3D跑酷类小游戏开发实战
今天,带领大家从零开始开发一款完整的3D跑酷类小游戏,主要面向有一定Egret2D开发经验的小伙伴,手把手教你学习EgretPro开发,快速开启您的EgretPro开发之旅。
下面是整个游戏的制作过程。
游戏制作
工欲善其事必先利其器,在开始制作游戏之前,您需要检查您是否安装了以下开发环境:
- 检查你的EgretPro是否更新到了1.6以及以上版本;
- 检查下是否安装了5.3.7以及以上的Egret2d引擎。
创建项目
首先,打开EgretPro,项目–库项目–新建。
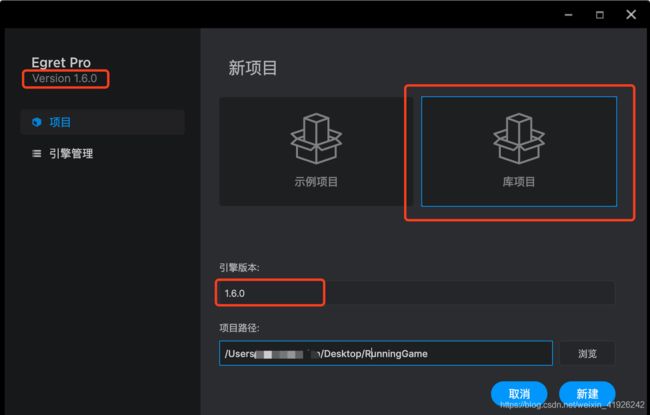
其次,创建完项目之后,EgretPro会自动打开刚才创建的库项目RunningGame,在resource/scenes目录下面创建一个场景RunningScene,双击在场景编辑中打开该场景。如下图所示:
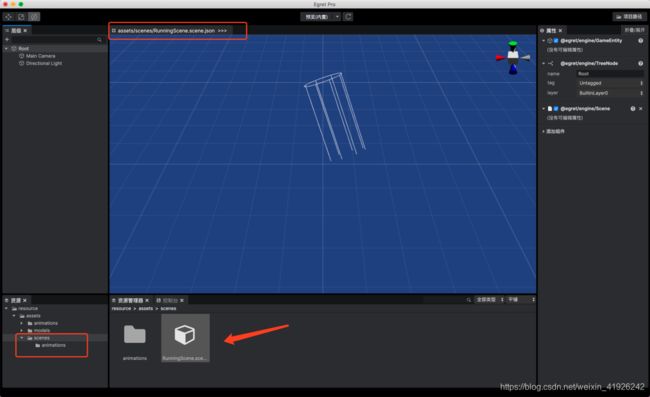
创建跑道
跑道是通过3个实体Cude拼接而成的,并且随着主角向前奔跑,跑道需要滚动起来,我们再这里通过组件的方式动态的创建跑道。
使用Vscode打开自己刚才创建的项目,然后在src目录下面创建一个文件夹game用来存放我们的组件代码,然后在game目录中创建RoadController.ts文件。
import { component } from "@egret/ecs";
import { Behaviour, GameEntity, EngineFactory, Vector3 } from "@egret/engine";
import { MeshFilter, DefaultMeshes, MeshRenderer, Material } from "@egret/render";
import { ResourceManager } from "@egret/core";
@component()
class RoadController extends Behaviour{
private roads:GameEntity[] = [];
private roadSize:Vector3 = Vector3.create(5,1,10);
async onStart(){
const RoadMaterial:Material = (await ResourceManager.instance.loadUri("assets/materials/ground.mat.json")).data;
//创建3个实体拼接成跑道
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
const road:GameEntity = EngineFactory.createGameEntity3D("road"+i);
road.addComponent(MeshFilter).mesh = DefaultMeshes.CUBE;
road.addComponent(MeshRenderer).material = RoadMaterial;
road.transform.localScale = this.roadSize;
road.transform.setPosition(0,0,i*this.roadSize.z);
this.roads.push(road);
}
}
onUpdate(){
}
}
然后把RoadController组件添加在场景的Root实体上,
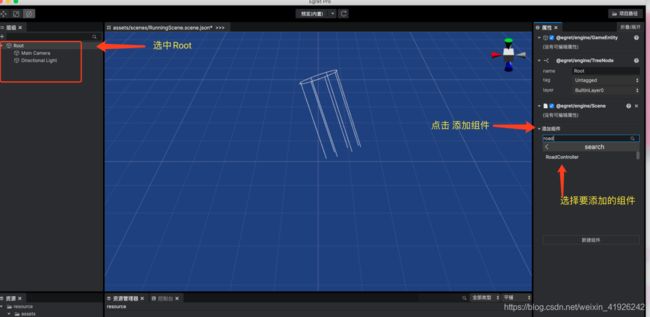
最后点击预览(内置)(或者预览浏览器)按钮,就可以看到下面的效果了。

摄像机的这个角度看上去有点别扭,你可以在运行界面,通过调试摄像机的TransForm参数来调整摄像机的位置与角度达到画面看上去比较舒服。
添加主角
将主角添加到场景中,并且向前奔跑,效果图如下:
第一步,将美术同学给的游戏素材BakedAnimation拷贝到项目目录resource/assets/animations中。

第二步,在EgretPro编辑器资源管理器中打开resource/assets/animations/BakedAnimation/Boy_standby_out目录,拖拽Boy_standby.gltf.prefab.json文件到场景中。

第三步,播放主角奔跑动画。有两种处理办法:
方法1:直接在pro编辑中进行操作。具体如下:
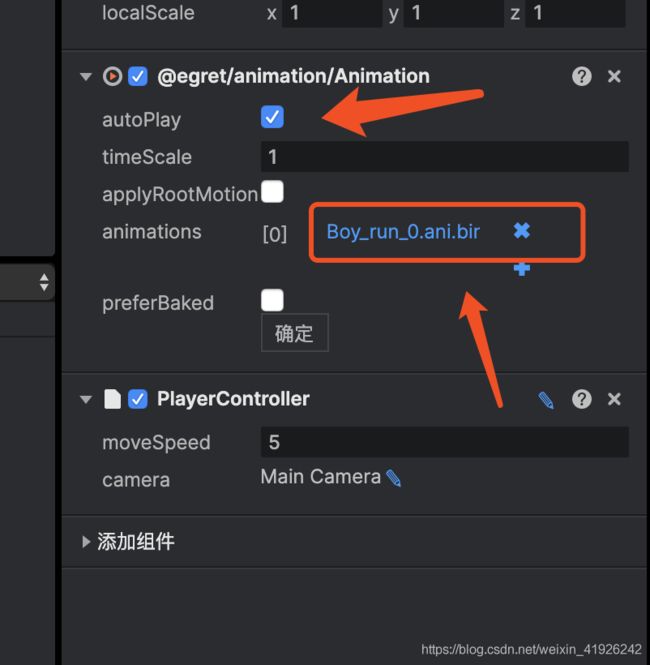
方法2:在pro编辑中去掉勾选autoPlay,通过脚本去实现,在game目录下面创建PlayerController文件;(记得把PlayerController组件挂在到主角实体上哦)
import { component } from "@egret/ecs";
import { Behaviour} from "@egret/engine";
import { Animation } from "@egret/animation";
@component()
class PlayerController extends Behaviour{
onStart(){
const animation = this.entity.getComponentInChildren(Animation);
animation.play("Boy_run_0");
}
}
到这步为止,我们的主角就在跑道上奔跑起来了,但是我们还需要让我们的玩家往前移动,我们需要在onUpdate函数中不断的更新主角的位置。同时我们还需要让摄像机跟随这主角进行同速度的移动,否则你会发现你的主角在你的屏幕中越跑越远,越来越小啦~
import { component } from "@egret/ecs";
import { Behaviour} from "@egret/engine";
import { Animation } from "@egret/animation";
@component()
class PlayerController extends Behaviour{
...
onUpdate(dt){
this.entity.transform.translate(0,0,this.moveSpeed*dt);
this.camera.transform.translate(0,0,this.moveSpeed*dt);
}
}
随着主角往前移动,我们发现走着走着,我们脚下的跑道没了~
这个时候我们需要在主角向前移动的同时不断的往前铺路,打开我们的RoadController.ts组件,
@component()
class RoadController extends Behaviour{
...
onUpdate(){
if(this.roads.length == 0) return;
const currentRoad = this.roads[0];
//当玩家跑过跑道之后,将跑道再次利用
if( this.player.transform.position.z > currentRoad.transform.position.z ){
const changeRoad = this.roads.shift();
changeRoad.transform.setPosition(0,0, this.roads[this.roads.length-1].transform.position.z+this.roadSize.z);
this.roads.push(changeRoad);
}
}
}
最后我们需要通过鼠标左键来控制主角左右移动。我们需要在onUpdate函数中,根据鼠标的移动来改变主角的位置。
@component()
class RoadController extends Behaviour{
onUpdate(dt){
let moveX = 0;
this.entity.transform.translate(0,0,this.moveSpeed*dt);
this.camera.transform.translate(0,0,this.moveSpeed*dt);
const _leftMouse = this.inputManager.getInput(InputCode.LeftMouse);
// 鼠标左键按下的时候记录下主角的位置
if(_leftMouse.isDown){
this.startPostionX = this.entity.transform.position.x;
}
//获取鼠标移动的距离
if(_leftMouse.isHold){
const point = _leftMouse.entity.getComponent(Pointer);
moveX = point.position.x - point.downPosition.x;
}
if (moveX) {
//增加一些跑道边界的限制
let playerNextPostionX = this.startPostionX + moveX/100;
if (playerNextPostionX > this.roadBound) {
playerNextPostionX = this.roadBound;
}
if (playerNextPostionX < -this.roadBound) {
playerNextPostionX = -this.roadBound;
}
//设置主角的位置
this.entity.transform.setPosition( playerNextPostionX,
this.entity.transform.position.y,
this.entity.transform.position.z);
}
}
}
添加金币
预制体是一个游戏对象及其组件的集合,目的是使游戏对象及资源能够被重复使用,相同的游戏对象可以通过一个预制体来创建,此过程可以理解为实例化
游戏中的金币散落在整个跑道上,在这里使用预制体来做金币是最合适的!
如何创建预制体?
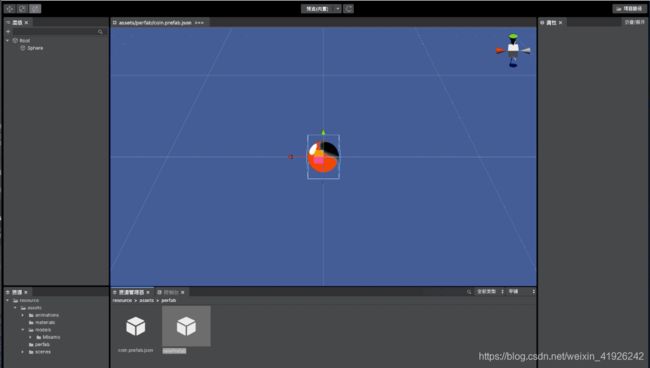
- 打开(或者创建)resource/perfab目录,然后在资源管理器模块,右键–》创建预制体coin.perfab.json。
- 双击刚刚创建的预制体,在层级栏中右键–>3D–>球体;
- 选中刚才创建的球体,在属性栏给其选择material项,选择,coin.mat.json;
首先,我们先来创建一个金币组件Coin.ts
import { component } from "@egret/ecs";
import { Behaviour, GameEntity } from "@egret/engine";
@component()
export class Coin extends Behaviour{
//因为金币需要在其他类中引用,所以需要将该类export出去
}
我们的金币都是散落在跑道上的,所以每创建一截跑道,我们就在该跑道上随机创建一些金币,金币的数量是随机的,位置也是随机的。接下来,需要在RoadController.ts组件中添加如下逻辑代码:
import { component } from "@egret/ecs";
import { Behaviour, GameEntity, EngineFactory, Vector3 } from "@egret/engine";
import { MeshFilter, DefaultMeshes, MeshRenderer, Material } from "@egret/render";
import { ResourceManager, serializedField, property, EditType } from "@egret/core";
import { Coin, CoinPool } from "./Coin";
@component()
class RoadController extends Behaviour{
...
private coinPerfabUrl:string = "assets/perfab/coin.prefab.json";
async onStart(){
const RoadMaterial:Material = (await ResourceManager.instance.loadUri("assets/materials/ground.mat.json")).data;
//创建3个实体拼接成跑道
for (let i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
...
//在每截跑道上创建金币
this.createCoins(road);
}
}
onUpdate(){
if(this.roads.length == 0) return;
const currentRoad = this.roads[0];
if( this.player.transform.position.z > currentRoad.transform.position.z ){
...
//添加金币
this.createCoins(changeRoad);
}
}
async createCoins(road:GameEntity){
//数量随机
const coindCnt = Math.floor(Math.random()*3) + 1;
for (let i = 0; i < coindCnt; i++) {
// 创建金币---预制体
coin = await EngineFactory.createPrefab(this.coinPerfabUrl) as GameEntity;
coin.addComponent(Coin);
//位置随机
coin.transform.setPosition(Math.random() * this.roadSize.x - this.roadSize.x / 2, 1, road.transform.position.z + i * 1.5)
}
}
}
这样子我们就可以在道路上面看见很多随机的金币啦!
但是如果是有一定开发经验的小伙伴肯定知道我们还需要一个金币池,来回收金币,避免一直创建金币。
接下来我们再来创建一个金币缓冲池。我直接在Coin.ts文件中添加一个CoinPool类。
// Coin.ts
export class CoinPool{
static coinPool:GameEntity[] = [];
}
当金币离开摄像机的渲染范围,我们就应该把金币放入到缓冲池中,同时金币实体不在参与渲染,使金币处于休眠状态。这些对金币的处理我们都放在系统类中去做。
系统便是来处理拥有一个或多个相同特征组件的实体集合的工具,其只拥有行为(即在系统中没有任何状态)。
我们系统类中获取所有的金币。那么如何在系统中获取所有的金币呢?
实体匹配器是用来定义具有某种组件特征的实体集合的规则,通过一个匹配器实例,就可以定义一个明确的实体集合的规则。
//举列子,我们通过实体匹配器获取场景中所有具有Transform 和MeshRender组件的实体集合
Matcher.create(GameEntity, true, Transform, MeshRenderer);
回归到我们的案例中,我们先创建一个金币系统类 CoinSystem.ts,在其中,我们要获取所有的金币,然后在每一帧中检查金币是否被玩家甩到背后,不需要渲染了,那么我们就把它回收到金币池中。具体看下面的代码:
import { System, system, Matcher } from "@egret/ecs";
import { GameEntity } from "@egret/engine";
import { Coin, CoinPool } from "./Coin";
@system()
export class CoinSystem extends System{
player:GameEntity = null;
//实体匹配器
getMatchers(){
//获取所有金币,返回集合,返回的集合存储在 this.grounps[0]中
return [
Matcher.create(GameEntity,true,Coin)
];
}
onFrame(){
const coins = this.groups[0].entities as GameEntity[];
for (const coin of coins) {
//如果金币远离了主角
if(coin.transform.position.z < this.player.transform.position.z-5){
coin.enabled = false;
coin.getComponent(Coin).enabled = false;
CoinPool.coinPool.push(coin);
}
}
}
}
系统并不像组件直接添加到实体上就可以起作用,我们需要在组件注册系统。接下来,在PlayerController中,添加如下两行代码。
//PlayerController.ts
...
onAwake(){
Application.instance.systemManager.registerSystem(CoinSystem);
Application.instance.systemManager.getSystem(CoinSystem).player = this.entity;
}
...
当创建金币的时候,我们首先考虑从缓冲池中获取。修改RoadController.ts中createCoins()函数
//RoadController.ts
async createCoins(road:GameEntity){
const coindCnt = Math.floor(Math.random()*3) + 1;
for (let i = 0; i < coindCnt; i++) {
let coin:GameEntity = null;
if(CoinPool.coinPool.length>0){
//获取缓冲池中的金币
coin = CoinPool.coinPool.pop();
coin.enabled = true;
coin.getComponent(Coin).enabled = true;
console.log("-----------");
}else{
// 创建金币---预置体
coin = await EngineFactory.createPrefab(this.coinPerfabUrl) as GameEntity;
coin.addComponent(Coin);
}
coin.transform.setPosition(Math.random() * this.roadSize.x - this.roadSize.x / 2, 1, road.transform.position.z + i * 1.5)
}
}
处理碰撞
接下来,我们要做的就是处理金币与主角之间的碰撞了,我们需要检查每一个金币,如果和主角发生了碰撞,那么我们的金币就有一个缓动动画然后消失。那么对金币与主角碰撞处理的这一个行为我们还是放在CoinSystem.ts系统类中去处理。
//CoinSystem.ts
onFrame(){
...
//判断玩家与金币的碰撞
if (coin.transform.position.getDistance(this.player.transform.position)<1) {
console.log("-----+++++");
coin.getComponent(Coin).enabled = false;
Tween.toPosition(coin.transform,1,{
y:3,
ease:Elastic.easeOut,
onComplete:()=>{
coin.enabled = false;
CoinPool.coinPool.push(coin);
}
})
}
添加UI界面
到这一步,我们的3D场景就完成啦!
接下来,我们需要给案例添加一个UI界面,也就是要加入一些2d的内容。在这里我需要给读者讲解一下如何在3d场景中添加UI界面?具体参考这里:Egret2d与EgretPro整合
第一步,将3d场景导出成第三方库pro-library;
第二步,创建一个2d项目,将第三库pro-library添加到2d项目中;
第三步,升级2D项目,修改index.html
egret.runEgret({
renderMode: "webgl",
audioType: 0,
calculateCanvasScaleFactor: function (context) {
const backingStore = context.backingStorePixelRatio ||
context.webkitBackingStorePixelRatio ||
context.mozBackingStorePixelRatio ||
context.msBackingStorePixelRatio ||
context.oBackingStorePixelRatio ||
context.backingStorePixelRatio || 1;
return (window.devicePixelRatio || 1) / backingStore;
},
pro: true, // 需要修改为true,以启动 EgretPro 环境
});
第四步,EgretPro 中的场景渲染为一个egret.Texture对象,Egret引擎只需要将egret.Texture添加到Bitmap对象当中,即可渲染到舞台。
const texture = await egret.pro.createTextureFrom3dScene("assets/scenes/animations/test.scene.json", 640, 640);
const bitmap = new egret.Bitmap(texture);
this.addChild(bitmap);
结合本案例,我们处理完上面的第一、二、三步,我的项目目录如下图:
然后我点击开始游戏按钮,添加跑酷的场景。具体看Main.ts文件。
//Main.ts文件
private async onButtonClick(e: egret.TouchEvent) {
const texture = await egret.pro.createTextureFrom3dScene("assets/scenes/RunningScene.scene.json",640,1136);
const bitmap = new egret.Bitmap(texture);
this.addChild(bitmap);
}
但是这个时候,大家发现我们的主角无法左右移动了,这个时候需要我们将2d的触摸事件传递到3d场景中。那么就需要通过egret.pro去完成通信。
//Main.ts
private createGameScene(){
//...
this.addEventListener(egret.TouchEvent.TOUCH_BEGIN,this.onTouchBegin,this);
this.addEventListener(egret.TouchEvent.TOUCH_MOVE,this.onTouchMove,this);
}
private startPostionX:number;
private onTouchBegin(e:egret.TouchEvent){
this.startPostionX = e.stageX;
//派发消息
egret.pro.dispatch("2dTouchBegin",1);
}
private onTouchMove(e:egret.TouchEvent){
const moveX = e.stageX - this.startPostionX;
//派发消息
egret.pro.dispatch("2dTouchMove",1,moveX);
}
那么我们需要在3d场景的PalyerContrller中接受消息并且处理消息。具体见下:
//PlayerController.ts
onStart(){
...
//监听2d的消息
Application.instance.egretProUtil.addEventListener("2dTouchBegin",1,this.touchBeginFrom2D,this);
Application.instance.egretProUtil.addEventListener("2dTouchMove",1,this.touchMoveFrom2D,this);
}
touchBeginFrom2D(){
this.startPostionX = this.entity.transform.position.x;
}
touchMoveFrom2D(messag:any){
let moveX = this.startPostionX + messag/100;
if(moveX > this.roadBound){
moveX = this.roadBound
}
if(moveX < -this.roadBound){
moveX = -this.roadBound;
}
this.entity.transform.setPosition(
moveX,
this.entity.transform.position.y,
this.entity.transform.position.z
);
}
然后,我们控制台输入指令:egret run -a 就可以运行你的项目啦!
小结
恭喜你完成了使用EgretPro制作的第一款游戏,在这里你可以下载完整的游戏源码。
通过本示例你可以学到手势识别、动画系统、金币系统、碰撞处理、UI系统、EgretPro与Egret2d项目交互等知识点同时你也可以学习了解到EgretPro与Egret2d之间的交互–使用EgretPro制作3D场景,然后把制作好的3D场景导出为第三库的形式添加到Egret2D项目,在Egret2D项目中处理UI系统,使用Egret.pro中的方法进行3D与2D之间的通信。
最后,您还可以继续在本示例的基础上添加功能继续完善您的游戏。期待您的完美作品!