【Vue.js源码解析 一】-- 响应式原理
前言
笔记来源:拉勾教育 大前端高薪训练营
阅读建议:建议通过左侧导航栏进行阅读
课程目标
- Vue.js 的静态成员和实例成员初始化过程
- 首次渲染的过程
- 数据响应式原理 – 最核心的特性之一
准备工作
Vue 源码的获取
-
项目地址:https://github.com/vuejs/vue
-
Fork 一份到自己仓库,克隆到本地,可以自己写注释提交到 github
-
为什么分析 Vue 2.6
1,到目前为止 Vue 3.0 的正式版还没有发布
2,新版本发布后,现有项目不会升级到 3.0,2.x 还有很长的一段过渡期
3,3.0 项目地址:https://github.com/vuejs/vue-next
源码目录结构
src 源码部分
├─compiler 编译相关
├─core Vue 核心库
├─platforms 平台相关代码
├─server SSR 服务端渲染
├─sfc .vue 文件编译为 js 对象
└─shared 公共的代码
了解 Flow
-
官网:https://flow.org/
-
JavaScript 的静态类型检查器
-
Flow 的静态类型检查错误是通过静态类型推断实现的
- 文件开头通过 // @flow 或者 /* @flow */ 声明
/* @flow */ function square(n: number): number { return n * n; } square("2"); // Error!
调试设置
打包
-
打包工具 Rollup
- Vue.js 源码的打包工具使用的是 Rollup,比 Webpack 轻量
- Webpack 把所有文件当做模块,Rollup 只处理 js 文件更适合在 Vue.js 这样的库中使用
- Rollup 打包不会生成冗余的代码
-
安装依赖
$ npm i -
设置 sourcemap
- package.json 文件中的 dev 脚本中添加参数
--sourcemap-w:watch 监视源码的变化,当源码发生变化时,立即重新打包;-c:设置配置文件--sourcemap:开启代码地图,在调试时,可以直接进入src中查看源码--environment:设置环境变量,通过设置的环境变量,打包不同版本的 Vue
{ "scripts": { "dev": "rollup -w -c scripts/config.js --sourcemap --environment TARGET:web- full-dev" } } - package.json 文件中的 dev 脚本中添加参数
-
执行 dev
-
npm run dev 执行打包,用的是 rollup,-w 参数是监听文件的变化,文件变化自动重新打包
-
结果:
-
调试
Vue 的不同构建版本
术语
- 完整版:同时包含编译器和运行时的版本。
- 编译器:用来将模板字符串(template)编译成为 JavaScript 渲染函数(render --> vnode)的代码,体积大、效率低。
- 运行时:用来创建 Vue 实例、渲染并处理虚拟 DOM 等的代码,体积小、效率高。基本上就是除去编译器的代码。
- UMD:UMD 版本通用的模块版本,支持多种模块方式。
vue.js默认文件就是运行时 + 编译器的UMD 版本 - CommonJS(cjs)**:CommonJS 版本用来配合老的打包工具比如 Browserify 或 webpack 1。
- ES Module:从 2.6 开始 Vue 会提供两个 ES Modules (ESM) 构建文件,为现代打包工具提供的版本。
- ESM 格式被设计为可以被静态分析,所以打包工具可以利用这一点来进行“tree-shaking”并将用不到的代码排除出最终的包。
- ES6 模块与 CommonJS 模块的差异
Runtime + Compiler vs. Runtime-only
-
举例比较,代码如下:
// compiler // 需要编译器,把 template 转换成 render 函数 // const vm = new Vue({ // el: '#app', // template: '{ { msg }}
', // data: { // msg: 'Hello Vue' // } // }) const vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', // template: '{ { msg }}
', render(h) { return h('h1', this.msg) }, data: { msg: 'Hello Vue' } }) -
推荐使用运行时版本,因为运行时版本相比完整版体积要小大约 30%
-
基于 Vue-CLI 创建的项目默认使用的是
vue.runtime.esm.js- 通过查看 webpack 的配置文件
$ vue inspect > output.js -
注意:
.vue文件中的模板是在构建时预编译的,最终打包后的结果不需要编译器,只需要运行时版本即可。
构建过程
寻找入口文件
查看 dist/vue.js 的构建过程
执行构建
-
运行构建命令,命令如下:
$ npm run dev即,package.json 中配置的 NPM Scripts 命令,配置如下:
--environment TARGET:web-full-dev设置环境变量 TARGET{ "scripts": { "dev": "rollup -w -c scripts/config.js --sourcemap --environment TARGET:web-full-dev" } }
scripts/config.js 的执行过程
-
作用:生成 rollup 构建的配置文件
-
使用环境变量 TARGET = web-full-dev
// 判断环境变量是否有 TARGET // 如果有的话 使用 genConfig() 生成 rollup 配置文件 if (process.env.TARGET) { // web-full-dev module.exports = genConfig(process.env.TARGET) } else { // 否则获取全部配置 exports.getBuild = genConfig exports.getAllBuilds = () => Object.keys(builds).map(genConfig) } -
genConfig(name)
-
根据环境变量 TARGET 获取配置信息
-
builds[name] 获取生成配置的信息
// Runtime+compiler development build (Browser) 'web-full-dev': { entry: resolve('web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js'), dest: resolve('dist/vue.js'), format: 'umd', env: 'development', alias: { he: './entity-decoder' }, banner }, -
-
resolve()
- 获取入口和出口文件的绝对路径
const aliases = require('./alias') // 将传入的路径转换为绝对路径 const resolve = p => { // 根据路径中的前半部分去 alias 模块中找别名对应的路径 const base = p.split('/')[0] // web / dist if (aliases[base]) { return path.resolve(aliases[base], p.slice(base.length + 1)) } else { return path.resolve(__dirname, '../', p) } } -
alias 模块
- 定义别名,简化路径书写
// 将传入的参数 转化为 绝对路径 // __dirname 当前文件所在的绝对路径 const resolve = p => path.resolve(__dirname, '../', p) module.exports = { vue: resolve('src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler'), compiler: resolve('src/compiler'), core: resolve('src/core'), shared: resolve('src/shared'), web: resolve('src/platforms/web'), weex: resolve('src/platforms/weex'), server: resolve('src/server'), sfc: resolve('src/sfc') }
结果
- 把 src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js 构建成 dist/vue.js,如果设置 --sourcemap 会生成 vue.js.map
- src/platform 文件夹下是 Vue 可以构建成不同平台下使用的库,目前有 weex 和 web,还有服务器端渲染的库
源码解析
从入口开始
src/platform/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
通过查看源码解决下面问题
-
观察以下代码,通过阅读源码,回答在页面上输出的结果
// 如果同时设置template和render此时会渲染什么? const vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', template: 'Hello Template
', render(h) { return h('h1', 'Hello Render') } }) -
阅读源码记录
// 保留 Vue 实例的 $mount 方法 const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount // 重写 ./runtime/index 文件中的 $mount // $mount 将生成的代码挂载到页面中 Vue.prototype.$mount = function ( // el: 创建 vue 实例时,传入的选项 el?: string | Element, // 非 SSR 情况下为 false,SSR 时为 true hydrating?: boolean ): Component { // 获取 el 对象,即 DOM 对象 el = el && query(el) /* istanbul ignore if */ // el 不能是 body 或者 html if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) { process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( `Do not mount Vue to or - mount to normal elements instead.` ) return this } // 创建 vue 实例时,传入的选项 const options = this.$options // resolve template/el and convert to render function if (!options.render) { // 把 template/el 转换成 render 函数 ...... } // 调用 mount 方法,渲染 DOM return mount.call(this, el, hydrating) } -
阅读源码,结论如下
- el 不能是 body 或者 html 标签
- 如果没有 render,把 template 转换成 render 函数
- 如果有 render 方法,直接调用 mount 挂载 DOM
-
调试的代码
const vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', template: 'Hello Template
', render(h) { return h('h1', 'Hello Render') } }) -
浏览器调试
-
渲染后,结果如下:
-
遗留问题
- Vue 的构造函数在哪?
- Vue 的实例成员 / Vue 的静态成员 从哪里来的?
Vue 的 构造函数 在哪里
-
src/platform/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js 中引用了
./runtime/index -
src/platform/web/runtime/index.js- 设置 Vue.config
// install platform specific utils // 判断是否是关键属性(表单元素的 input/checked/selected/muted) // 如果是这些属性,设置 el.props 属性(属性不设置到标签上) Vue.config.mustUseProp = mustUseProp Vue.config.isReservedTag = isReservedTag Vue.config.isReservedAttr = isReservedAttr Vue.config.getTagNamespace = getTagNamespace Vue.config.isUnknownElement = isUnknownElement- 设置平台相关的指令和组件
- 指令 v-model、v-show
- 组件 transition、transition-group
- 设置平台相关的 patch 方法(打补丁方法,对比新旧的 VNode)
- 设置 $mount 方法,挂载 DOM
// install platform runtime directives & components // 注册跟平台相关的全局的指令和组件 // extend() ,将第二个参数的对象所有成员,复制到第一个对象成员中 // extend() ,复制对象成员的功能 extend(Vue.options.directives, platformDirectives) extend(Vue.options.components, platformComponents) // install platform patch function // __patch__ 将 vnode 转换成 真实 DOM // noop 是一个空函数 Vue.prototype.__patch__ = inBrowser ? patch : noop // public mount method Vue.prototype.$mount = function ( el?: string | Element, hydrating?: boolean ): Component { el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating) } -
src/platform/web/runtime/index.js 中引用了
core/index -
src/core/index.js// 给 Vue 的构造函数挂载 静态方法 initGlobalAPI(Vue) -
src/core/index.js 中引用了
./instance/index -
src/core/instance/index.js- 定义了 Vue 的构造函数
// 1. 创建 Vue 构造函数 // 此处不用 class 的原因,是因为方便后续给Vue 实例混入实例成员 function Vue (options) { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !(this instanceof Vue) // this 是否指向 Vue 的实例 ) { warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword') } // 调用 _init() 方法 this._init(options) } // 2. 注册 Vue 实例成员 // 注册 vm 的 _init() 方法,初始化 vm initMixin(Vue) // 注册 vm 的 $data/$props/$set/$delete/$watch stateMixin(Vue) // 初始化事件相关方法 // $on/$once/$off/$emit eventsMixin(Vue) // 初始化生命周期相关的混入方法 // _update()/$forceUpdate/$destroy lifecycleMixin(Vue) // 混入 render // $nextTick/_render renderMixin(Vue)
四个导出 Vue 的模块
-
src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
- web 平台相关的入口,重点实现编译
- 重写了平台相关的 $mount() 方法,将
template转换成render函数 - 注册了 Vue.compile() 方法,传递一个 HTML 字符串返回 render 函数
-
src/platforms/web/runtime/index.js
- web 平台相关
- 注册和平台相关的全局指令:
v-model、v-show - 注册和平台相关的全局组件:
v-transition、v-transition-group - 全局方法:
__patch__:把虚拟 DOM 转换成真实 DOM$mount:挂载方法,将 DOM 渲染到页面中
-
src/core/index.js
- 与平台无关
- 设置了 Vue 的静态方法,initGlobalAPI(Vue)
-
src/core/instance/index.js
- 与平台无关
- 定义了构造函数,调用了 this._init(options) 方法
- 给 Vue 中混入了常用的实例成员
Vue 的初始化
src/core/global-api/index.js
-
初始化 Vue 的静态方法
src/core/index.js
// 注册 Vue 的静态属性/方法 initGlobalAPI(Vue)src/core/global-api/index.js
// 初始化 Vue.config 对象 // 在 Vue 中 定义 config 属性 Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'config', configDef) // exposed util methods. // NOTE: these are not considered part of the public API - avoid relying on // them unless you are aware of the risk. // 这些工具方法不视作全局API的一部分,除非你已经意识到某些风险,否则不要去依赖他们 Vue.util = { warn, extend, mergeOptions, defineReactive } // 静态方法 set/delete/nextTick Vue.set = set Vue.delete = del Vue.nextTick = nextTick // 2.6 explicit observable API // 让一个对象可响应,设置响应式数据 Vue.observable = <T>(obj: T): T => { observe(obj) return obj } // 初始化 Vue.options 对象,并给其扩展 // components/directives/filters Vue.options = Object.create(null) // 原型等于 null,即不需要原型,提高性能 ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => { Vue.options[type + 's'] = Object.create(null) }) // this is used to identify the "base" constructor to extend all plain-object // components with in Weex's multi-instance scenarios. Vue.options._base = Vue // 设置 keep-alive 组件 // Vue.options.components 注册全局组件 extend(Vue.options.components, builtInComponents) // 注册 Vue.use() 用来注册插件 initUse(Vue) // 注册 Vue.mixin() 实现混入 initMixin(Vue) // 注册 Vue.extend() 基于传入的 options 返回一个组件的构造函数 initExtend(Vue) // 注册 Vue.directive()、Vue.component()、Vue.filter() initAssetRegisters(Vue)
src/core/instance/index.js
-
定义 Vue 的构造函数
// 此处不用 class 的原因,是因为方便后续给Vue 实例混入实例成员 // 1,创建 Vue 构造函数 function Vue (options) { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !(this instanceof Vue) // this 是否指向 Vue 的实例 ) { warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword') } // 调用 _init() 方法 this._init(options) } -
初始化 Vue 的实例成员
// 2,注册 Vue 实例成员 // 注册 vm 的 _init() 方法,初始化 vm initMixin(Vue) // 注册 vm 的属性:$data/$props // 注册 vm 的方法:$set/$delete/$watch stateMixin(Vue) // 初始化事件相关方法 // $on/$once/$off/$emit eventsMixin(Vue) // 初始化生命周期相关的混入方法 // _update()/$forceUpdate/$destroy lifecycleMixin(Vue) // 混入 render // $nextTick/_render renderMixin(Vue) -
initMixin(Vue)
src/core/instance/init.js- 初始化 _init() 方法
export function initMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) { // 给 Vue 实例增加 _init() 方法 // 合并 options / 初始化操作 // 整个 Vue 的入口 Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) { const vm: Component = this // a uid // 唯一标识 vm._uid = uid++ let startTag, endTag /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { startTag = `vue-perf-start:${ vm._uid}` endTag = `vue-perf-end:${ vm._uid}` mark(startTag) } // a flag to avoid this being observed // 如果是 Vue 实例,则不需要被 observe vm._isVue = true // merge options // 合并 options if (options && options._isComponent) { // optimize internal component instantiation // since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the // internal component options needs special treatment. initInternalComponent(vm, options) } else { vm.$options = mergeOptions( resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor), options || { }, vm ) } /* istanbul ignore else */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { initProxy(vm) } else { vm._renderProxy = vm } // expose real self vm._self = vm // vm 的生命周期相关变量初始化 // $children/$parent/$root/$refs initLifecycle(vm) // vm 的事件监听初始化,父组件绑定在当前组件上的事件 initEvents(vm) // vm 的编译 render 初始化 // $slots/$scopedSlots/_c/$createElement/$attrs/$listeners initRender(vm) // beforeCreate 生命钩子的回调 callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate') // 把 inject 的成员注入到 vm 上,实现依赖注入 initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props // 初始化 vm 的 _props/methods/_data/computed/watch initState(vm) // 初始化 provide,实现依赖注入 initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props // created 生命钩子的回调 callHook(vm, 'created') /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false) mark(endTag) measure(`vue ${ vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag) } if (vm.$options.el) { // 调用 $mount() 挂载整个页面 vm.$mount(vm.$options.el) } } }
首次渲染过程
-
Vue 初始化完毕,开始真正的执行
-
调用 new Vue() 之前,已经初始化完毕
-
通过调试代码,记录首次渲染过程
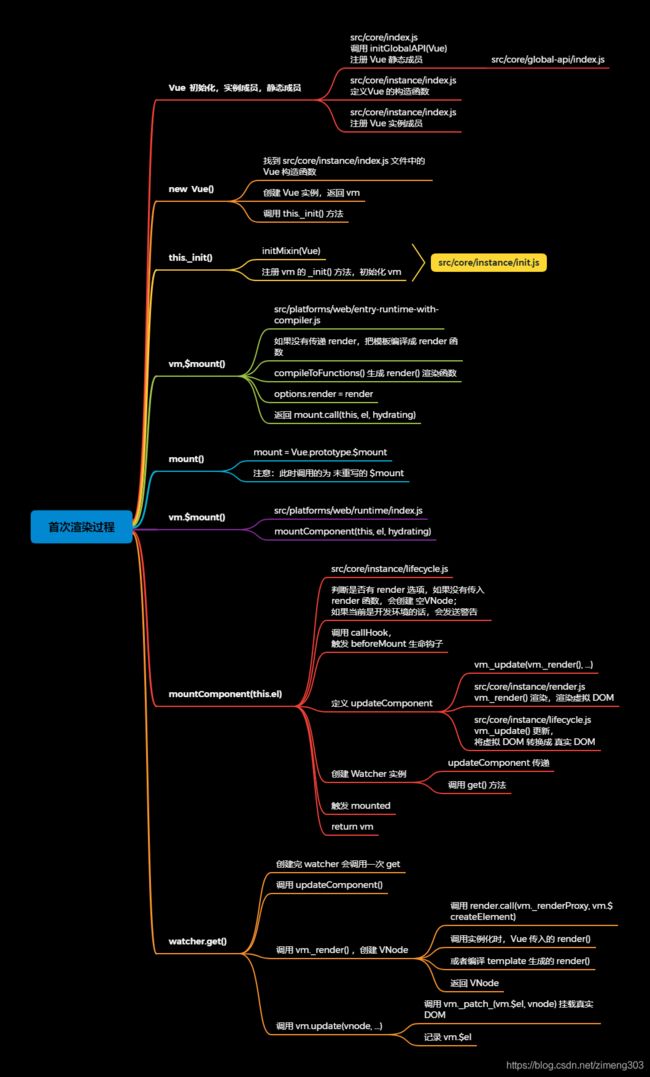
思维导图
文字汇总
-
1,在
src/core/index.js中调用 initGlobalAPI(Vue) ,初始化 Vue 静态成员initGlobalAPI(Vue) 在
src/core/global-api/index.js中定义 -
2,在
src/core/instance/index.js中,定义 Vue 的构造函数 -
3,在
src/core/instance/index.js,调用多个注册 Vue 实例成员的方法,实现 Vue 的初始化; -
4,执行 new Vue() 时,会找到
src/core/instance/index.js文件中的 Vue 构造函数,并创建 Vue 的实例,调用 init() 方法; -
5,_init() 是在
src/core/instance/init.js文件中定义的的 initMixin() 中 注册的,初始化 vm,并且调用 vm.$mount() 挂载整个页面; -
6,首先,会找到
src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js中定义的 m o u n t ( ) 方 法 , 根 据 用 户 传 入 的 t h i s . mount() 方法,根据用户传入的 this. mount()方法,根据用户传入的this.options ,判断是否传入了 render 函数,若没有,则调用 compileToFunctions() 将 template 转化为 render 函数。最后会返回 mount.call(this, el, hydrating),调用 mount(); -
7,然后,会执行
src/platforms/web/runtime/index.js中定义的 $mount(),并返回 mountComponent(this, el, hydrating) ; -
8, mountComponent() 在
src/core/instance/lifecycle.js中定义,1)会先判断用户是否传入 render 函数,如果没有传入 render 函数,会创建 空VNode;并且如果当前是开发环境的话,会发送警告。
2)会调用 callHook(),触发 beforeMount 生命钩子;
3)定义 updateComponent (更新组件),实现挂载,会调用 vm.
_update(vm._render(), hydrating) ,vm._update()在src/core/instance/lifecycle.js中定义,将 VNode 转换为 真实DOM,vm._render在src/core/instance/render.js中定义,渲染虚拟 DOM;4)创建 Watcher 实例,并且传递 updateComponent ,调用 get() 方法;
-
9,在
src/core/observer/watcher.js中定义 Watcher 类,1)创建完 watcher 会调用一次 get();
2)调用 updateComponent();
3)调用 vm._render() ,创建 VNode;
4)调用 vm.update(vnode, …)
-
10, 在 mountComponent() 的最后,会触发 mounted 生命钩子,此时页面渲染完成;并返回 vm (Vue 实例)。
数据响应式原理
通过查看源码解决下面问题
- vm.msg = { count: 0 } ,重新给属性赋值,是否是响应式的?
- vm.arr[0] = 4 ,给数组元素赋值,视图是否会更新
- vm.arr.length = 0 ,修改数组的 length,视图是否会更新
- vm.arr.push(4) ,视图是否会更新
响应式处理的入口
整个响应式处理的过程是比较复杂的,下面我们先从
-
src\core\instance\init.js
- initState(vm) vm 状态的初始化
- 初始化了 _data、_props、methods 等
-
src\core\instance\state.js// 数据的初始化 if (opts.data) { initData(vm) } else { // observe() 将对象转换为响应式对象 observe(vm._data = { }, true /* asRootData */) } -
initData(vm) vm 数据的初始化
function initData (vm: Component) { let data = vm.$options.data // 初始化 _data,组件中 data 是函数,调用函数返回结果 // 否则直接返回 data data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function' ? getData(data, vm) : data || { } ...... // proxy data on instance // 获取 data 中的所有属性 const keys = Object.keys(data) // 获取 props / methods const props = vm.$options.props const methods = vm.$options.methods let i = keys.length // 判断 data 上的成员是否和 props/methods 重名 ...... // observe data // 响应式处理 observe(data, true /* asRootData */) } -
src/core/observer/index.js
- observe(value, asRootData)
- 负责为每一个 Object 类型的 value 创建一个 observer 实例
/** * Attempt to create an observer instance for a value, * returns the new observer if successfully observed, * or the existing observer if the value already has one. */ // 创建一个 observer 实例, // 如果存在,则返回存在的 observer 实例; // 如果不存在,则返回一个新的 observer 实例 export function observe(value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void { // 判断 value 是否是对象 或者 value 是否是 VNode 的实例 if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) { return } // ob 是 Observer 的实例 let ob: Observer | void // 如果 value 有 __ob__(observer对象) 属性 结束 if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) { // 此处相当于做了缓存处理 ob = value.__ob__ } else if ( shouldObserve && !isServerRendering() && (Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) && Object.isExtensible(value) && !value._isVue ) { // 创建一个 Observer 对象 ob = new Observer(value) } if (asRootData && ob) { ob.vmCount++ } return ob }
Observer
-
src/core/observer/index.js- 对对象做响应化处理
- 对数组做响应化处理
// 对数组或对象做响应式处理 export class Observer { // 观察对象 value: any; // 依赖对象 dep: Dep; // 实例计数器 vmCount: number; // number of vms that have this object as root $data constructor(value: any) { this.value = value this.dep = new Dep() // 初始化实例的 vmCount 为0 this.vmCount = 0 // 将当前 observer 实例 挂载到 观察对象的 __ob__ 属性 // def(), 对 Object.defineProperty() 的封装 // this 指向 Observer 的实例 ob // vm._data.__ob__ = value.__ob__ = this = new Observer(value) def(value, '__ob__', this) // 数组的响应式处理 if (Array.isArray(value)) { if (hasProto) { protoAugment(value, arrayMethods) } else { copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys) } // 为数组中的每一个对象创建一个 observer 实例 this.observeArray(value) } else { // 遍历对象中的每一个属性,转换成 setter / getter this.walk(value) } } /** * Walk through all properties and convert them into * getter/setters. This method should only be called when * value type is Object. */ walk(obj: Object) { // 获取观察对象的每一个属性 const keys = Object.keys(obj) // 遍历每一个属性,设置为响应式数据 for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) { defineReactive(obj, keys[i]) } } /** * Observe a list of Array items. */ observeArray(items: Array<any>) { for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) { observe(items[i]) } } } -
walk(obj)
- 遍历 obj 的所有属性,为每一个属性调用 defifineReactive() 方法,设置 getter/setter
defifineReactive()
-
src/core/observer/index.js
-
defifineReactive(obj, key, val, customSetter, shallow)
- 为一个对象定义一个响应式的属性,每一个属性对应一个 dep 对象
- 如果该属性的值是对象,继续调用 observe
- 如果给属性赋新值,继续调用 observe
- 如果数据更新发送通知
对象响应式处理
src/core/observer/index.js/** * Define a reactive property on an Object. */ // 为一个对象定义一个响应式的属性 export function defineReactive( // 目标对象 obj: Object, // 转换的属性 key: string, // 转换的属性的属性值 val: any, // 用户自定义的 setter 函数 customSetter?: ?Function, // true,只监听对象的第一层属性; // false,深度监听,即当内部的属性为对象时,深度监听属性内部的属性 shallow?: boolean ) { // 创建依赖对象实例 // 负责为当前属性 key 收集依赖,即收集当前观察属性的 Watcher const dep = new Dep() // 获取 obj 的属性描述符对象 const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key) // property.configurable === false // 即 不可以通过 delete 删除, // 并且不可以通过 Object.defineProperty() 进行重新设置 if (property && property.configurable === false) { return } // 提供预定义的存取器函数 // cater for pre-defined getter/setters const getter = property && property.get const setter = property && property.set if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) { val = obj[key] } // 判断是否递归观察子对象,并将子对象属性都转换成 getter/setter,返回子观察对象 let childOb = !shallow && observe(val) Object.defineProperty(obj, key, { enumerable: true, configurable: true, get: function reactiveGetter() { // 如果预定义的 getter 存在则 value 等于 getter 调用的返回值 // 否则直接赋予属性值 const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val // 如果存在当前依赖目标,即 watcher 对象,则建立依赖 if (Dep.target) { // 收集依赖 // dep() 添加相互的依赖 // 1个组件对应一个 watcher 对象 // 1个watcher会对应多个dep(要观察的属性很多) // 手动创建多个 watcher 监听1个属性的变化,1个dep可以对应多个watcher dep.depend() // 如果子观察目标存在,建立子对象的依赖关系 if (childOb) { // 给子对象添加依赖 childOb.dep.depend() // 如果属性是数组,则特殊处理收集数组对象依赖 if (Array.isArray(value)) { dependArray(value) } } } // 返回属性值 return value }, set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) { // 如果预定义的 getter 存在则 value 等于 getter 调用的返回值 // 否则直接赋予属性值 const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val // 如果新值等于旧值 或者 新值旧值为 NaN,则不执行 /* eslint-disable no-self-compare */ if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) { return } /* eslint-enable no-self-compare */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) { customSetter() } // 如果没有 setter 直接返回 // #7981: for accessor properties without setter if (getter && !setter) return // 如果预定义 setter 存在则调用,否则直接更新新值 if (setter) { setter.call(obj, newVal) } else { val = newVal } // 如果新值是对象,观察子对象并返回子的 observer 对象 childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal) // 派发更新(发布更改通知) dep.notify() } }) }
数组的响应式处理
-
src/core/observer/index.js- Observer 的构造函数中
// 数组的响应式处理 if (Array.isArray(value)) { // 判断当前浏览器是否支持对象的原型属性(__proto__) // 处理兼容性 if (hasProto) { // 重新设置当前对象的原型属性(__proto__) // 当前对象的原型属性 指向 arrayMethods protoAugment(value, arrayMethods) } else { // arrayKeys 获取修改数组的方法 // 将修改后数组方法,重新设置到数据对象的原型中 copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys) } // 为数组中的每一个对象创建一个 observer 实例 this.observeArray(value) } else { // 遍历对象中的每一个属性,转换成 setter / getter this.walk(value) } function protoAugment(target, src: Object) { /* eslint-disable no-proto */ target.__proto__ = src /* eslint-enable no-proto */ } /* istanbul ignore next */ function copyAugment(target: Object, src: Object, keys: Array<string>) { for (let i = 0, l = keys.length; i < l; i++) { const key = keys[i] def(target, key, src[key]) } } -
处理数组修改数据的方法
src/core/observer/array.js
const arrayProto = Array.prototype // 克隆数组的原型,即 使用数组的原型创建一个新的对象 export const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto) // 修改数组元素的方法 const methodsToPatch = [ 'push', 'pop', 'shift', 'unshift', 'splice', 'sort', 'reverse' ] /** * Intercept mutating methods and emit events */ methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) { // cache original method // 保存数组原方法 const original = arrayProto[method] // 调用 Object.defineProperty() 重新定义修改数组的方法 def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator (...args) { // 执行数组的原始方法 const result = original.apply(this, args) // 获取数组对象的 ob 对象 const ob = this.__ob__ let inserted switch (method) { case 'push': case 'unshift': inserted = args break case 'splice': inserted = args.slice(2) break } // 对插入的新元素,重新遍历数组元素 设置为响应式数据 if (inserted) ob.observeArray(inserted) // notify change // 调用了修改数组的方法,调用数组的 ob对象发送通知 ob.dep.notify() return result }) })
Dep 类
-
src/core/observer/dep.js
-
依赖对象
-
记录 watcher 对象
-
depend() – watcher 记录对应的 dep
-
发布通知
1. 在 defineReactive() 的 getter 中创建 dep 对象,并判断 Dep.target 是否有值(一会 再来看有什么 时候有值得), 调用 dep.depend() 2. dep.depend() 内部调用 Dep.target.addDep(this),也就是 watcher 的 addDep() 方 法,它内部最 调用 dep.addSub(this),把 watcher 对象,添加到 dep.subs.push(watcher) 中,也 就是把订阅者 添加到 dep 的 subs 数组中,当数据变化的时候调用 watcher 对象的 update() 方法 3. 什么时候设置的 Dep.target? 通过简单的案例调试观察。调用 mountComponent() 方法的时 候,创建了 渲染 watcher 对象,执行 watcher 中的 get() 方法 4. get() 方法内部调用 pushTarget(this),把当前 Dep.target = watcher,同时把当前 watcher 入栈, 因为有父子组件嵌套的时候先把父组件对应的 watcher 入栈,再去处理子组件的 watcher,子 组件的处理完毕 后,再把父组件对应的 watcher 出栈,继续操作 5. Dep.target 用来存放目前正在使用的watcher。全局唯一,并且一次也只能有一个 watcher 被使用 -
src/core/observer/dep.js/** * A dep is an observable that can have multiple * directives subscribing to it. */ // dep 是个可观察对象,可以有多个指令订阅它 export default class Dep { // 静态属性,watcher 对象 static target: ?Watcher; // dep 实例 Id id: number; // dep 实例对应的 watcher 对象/订阅者数组 subs: Array<Watcher>; constructor () { this.id = uid++ this.subs = [] } // 添加新的订阅者 watcher 对象 addSub (sub: Watcher) { this.subs.push(sub) } // 移除订阅者 removeSub (sub: Watcher) { remove(this.subs, sub) } // 将观察对象和 watcher 建立依赖 depend () { if (Dep.target) { // 如果 target 存在,把 dep 对象添加到 watcher 的依赖中 Dep.target.addDep(this) } } // 发布通知 notify () { // stabilize the subscriber list first const subs = this.subs.slice() if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) { // subs aren't sorted in scheduler if not running async // we need to sort them now to make sure they fire in correct // order subs.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id) } for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) { subs[i].update() } } } // The current target watcher being evaluated. // This is globally unique because only one watcher // can be evaluated at a time. // Dep.target 用来存放目前正在使用的 watcher // 全局唯一,并且一次也只能有一个 watcher 被使用 Dep.target = null const targetStack = [] // 入栈并将当前 watcher 赋值给 Dep.target export function pushTarget (target: ?Watcher) { // 每一个组件都有一个watcher,组件中存在嵌套时,需要存储父组件中的 watcher targetStack.push(target) Dep.target = target } export function popTarget () { // 出栈操作 targetStack.pop() Dep.target = targetStack[targetStack.length - 1] }
Watcher 类
-
Watcher 分为三种,Computed Watcher、用户 Watcher (侦听器)、渲染 Watcher
-
渲染 Watcher 的创建时机
src/core/instance/lifecycle.js
export function mountComponent ( vm: Component, el: ?Element, hydrating?: boolean ): Component { vm.$el = el ...... callHook(vm, 'beforeMount') // 更新组件,实现挂载 let updateComponent /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { ...... } else { updateComponent = () => { // _update 将 VNode 转换为 真实DOM vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating) } } // we set this to vm._watcher inside the watcher's constructor // since the watcher's initial patch may call $forceUpdate (e.g. inside child // component's mounted hook), which relies on vm._watcher being already defined new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, { // 执行 updateComponent before () { if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) { callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate') } } }, true /* isRenderWatcher */) hydrating = false // manually mounted instance, call mounted on self // mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook if (vm.$vnode == null) { vm._isMounted = true // 页面挂载完毕 callHook(vm, 'mounted') } return vm } -
渲染 wacher 创建的位置 lifecycle.js 的 mountComponent 函数中
-
Wacher 的构造函数初始化,处理 expOrFn (渲染 watcher 和侦听器处理不同)
-
调用 this.get() ,它里面调用 pushTarget() 然后 this.getter.call(vm, vm) (对于渲染 wacher 调用 updateComponent),如果是用户 wacher 会获取属性的值(触发get操作)
-
当数据更新的时候,dep 中调用 notify() 方法,notify() 中调用 wacher 的 update() 方法
-
update() 中调用 queueWatcher()
-
queueWatcher() 是一个核心方法,去除重复操作,调用 flflushSchedulerQueue() 刷新队列并执行watcher
-
flflushSchedulerQueue() 中对 wacher 排序,遍历所有 wacher ,如果有 before,触发生命周期的钩子函数 beforeUpdate,执行 wacher.run(),它内部调用 this.get(),然后调用 this.cb() (渲染wacher 的 cb 是 noop)
-
整个流程结束
响应式处理过程
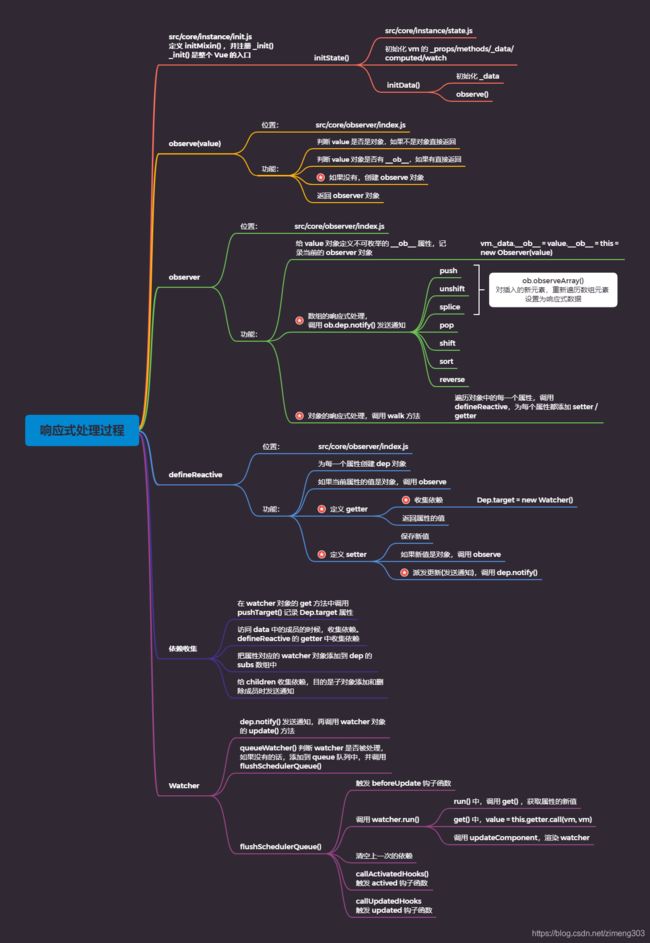
思维导图
文字汇总
-
使用 new Vue() 创建 Vue 实例时,触发
src\core\instance\index.js中的 Vue 构造函数,从而调用_init()方法,_init()方法是在initMixin()中进行注册的;在src/core/instance/init.js中导出initMixin(),并在initMixin()中注册_init()方法,_init()是整个 Vue 的入口;在_init()中调用initState()初始化 vm 的_props/methods/_data/computed/watch,在initState方法中调用了initData(),initData()是把data中的成员 注入到 Vue 实例中,并且调用observe(data)将data`对象转化成响应式的对象。 -
在
src/core/observer/index.js中定义observe(),observe()是数据响应式的入口,-
判断 value 是否是对象 或者 value 是否是 VNode 的实例,如果不是对象,但是是 VNode 则直接返回;
-
判断 value 对象是否有
__ob__,- 如果有直接返回
observer对象,类似于缓存,提升性能 - 如果没有,则创建 observe 对象,返回 observer 对象。
- 如果有直接返回
-
-
创建 observer 对象,即 new 一个 Observer 的实例。Observer 构造函数 在
src/core/observer/index.js中定义,给当前传入的value对象(即 vm._data) 添加不可枚举的__ob__属性,并将当前的observer实例对象挂载到value.__ob__中,然后再进行数组的响应式处理和对象的响应式处理。- 数组的响应式处理,就是重写数组中修改原数组的方法,如
push、pop、shift等,当执行数组的push、unshift、splice(插入或替换元素) 方法 ,对数组中新插入的元素,会调用observer实例的observeArray()方法,重新遍历数组元素,并将其设置为响应式数据。最后,调用数组的observer对象中的dep依赖的notify()方法,进行发送通知操作。 - 对象的响应式处理,就是调用
observer对象的walk()方法,遍历对象中的每一个属性,调用defineReactive(),为每一个属性添加setter/getter。
- 数组的响应式处理,就是重写数组中修改原数组的方法,如
-
defineReactive方法,为每一个属性创建dep实例对象,dep负责为当前属性 key 收集依赖,即收集当前观察属性的 Watcher。如果当前属性的值是对象,会进行深度监听,并调用observe。defineReactive中利用Object.defineProperty()为属性添加getter和setter。其中,getter的作用是收集依赖,即为当前的Watcher对象添加依赖,1个watcher会对应多个dep(即,要观察的属性很多) 。如果这个属性的值是对象,那也要给子对象添加依赖,最后返回属性的值。在setter中,先保存新值,如果新值是对象,也要调用observe,观察子对象并返回子对象的 observer 对象,然后,调用dep.notify(),进行派发更新(发送通知)。 -
收集依赖时,在
watcher对象的get方法中调用pushTarget,记录Dep.target属性。访问data中的成员的时候收集依赖,defineReactive的getter中收集依赖。把属性对应的watcher对象添加到dep的subs数组中,给childOb收集依赖,目的是子对象添加和删除成员时发送通知。 -
在数据发生变化的时候,会调用
dep.notify()发送通知,在dep.notify()中会调用watcher对象的update()方法,update()中的调用的queueWatcher()去判断watcher是否被处理,如果watcher没有被处理,则添加到queue队列中,并调用flushScheduleQueue()。 -
在
flushScheduleQueue()中,会渲染 Watcher, 触发beforeUpdate生命钩子函数,并调用watcher.run():run()中,调用get(),获取属性的新值,get() 中,使用value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)获取新值,调用this.cb(),即调用updateComponent,渲染watcher。最后,调用resetSchedulerState(),清空上一次的依赖;调用callActivatedHooks(activatedQueue),触发 actived 钩子函数;调用callUpdatedHooks(updatedQueue),触发 updated 钩子函数。
调试响应式数据执行过程
-
数组响应式处理的核心过程和数组收集依赖的过程
-
当数组的数据改变的时候 watcher 的执行过程
<div id="app"> { { arr }} div> <script src="../../dist/vue.js">script> <script> const vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { arr: [2, 3, 5] } }) script>
回答以下问题
-
检测变化的注意事项
methods: { handler () { this.obj.count = 555 this.arr[0] = 1 this.arr.length = 0 this.arr.push(4) } } -
转换成响应式数据
methods: { handler () { this.$set(this.obj, 'count', 555) this.$set(this.arr, 0, 1) this.arr.splice(0) } }
实例方法/数据
vm.$set
-
功能
向响应式对象中添加一个属性,并确保这个新属性同样是响应式的,且触发视图更新。它必须用于向响应式对象上添加新属性,因为 Vue 无法探测普通的新增属性 (比如this.myObject.newProperty = ‘hi’)
注意:
对象不能是 Vue 实例,或者 Vue 实例的根数据对象。 -
示例
vm.$set(obj, 'foo', 'test')
定义位置
-
Vue.set()
src/core/global-api/index.js
// 静态方法 set/delete/nextTick Vue.set = set Vue.delete = del Vue.nextTick = nextTick -
vm.$set()
src/core/instance/index.js
// 注册 vm 的 $data/$props/$set/$delete/$watch // instance/state.js stateMixin(Vue) // instance/state.js Vue.prototype.$set = set Vue.prototype.$delete = del
源码
-
set() 方法
src/core/observer/index.js
/** * Set a property on an object. Adds the new property and * triggers change notification if the property doesn't * already exist. */ export function set(target: Array<any> | Object, key: any, val: any): any { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && (isUndef(target) || isPrimitive(target)) ) { warn(`Cannot set reactive property on undefined, null, or primitive value: ${ (target: any)}`) } // 判断 target 是否是对象,key 是否是合法的索引 if (Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) { target.length = Math.max(target.length, key) // 通过 splice 对 key 位置的元素进行替换 // splice 在 array.js 进行了响应化的处理 target.splice(key, 1, val) return val } // 如果 key 在对象中已经存在,直接赋值 if (key in target && !(key in Object.prototype)) { target[key] = val return val } // 获取 target 中的 observer 对象 const ob = (target: any).__ob__ // 如果 target 是 vue 实例或者 $data,直接返回 if (target._isVue || (ob && ob.vmCount)) { process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( 'Avoid adding reactive properties to a Vue instance or its root $data ' + 'at runtime - declare it upfront in the data option.' ) return val } // 如果 ob 不存在,target 不是响应式对象,直接赋值 if (!ob) { target[key] = val return val } // 把 key 设置为响应式属性 defineReactive(ob.value, key, val) // 发送通知,更新视图 ob.dep.notify() return val }调试
<div id="app"> { { obj.mag }} <hr> { { obj.foo }} div> <script src="../../dist/vue.js">script> <script> const vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { obj: { msg: 'Hello Set' } } }) // 非响应式数据 // vm.obj.foo = 'test' vm.$set(vm.obj, 'foo', 'test') script>回顾 defifineReactive 中的 childOb,给每一个响应式对象设置一个 ob
调用 $set 的时候,会获取 ob 对象,并通过 ob.dep.notify() 发送通知
vm.$delete
-
功能
删除对象的属性。如果对象是响应式的,确保删除能触发更新视图。这个方法主要用于避开 Vue不能检测到属性被删除的限制,但是你应该很少会使用它。
注意:
目标对象不能是一个 Vue 实例或 Vue 实例的根数据对象。 -
示例
vm.$delete(vm.obj, 'msg') 1
定义位置
-
Vue.delete()
src/core/global-api/index.js
// 静态方法 set/delete/nextTick Vue.set = set Vue.delete = del Vue.nextTick = nextTick -
vm.$delete()
src/core/instance/index.js
// 注册 vm 的 $data/$props/$set/$delete/$watch stateMixin(Vue) // instance/state.js Vue.prototype.$set = set Vue.prototype.$delete = del
源码
src/core/observer/index.js/** * Delete a property and trigger change if necessary. */ export function del(target: Array<any> | Object, key: any) { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && (isUndef(target) || isPrimitive(target)) ) { warn(`Cannot delete reactive property on undefined, null, or primitive value: ${ (target: any)}`) } // 判断是否是数组,以及 key 是否合法 if (Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) { // 如果是数组,通过 splice 删除 // splice 做过响应式处理 target.splice(key, 1) return } // 获取 target 的 ob 对象 const ob = (target: any).__ob__ // target 如果是 Vue 实例或者 $data 对象,直接返回 if (target._isVue || (ob && ob.vmCount)) { process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( 'Avoid deleting properties on a Vue instance or its root $data ' + '- just set it to null.' ) return } // 如果 target 对象没有 key 属性,直接返回 if (!hasOwn(target, key)) { return } // 删除属性 delete target[key] if (!ob) { return } // 通过 ob 发送通知 ob.dep.notify() }
vm.$watch
vm.$watch( expOrFn, callback, [options] )
-
功能
观察 Vue 实例变化的一个表达式或计算属性函数。回调函数得到的参数为新值和旧值。表达式只接受监督的键路径。对于更复杂的表达式,用一个函数取代。
-
参数
- expOrFn:要监视的 $data 中的属性,可以是表达式或函数
- callback:数据变化后执行的函数
- 函数:回调函数
- 对象:具有 handler 属性(字符串或者函数),如果该属性为字符串则 methods 中相应的定义
- options:可选的选项
- deep:布尔类型,深度监听
- immediate:布尔类型,是否立即执行一次回调函数
-
示例
const vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { a: '1', b: '2', msg: 'Hello Vue', user: { firstName: '诸葛', lastName: '亮' } } }) // expOrFn 是表达式 vm.$watch('msg', function (newVal, oldVal) { console.log(newVal, oldVal) }) vm.$watch('user.firstName', function (newVal, oldVal) { console.log(newVal) }) // expOrFn 是函数 vm.$watch(function () { return this.a + this.b }, function (newVal, oldVal) { console.log(newVal) }) // deep 是 true,消耗性能 vm.$watch('user', function (newVal, oldVal) { // 此时的 newVal 是 user 对象 console.log(newVal === vm.user) }, { deep: true }) // immediate 是 true vm.$watch('msg', function (newVal, oldVal) { console.log(newVal) }, { immediate: true })
三种类型的 Watcher 对象
-
没有静态方法,因为 $watch 方法中要使用 Vue 的实例
-
Watcher 分三种:计算属性 Watcher、用户 Watcher (侦听器)、渲染 Watcher
-
创建顺序:计算属性 Watcher、用户 Watcher (侦听器)、渲染 Watcher
-
vm.$watch()
- src/core/instance/state.js
源码
src/core/instance/state.jsVue.prototype.$watch = function ( expOrFn: string | Function, cb: any, options?: Object ): Function { // 获取 Vue 实例 this const vm: Component = this if (isPlainObject(cb)) { // 判断如果 cb 是对象执行 createWatcher return createWatcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options) } options = options || { } // 标记为用户 watcher options.user = true // 创建用户 watcher 对象 const watcher = new Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options) // 判断 immediate,如果为 true if (options.immediate) { // 立即执行一次 cb 回调,并且把当前值传入 try { cb.call(vm, watcher.value) } catch (error) { handleError(error, vm, `callback for immediate watcher "${ watcher.expression}"`) } } // 返回取消监听的方法 return function unwatchFn () { watcher.teardown() } }
调试
-
查看 watcher 的创建顺序
- 计算属性 watcher
- 用户 wacher(侦听器)
- 渲染 wacher
-
查看渲染 watcher 的执行过程
- 当数据更新,defifineReactive 的 set 方法中调用 dep.notify()
- 调用 watcher 的 update()
- 调用 queueWatcher(),把 wacher 存入队列,如果已经存入,不重复添加
- 循环调用 flflushSchedulerQueue()
- 通过 nextTick(),在消息循环结束之前时候调用 flflushSchedulerQueue()
- 调用 wacher.run()
- 调用 wacher.get() 获取最新值
- 如果是渲染 wacher 结束
- 如果是用户 watcher,调用 this.cb()
异步更新队列 -nextTick()
-
Vue 更新 DOM 是异步执行的,批量的
- 在下次 DOM 更新循环结束之后执行延迟回调。在修改数据之后立即使用这个方法,获取更新后的 DOM。
-
vm.$nextTick(function () { /* 操作 DOM */ }) / Vue.nextTick(function () {})
vm.$nextTick() 代码演示
- 调试,代码如下:
<div id="app"> <p id="p" ref="p1">{ { msg }}p> { { name }}<br> { { title }}<br> div> <script src="../../dist/vue.js">script> <script> const vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { msg: 'Hello nextTick', name: 'Vue.js', title: 'Title' }, mounted() { this.msg = 'Hello World' this.name = 'Hello snabbdom' this.title = 'Vue.js' Vue.nextTick(() => { console.log(this.$refs.p1.textContent) }) } }) script>
定义位置
src/core/instance/render.jsVue.prototype.$nextTick = function (fn: Function) { return nextTick(fn, this) }
源码
-
手动调用 vm.$nextTick()
-
在 Watcher 的 queueWatcher 中执行 nextTick()
-
src/core/util/next-tick.jslet timerFunc // The nextTick behavior leverages the microtask queue, which can be accessed // via either native Promise.then or MutationObserver. // MutationObserver has wider support, however it is seriously bugged in // UIWebView in iOS >= 9.3.3 when triggered in touch event handlers. It // completely stops working after triggering a few times... so, if native // Promise is available, we will use it: /* istanbul ignore next, $flow-disable-line */ if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) { const p = Promise.resolve() timerFunc = () => { // 微任务,在本次同步任务执行完毕以后,执行微任务 p.then(flushCallbacks) // In problematic UIWebViews, Promise.then doesn't completely break, but // it can get stuck in a weird state where callbacks are pushed into the // microtask queue but the queue isn't being flushed, until the browser // needs to do some other work, e.g. handle a timer. Therefore we can // "force" the microtask queue to be flushed by adding an empty timer. if (isIOS) setTimeout(noop) } // 是否使用 微任务 isUsingMicroTask = true // MutationObserver 监听 DOM 对象的改变 } else if (!isIE && typeof MutationObserver !== 'undefined' && ( isNative(MutationObserver) || // PhantomJS and iOS 7.x MutationObserver.toString() === '[object MutationObserverConstructor]' )) { // Use MutationObserver where native Promise is not available, // e.g. PhantomJS, iOS7, Android 4.4 // (#6466 MutationObserver is unreliable in IE11) let counter = 1 const observer = new MutationObserver(flushCallbacks) const textNode = document.createTextNode(String(counter)) observer.observe(textNode, { characterData: true }) timerFunc = () => { counter = (counter + 1) % 2 textNode.data = String(counter) } isUsingMicroTask = true } else if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) { // Fallback to setImmediate. // Technically it leverages the (macro) task queue, // but it is still a better choice than setTimeout. // setImmediate 只有 IE 和 Node 支持,始终在 setTimeout 之前执行 timerFunc = () => { setImmediate(flushCallbacks) } } else { // Fallback to setTimeout. timerFunc = () => { setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0) } } export function nextTick (cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) { let _resolve // 把 cb 加上异常处理存入 callbacks 数组中 callbacks.push(() => { if (cb) { try { // 调用 cb() 回调函数 cb.call(ctx) } catch (e) { handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick') } } else if (_resolve) { _resolve(ctx) } }) // 判断队列是否正在被处理 if (!pending) { pending = true // 调用 timerFunc() } // $flow-disable-line if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') { // 返回 promise 对象 return new Promise(resolve => { _resolve = resolve }) } }