【Vue-Router】模拟源码,解析 Vue-Router 的实现原理
前言
笔记来源:拉勾教育 大前端高薪训练营
阅读建议:建议通过左侧导航栏进行阅读
Vue-Router
基础知识
编程式导航
this.$router.replace()
this.$router.push()
this.$router.go()
Hash 和 History
客户端路由的实现模式,当路径发生变化时,不会向服务器发生请求,都是 JavaScript 监视路径的变化,然后根据不同的地址渲染不同的内容。
表现形式的区别
-
Hash 模式
https://music.163.com/#/playlist?id=3102961863
-
History 模式
https://music.163.com/playlist/3102961863
需要服务端配置支持
原理的区别
-
Hash 模式是基于锚点,以及 onhashchange 事件;
通过 锚点的值 作为路由地址,当地址发生变化后,触发 onhashchange 事件。
即 根据路径决定页面中呈现的内容。 -
History 模式是基于 HTML5中的 History API
history.pushState() IE10 以后才支持
当调用 history.push() 时,路径会发生变化,要向服务器发生请求;
当调用 history.pushState() 时,不会向服务器发生请求,只会改变浏览器路径栏中的地址,并且将地址记录到历史记录中。
也就是说,可以使用 pushState() 实现客户端路由。但是,需要在IE10以后使用。
history.replaceState()
History 模式
- History 需要服务器的支持
- 单页应用中,服务端不存在 http://www.testurl.com/login 这样的地址,会返回找不到该页面
- 在服务端应该除了静态资源外都返回单页应用的 index.html
nginx 配置
-
从官网下载 nginx 的压缩包
-
把压缩包解压到 c 盘根目录,c:\nginx-1.18.0 文件夹
注意:目录不能有中文
-
打开命令行,切换到目录 c:\nginx-1.18.0
-
启动 nginx
$ start nginx -
重启
$ nginx -s reload -
停止
$ nginx -s stop
总结
Hash 模式
- URL 中 # 后面的内容作为路径地址
- 监听 hashchange 事件
- 根据当前路由地址找到对应组件重新渲染
History 模式
- 通过 history.pushState() 方法改变地址栏
- 监听 popstate 事件
- 根据当前路由地址找到对应组件重新渲染
模拟实现
前置知识
在模拟 Vue-Router 的过程中,我们需要简单了解一些相关的知识。
插件
插件通常用来为 Vue 添加全局功能。插件的功能范围没有严格的限制——一般有下面几种:
- 添加全局方法或者 property。如:vue-custom-element
- 添加全局资源:指令/过滤器/过渡等。如 vue-touch
- 通过全局混入来添加一些组件选项。如 vue-router
- 添加 Vue 实例方法,通过把它们添加到 Vue.prototype 上实现。
- 一个库,提供自己的 API,同时提供上面提到的一个或多个功能。如 vue-router
使用插件
- 通过全局方法
Vue.use()使用插件。它需要在你调用 new Vue() 启动应用之前完成:// 调用 `MyPlugin.install(Vue)` Vue.use(MyPlugin) new Vue({ // ...组件选项 }) - 也可以传入一个可选的选项对象:
Vue.use(MyPlugin, { someOption: true })Vue.use会自动阻止多次注册相同插件,届时即使多次调用也只会注册一次该插件。
开发插件
Vue.js 的插件应该暴露一个 install 方法。
- 具体实现,代码如下:
/** * 第一个参数是 Vue 构造器,第二个参数是一个可选的选项对象 */ MyPlugin.install = function (Vue, options) { // 1. 添加全局方法或 property Vue.myGlobalMethod = function () { // 逻辑... } // 2. 添加全局资源 Vue.directive('my-directive', { bind (el, binding, vnode, oldVnode) { // 逻辑... } ... }) // 3. 注入组件选项 Vue.mixin({ created: function () { // 逻辑... } ... }) // 4. 添加实例方法 Vue.prototype.$myMethod = function (methodOptions) { // 逻辑... } }
组件
注册全局组件
-
使用
Vue.component来注册全局组件:Vue.component('my-component-name', { // ... 选项 ... })第一个参数是 组件名,全局组件在注册之后可以用在任何新创建的 Vue 根实例 (new Vue) 的模板中。
-
使用
props向子组件传递数据Vue.component('blog-post', { props: ['title'] })
混入 mixin
混入(mixin),用来分发 Vue 组件中的可复用功能。一个混入对象可以包含任意组件选项。当组件使用混入对象时,所有混入对象的选项将被“混合”进入该组件本身的选项。
基本实现
- 具体实现,代码如下:
// 定义一个混入对象 var myMixin = { created: function () { this.hello() }, methods: { hello: function () { console.log('hello from mixin!') } } } // 定义一个使用混入对象的组件 var Component = Vue.extend({ mixins: [myMixin] }) var component = new Component() // => "hello from mixin!"
全局混入
混入也可以进行全局注册。使用时格外小心!一旦使用全局混入,它将影响每一个之后创建的 Vue 实例。使用恰当时,这可以用来为自定义选项注入处理逻辑。
- 具体实现,代码如下:
// 为自定义的选项 'myOption' 注入一个处理器。 Vue.mixin({ created: function () { var myOption = this.$options.myOption if (myOption) { console.log(myOption) } } }) new Vue({ myOption: 'hello!' }) // => "hello!"
Vue.observable(object)
基本用法
创建响应式对象,创建出的对象可以直接用在渲染函数或者计算属性上面,并且会在发生变更时触发相应的更新。也可以作为最小化的跨组件状态存储器,用于简单的场景:
- 具体实现,代码如下:
const state = Vue.observable({ count: 0 }) const Demo = { render(h) { return h('button', { on: { click: () => { state.count++ }} }, `count is: ${ state.count}`) } }在 Vue 2.x 中,被传入的对象会直接被
Vue.observable变更,所以如这里展示的,它和被返回的对象是同一个对象。
在 Vue 3.x 中,则会返回一个可响应的代理,而对源对象直接进行变更仍然是不可响应的。
因此,为了向前兼容,我们推荐始终操作使用Vue.observable返回的对象,而不是传入源对象。
插槽 slot
元素作为承载分发内容的出口。插槽内可以包含任何模板代码,包括 HTML、其他组件等
- 具体实现,代码示例如下:
Vue.component('alert-box', { template: `Error!` })
render 函数
类型:(createElement: () => VNode) => VNode
详细:
字符串模板的代替方案,允许你发挥 JavaScript 最大的编程能力。该渲染函数接收一个 createElement方法作为第一个参数用来创建 VNode。
如果组件是一个函数组件,渲染函数还会接收一个额外的 context 参数,为没有实例的函数组件提供上下文信息。
Vue 选项中的
render函数若存在,则 Vue 构造函数不会从template选项或通过el选项指定的挂载元素中提取出的 HTML 模板编译渲染函数。
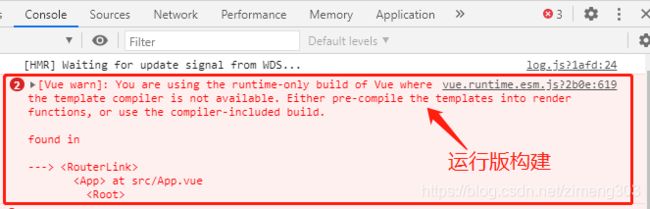
构建版本
运行版 Vue
不支持 template 模板,需要打包的时候提前编译。
- 使用 render 函数,替代 template 模板,代码如下
export default class VueRouter { initComponents (Vue) { Vue.component('router-link', { props: { to: String }, // h 函数,创建虚拟 DOM render (h) { return h() } }) } }
完整版 Vue
包含运行时和编译器,体积比运行时版大 10K 左右,程序运行的时候把模板转换成 render 函数。
- 在 vue.config.js 中,开启使用包含运行时编译器的Vue核心版本,代码如下:
module.exports = { runtimeCompiler: true // 默认 false }
实现原理
下面,我们通过模拟源码的方式,进行分析 Vue-Router 的实现原理。
模拟 History 模式
install()
install() 方法是 VueRouter 类中的静态方法,当使用 Vue.use(fun | obj) 注册插件时,会调用 install() 方法。
- install() 源码,分析如下:
let _Vue = null export default class VueRouter { /** * Vue.use() 注册插件时,调用 * @param Vue Vue构造函数 */ static install(Vue) { // 1,判断当前插件是否已经被安装 if (VueRouter.install.installed) { return } VueRouter.install.installed = true // 2,把Vue构造函数记录到全局变量中 _Vue = Vue // 3,把创建Vue实例时,传入的 router对象 注入到Vue实例上 // 混入 _Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate() { // 判断当前传入的是否是 router 对象,即排除传入组件的情况 if (this.$options.router) { _Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router } } }) } }
Constructor()
VueRouter 类的构造函数,接收一个 Options 选项,它的的返回值是一个 VueRouter 对象。
在构造函数中,需要初始化三个属性:
1,options,记录构造函数中传入的对象(路由规则);
2,data,存储当前的路由地址,当路由变化时,需要加载对应的组件,因此,需要设置成一个响应式的对象;
3,routeMap,是一个对象,用来记录路由地址和组件的对应关系,将来会把路由规则解析到 routeMap 中。
- constructor() 源码,分析如下:
let _Vue = null export default class VueRouter { // 构造函数 constructor (options) { // 记录构造函数中传入的选项 this.options = options // 当options中传入的 routes(路由规则) 解析出来以后,会将其存储到 routeMap 对象中,以便在router-view组件中,可以根据路由地址在routeMap中找到对应的组件,并将其渲染到浏览器中 // 键:路由地址 值:地址所对应的路由组件 this.routeMap = { } // 响应式对象,使用 Vue.observable() 创建 this.data = _Vue.observable({ current: '/' // 记录当前的路由地址,默认 '/' }) } }
createRouteMap()
createRouteMap(),会把构造函数中选项的 routes(路由规则),转换成键值对的形式,存储到 routeMap对象中。
- createRouteMap() 源码,分析如下:
export default class VueRouter { // 其余代码 省略 createRouteMap () { // 遍历所有的路由规则,把路由规则解析成键值对的形式,存储到 routeMap 中 this.options.routes.forEach(route => { this.routeMap[route.path] = route.component }) } }
initComponents()
initComponents() ,创建 router-link 和 router-view 组件。
-
initComponents() 源码,注册 router-link 组件,分析如下:
export default class VueRouter { // 创建 router-link 和 router-view 组件 // 传入Vue构造函数 // 不使用_Vue,减少与外部的依赖 initComponents (Vue) { Vue.component('router-link', { props: { to: String }, // 使用插槽,进行中间内容的填充 template: '' }) } } 运行结果,如下图所示:
-
使用 render 函数,解决上述问题,代码如下:
export default class VueRouter { initComponents (Vue) { Vue.component('router-link', { props: { to: String }, // h 函数,创建虚拟 DOM render (h) { /** * @param 创建元素对应的选择器 * @param 添加标签属性,对象 * @param 生成标签的子元素,数组 */ return h('a', { attrs: { href: this.to } }, [this.$slots.default]) // 获取默认插槽 } }) } } -
注册 router-view 组件,代码如下:
export default class VueRouter { // 其余代码 省略 initComponents (Vue) { Vue.component('router-link', { props: { to: String }, // h 函数,创建虚拟 DOM render (h) { return h('a', { attrs: { href: this.to, on: { click: this.clickHandler // 注册点击事件 } } }, [this.$slots.default]) // 获取默认插槽 }, methods: { clickHandler (e) { // 改变浏览器的地址栏,但不向服务器发送请求,只在客户端进行操作 /** * @param data 触发popstate事件,传给 popstate 的事件对象 * @param title 网页的标题 * @param url? 地址 */ history.pushState({ }, '', this.to) // 将当前的路径记录到 data.current 中 // 响应式对象,当值改变时,自动加载对应的组件,进行渲染视图 this.$router.data.current = this.to e.preventDefault() // 阻止默认事件 } } }) const self = this Vue.component('router-view', { // h 函数,可以直接把一个组件转换成 虚拟 DOM render (h) { // 通过当前路由地址,在routeMap中找到对应组件 const component = self.routeMap[self.data.current] return h(component) } }) } }
initEvent()
initEvent(),注册 popstate 事件,当历史发生变化时,进行触发。即点击浏览器的前进后退按钮时,触发 popstate 事件。
- initEvent() ,注册 popstate 事件,代码如下:
export default class VueRouter { initEvent () { window.addEventListener('popstate', () => { this.data.current = window.location.pathname }) } }
init()
init() ,用来初始化调用其他函数。
- init() 源码,,代码如下:
export default class VueRouter { // 其余代码省略 static install (Vue) { _Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate () { if (this.$options.router) { _Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router this.$options.router.init() } } }) } init () { this.createRouteMap() this.initComponents(_Vue) this.initEvent() } }
Hash 模式
hash 模式下,触发 onhashchange 事件,其余方面与 history 模式类似。
- 具体实现,代码示例如下:
let _Vue = null export default class VueRouter { // 使用 Vue.use() 注册插件时,此方法被调用 static install (Vue) { // 判断当前插件是否已被安装 if (VueRouter.install.installed) { return } VueRouter.install.installed = true _Vue = Vue _Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate () { if (this.$options.router) { _Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router this.$options.router.init() } } }) } constructor (options) { this.options = options this.routeMap = { } this.current = '' // 当模式为 hash,初始进入时,进行拼接 window.location.hash = window.location.hash ? window.location.hash : '#/' this.data = _Vue.observable({ current: window.location.hash }) } init () { this.createRouteMap() this.initComponents(_Vue) this.initEvent() } createRouteMap () { this.options.routes.forEach(route => { this.routeMap[route.path] = route.component }) } // 初始化组件 initComponents (Vue) { const self = this // 定义全局组件 router-link Vue.component('router-link', { // 使用 props 传递属性 props: { to: String }, render (h) { return h('a', { attrs: { href: '#' }, class: { 'router-link-active': this.to === '/', 'router-link-exact-active': self.data.current === this.to }, on: { click: this.clickHandler } }, [this.$slots.default]) // 获取默认插槽 }, methods: { clickHandler (e) { e.preventDefault() // 当模式为 hash 时,执行的操作 window.location.hash = this.to } } }) // router-view _Vue.component('router-view', { render (h) { // 当路由路径是 hash 时,去掉 # ,以便获取对应的组件 if (self.data.current.startsWith('#')) { self.data.current = self.data.current.substr(1) } const component = self.routeMap[self.data.current] return h(component) } }) } initEvent () { // 当地址发生变化后,触发 onhashchange 事件 window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => { const current = window.location.hash.substr(1) this.data.current = current || this.data.current }) } }
以上单独模拟了 hash 和 history 模式的路由实现,这两种可以整合成一套代码,进行不同模式下,匹配不同的路由操作。
具体代码实现,参见:
https://gitee.com/zimeng303/lago-training-camp/tree/master/work/Module%2003/01-part-code/vue-hash
参考网址
VueJs官网