本文首发于微信公众号【WriteOnRead】,欢迎关注。
1. 概述
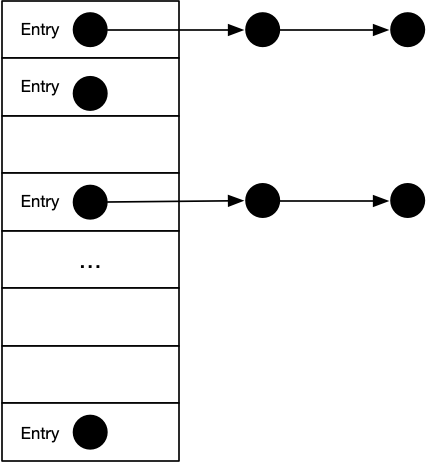
与 HashMap 类似,Hashtable 也是散列表的实现。它的内部结构可以理解为「数组 + 链表」的形式,结构示意图如下:
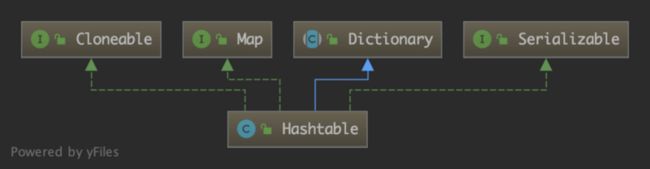
Hashtable 的类继承结构与签名如下:
public class Hashtable
extends Dictionary
implements Map, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {} Hashtable 的 key 和 value 都不能为空(HashMap 的 key 和 value 都允许为空),并且 key 必须要实现 hashCode 方法和 equals 方法。
PS: Hashtable 目前使用不是很多,若无线程安全的需求,推荐使用 HashMap;若需要线程安全的高并发实现,推荐使用 ConcurrentHashMap。
2. 代码分析
2.1 Entry 类
Entry 类实现了 Map.Entry 接口,是 Hashtable 中的节点类。代码如下:
private static class Entry implements Map.Entry {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Entry next;
protected Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Entry next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
return (key==null ? e.getKey()==null : key.equals(e.getKey())) &&
(value==null ? e.getValue()==null : value.equals(e.getValue()));
}
public int hashCode() {
return hash ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
// ...
} 2.2 成员变量
// Hashtable 内部存储元素的数组
private transient Entry[] table;
// Hashtable 的阈值 (int)(capacity * loadFactor)
private int threshold;
// 负载因子
private float loadFactor;
// 数组能够分配的最大容量
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;2.3 构造器
// 构造一个空的 Hashtable,初始容量为 11,负载因子为 0.75
public Hashtable() {
this(11, 0.75f);
}
// 构造一个空的 Hashtable,指定初始容量,负载因子为 0.75
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0.75f);
}
// 构造一个空的 Hashtable,指定初始容量和负载因子
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor);
if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
table = new Entry[initialCapacity];
threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
}
// 使用给定的 Map 构造一个 Hashtable
public Hashtable(Map t) {
this(Math.max(2*t.size(), 11), 0.75f);
putAll(t);
}2.4 主要方法
- put 方法
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null (value 不能为空)
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry tab[] = table;
// 计算 key 在 table 中的索引
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
// 判断 key 在 table 中是否已存在,若存在,则用 value 替换旧值
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry entry = (Entry)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
// 若不存在,则执行 addEntry 方法,将 key-value 添加到 table
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
} 可以看到,key 或 value 有一个为空都会抛出 NullPointerException 异常,因此二者都不能为空。
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++;
Entry tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
// 超过阈值,则扩容
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
// 将 key-value 添加到 table 中(头插法,即插到链表的头部)
// 即:先拿到 index 位置的元素,若为空,表示插入 entry 后则只有一个元素;
// 若不为空,表示该位置已有元素,将已有元素 e 连接到新的 entry 后面
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry e = (Entry) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
} 扩容操作 rehash() 如下:
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry[] oldMap = table;
// overflow-conscious code
// 新容量为旧容量的 2 倍加 1
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
// 若新容量的值超过最大容量 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,且旧容量为 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,则直接返回;
// 若旧容量值不为 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,则新容量为 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE.
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
// 新建一个 Entry 数组,容量为上面计算的容量大小
Entry[] newMap = new Entry[newCapacity];
modCount++;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
table = newMap;
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry old = (Entry)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
Entry e = old;
old = old.next;
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
// 注意这里会调换顺序
e.next = (Entry)newMap[index];
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
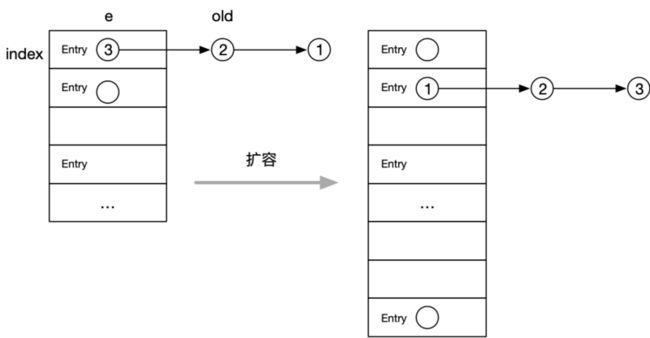
} 扩容操作,若 index 位置为链表,且插入顺序为 1、2、3,则在该位置的存储顺序为 3、2、1。扩容时,会从前往后读取元素并操作,因此扩容后的顺序为 3、2、1。示意图:
值得注意的是,put 方法(包括后面分析的 get 和 remove 等方法)带有 synchronized 关键字,Hashtable 就是通过这种方式实现线程安全的。这里锁定的是整个 table,因此并发效率较低,这也是高并发场景下推荐使用 ConcurrentHashMap 的原因。
- get 方法
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
return null;
}分析过 put 方法后,get 方法和 remove 方法分析起来就比较简单了,它们和 put 方法类似。
- remove 方法
public synchronized V remove(Object key) {
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry e = (Entry)tab[index];
for(Entry prev = null ; e != null ; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count--;
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = null;
return oldValue;
}
}
return null;
} 三种集合视图 EntrySet、keySet 和 values 分别如下:
private transient volatile Set keySet;
private transient volatile Set> entrySet;
private transient volatile Collection values;
public Set keySet() {
if (keySet == null)
keySet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new KeySet(), this);
return keySet;
}
public Set> entrySet() {
if (entrySet==null)
entrySet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new EntrySet(), this);
return entrySet;
}
public Collection values() {
if (values==null)
values = Collections.synchronizedCollection(new ValueCollection(),
this);
return values;
} 3. 小结
- Hashtable 是散列表的实现,处理散列冲突使用的是链表法,内部结构可以理解为「数组 + 链表」;
- 默认初始化容量为 11,默认负载因子为 0.75;
- 线程安全,使用 synchronized 关键字,并发效率低;
- 若无需保证线程安全,推荐使用 HashMap;若需要线程安全的高并发场景,推荐使用 ConcurrentHashMap。
![]()