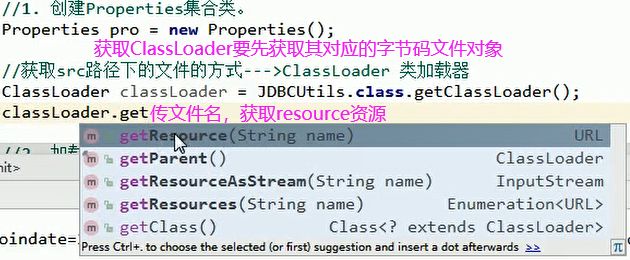
//1. 创建Properties集合类。
Properties pro = new Properties();
//获取src路径下的文件的方式--->ClassLoader 类加载器:加载字节码文件进内存、获取src下资源文件的路径
//获取ClassLoader要先获取其对应的字节码文件对象
ClassLoader classLoader = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader();
//以src为相对的根路径 统一资源定位符URL
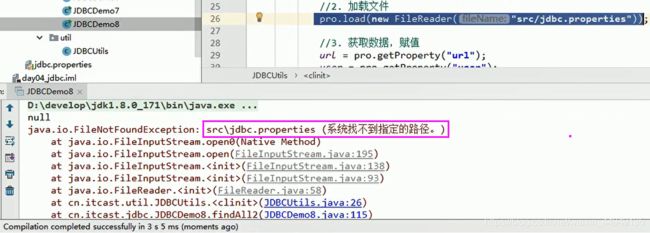
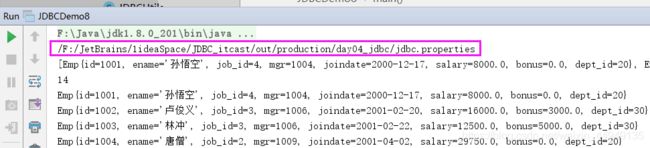
URL res = classLoader.getResource("jdbc.properties"); // 传文件名,获取resource资源
String path = res.getPath();
// System.out.println(path);///D:/IdeaProjects/itcast/out/production/day04_jdbc/jdbc.properties
//2. 加载文件
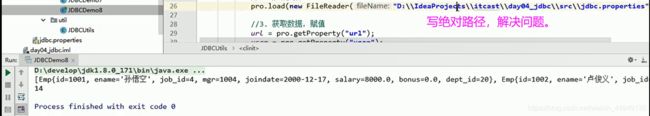
// pro.load(new FileReader("D:\\IdeaProjects\\itcast\\day04_jdbc\\src\\jdbc.properties"));
pro.load(new FileReader(path));
//3. 获取数据,赋值
url = pro.getProperty("url");
user = pro.getProperty("user");
password = pro.getProperty("password");
driver = pro.getProperty("driver");
//4. 注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取连接
*
* @return 连接对象
*/
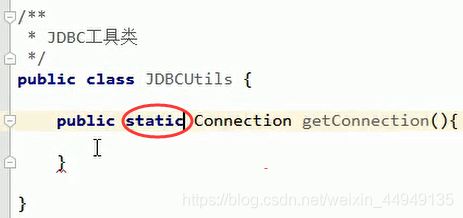
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
}
/**
* 释放资源
*
* @param stmt
* @param conn
*/
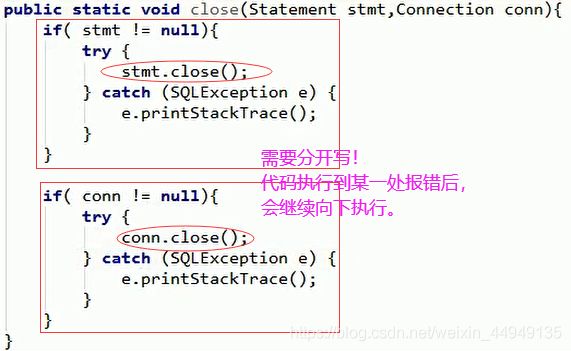
public static void close(Statement stmt, Connection conn) {
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 释放资源
*
* @param stmt
* @param conn
*/
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement stmt, Connection conn) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}JDBC练习_登录案例
* 练习:
* 需求:
1. 通过键盘录入用户名和密码
2. 判断用户是否登录成功
* select * from user where username = "" and password = "";
* 如果这个sql有查询结果,则成功,反之,则失败* 步骤:
1. 创建数据库表 user
CREATE TABLE USER(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
username VARCHAR(32),
PASSWORD VARCHAR(32)
);INSERT INTO USER VALUES(NULL,'zhangsan','123');
INSERT INTO USER VALUES(NULL,'lisi','234');2. 代码实现:...
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import cn.itcast.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 练习:
* * 需求:
* 1. 通过键盘录入用户名和密码
* 2. 判断用户是否登录成功
*/
public class JDBCDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.键盘录入,接受用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
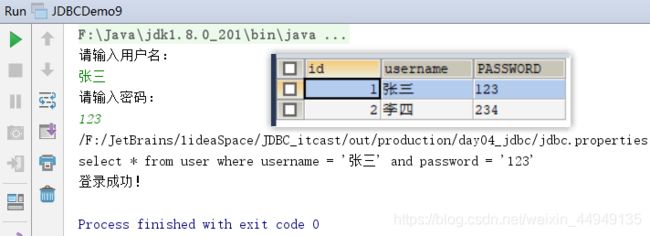
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password = sc.nextLine();
//2.调用方法 非静态方法,需要创建对象来调用
boolean flag = new JDBCDemo9().login(username, password);
//3.判断结果,输出不同语句
if (flag) {
//登录成功
System.out.println("登录成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
/**
* 登录方法
*/
public boolean login(String username, String password) {
if (username == null || password == null) {
return false;
}
//连接数据库判断是否登录成功
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//1.获取连接
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "select * from user where username = '" + username + "' and password = '" + password + "' ";
System.out.println(sql);
//3.获取执行sql的对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//4.执行查询
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//5.判断
/* if(rs.next()){//如果有下一行,则返回true
return true;
}else{
return false;
}*/
return rs.next();//如果有下一行,则返回true
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, stmt, conn);
}
return false;
}
}06 PreparedStatement类详解
JDBC各个类详解_PreparedStatement
5. PreparedStatement:执行sql的对象
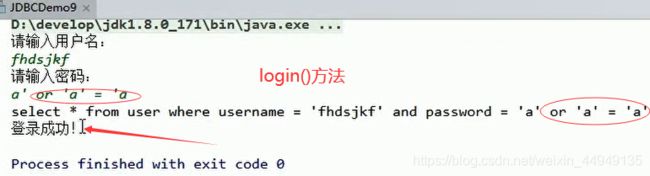
1. SQL注入问题:在拼接sql时,有一些sql的特殊关键字参与字符串的拼接,会造成安全性问题。
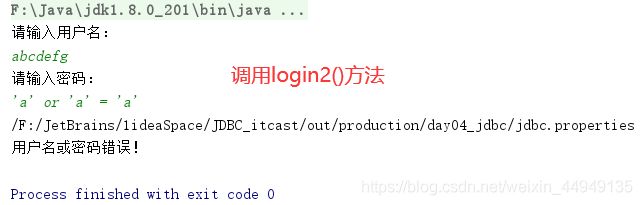
1. 输入用户随便,输入密码:a' or 'a' = 'a
2. sql:select * from user where username = 'fhdsjkf' and password = 'a' or 'a' = 'a'2. 解决sql注入问题:使用PreparedStatement对象来解决
3. 预编译的SQL:参数使用?作为占位符
4. 步骤:
1. 导入驱动jar包 mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar
2. 注册驱动
3. 获取数据库连接对象 Connection
4. 定义sql
* 注意:sql的参数使用?作为占位符, 如:select * from user where username = ? and password = ?;
5. 获取执行sql语句的对象 PreparedStatement Connection.prepareStatement(String sql)
6. 给?赋值:
* 方法: setXxx(参数1,参数2)
* 参数1:?的位置编号 从1 开始
* 参数2:?的值
7. 执行sql,接受返回结果,不需要传递sql语句
8. 处理结果
9. 释放资源5. 注意:后期都会使用PreparedStatement来完成增删改查的所有操作
1. 可以防止SQL注入
2. 效率更高
登录案例——解决sql注入问题
package cn.itcast.jdbc;
import cn.itcast.util.JDBCUtils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 练习:
* * 需求:
* 1. 通过键盘录入用户名和密码
* 2. 判断用户是否登录成功
*/
public class JDBCDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.键盘录入,接受用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password = sc.nextLine();
//2.调用方法 非静态方法,需要创建对象来调用
boolean flag = new JDBCDemo9().login(username, password);
//3.判断结果,输出不同语句
if (flag) {
//登录成功
System.out.println("登录成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
}
}
/**
* 登录方法
*/
public boolean login(String username, String password) {
if (username == null || password == null) {
return false;
}
//连接数据库判断是否登录成功
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//1.获取连接
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "select * from user where username = '" + username + "' and password = '" + password + "' ";
System.out.println(sql);
//3.获取执行sql的对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//4.执行查询
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//5.判断
/* if(rs.next()){//如果有下一行,则返回true
return true;
}else{
return false;
}*/
return rs.next();//如果有下一行,则返回true
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, stmt, conn);
}
return false;
}
/**
* 登录方法,使用PreparedStatement实现
*/
public boolean login2(String username, String password) {
if (username == null || password == null) {
return false;
}
//连接数据库判断是否登录成功
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//1.获取连接
try {
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.定义sql
String sql = "select * from user where username = ? and password = ?";
//3.获取执行sql的对象
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//给?赋值
pstmt.setString(1, username);
pstmt.setString(2, password);
//4.执行查询,不需要传递sql
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
//5.判断
/* if(rs.next()){//如果有下一行,则返回true
return true;
}else{
return false;
}*/
return rs.next();//如果有下一行,则返回true
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs, pstmt, conn);
}
return false;
}
}加油加油加油,宁死不破~~~