吴恩达机器学习在线课程--【实验三】完成和总结--包括完整代码
>吴恩达机器学习课程链接
>课程总结和笔记链接
实验三的原始代码和使用数据可至课程链接-课时67-章节9编程作业中下载
Machine Learning Online Class - Exercise 3: One-vs-all and Neural Networks
- One-vs-all
-
- Part 1: Loading and Visualizing Data
- Part 2a: Vectorize Logistic Regression
- Part 2b: One-vs-All Training
- Part 3: Predict for One-Vs-All
- 主函数
- Neural Networks
-
- Part 1: Loading and Visualizing Data
- Part 2: Loading Pameters
- Part 3: Implement Predict
- 主函数
包括了实验二中的使用了正则化项后的逻辑回归的最优化参数求解,重点是应用于多分类,采用一对多形式,对每一种分类进行“是/否”预测,得到分类。
环境——Matlab R2018b/Octave
One-vs-all
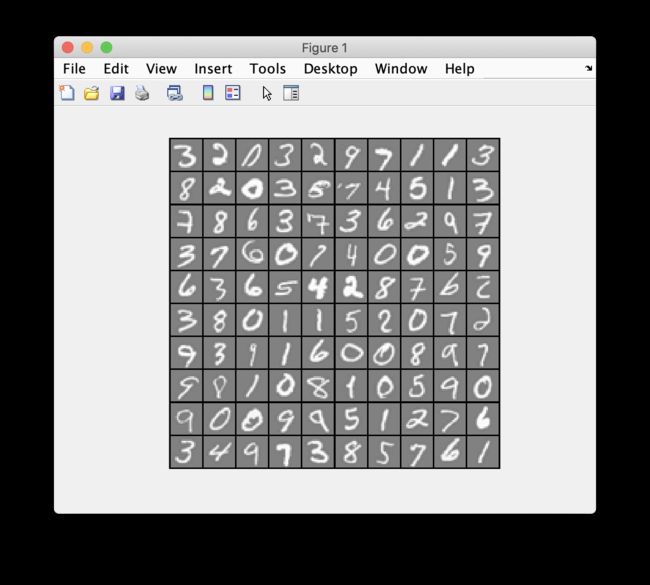
Part 1: Loading and Visualizing Data
这个训练集一共有5000条数据,每条数据包含400维特征。一共10个分类。
运行结果
Part 2a: Vectorize Logistic Regression
lrCostFunction.m
加入正则化项的逻辑回归的损失函数计算,和实验二中的相同。
function [J, grad] = lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lambda)
%LRCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with
%regularization
% J = LRCOSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters.
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Hint: The computation of the cost function and gradients can be
% efficiently vectorized. For example, consider the computation
%
% sigmoid(X * theta)
%
% Each row of the resulting matrix will contain the value of the
% prediction for that example. You can make use of this to vectorize
% the cost function and gradient computations.
%
% Hint: When computing the gradient of the regularized cost function,
% there're many possible vectorized solutions, but one solution
% looks like:
% grad = (unregularized gradient for logistic regression)
% temp = theta;
% temp(1) = 0; % because we don't add anything for j = 0
% grad = grad + YOUR_CODE_HERE (using the temp variable)
%
pos = y == 1;
neg = y == 0;
h_pos = sigmoid(X(pos, :) * theta);
J_pos = sum(-log(h_pos));
h_neg = sigmoid(X(neg, :) * theta);
J_neg = sum(-log(1 - h_neg));
J_reg = lambda/2 * sum(theta(2:end, :) .^ 2);
J = (J_pos + J_neg + J_reg)/m;
grad = (sum(X .* (sigmoid(X * theta) - y)))' / m;
grad_reg = ((lambda * theta(2:end, :)) / m);
grad(2:end, :) = grad(2:end, :) + grad_reg;
% =============================================================
grad = grad(:);
end
运行结果
Testing lrCostFunction() with regularization
Cost: 2.534819
Expected cost: 2.534819
Gradients:
0.146561
-0.548558
0.724722
1.398003
Expected gradients:
0.146561
-0.548558
0.724722
1.398003
Program paused. Press enter to continue.
Part 2b: One-vs-All Training
oneVsAll.m
通过最小化损失函数计算所有十个类别的最优参数。
参数为10行400列矩阵。
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda)
%ONEVSALL trains multiple logistic regression classifiers and returns all
%the classifiers in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta
%corresponds to the classifier for label i
% [all_theta] = ONEVSALL(X, y, num_labels, lambda) trains num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers and returns each of these classifiers
% in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta corresponds
% to the classifier for label i
% Some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);%5000
n = size(X, 2);%400
% You need to return the following variables correctly
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + 1);%10*401
% Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: You should complete the following code to train num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers with regularization
% parameter lambda.
%
% Hint: theta(:) will return a column vector.
%
% Hint: You can use y == c to obtain a vector of 1's and 0's that tell you
% whether the ground truth is true/false for this class.
%
% Note: For this assignment, we recommend using fmincg to optimize the cost
% function. It is okay to use a for-loop (for c = 1:num_labels) to
% loop over the different classes.
%
% fmincg works similarly to fminunc, but is more efficient when we
% are dealing with large number of parameters.
%
% Example Code for fmincg:
%
% % Set Initial theta
% initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
%
% % Set options for fminunc
% options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
%
% % Run fmincg to obtain the optimal theta
% % This function will return theta and the cost
% [theta] = ...
% fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)), ...
% initial_theta, options);
%
for c = 1:num_labels
% Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
% Set Options
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
% Optimize
[all_theta(c, :), J, exit_flag] = ...
fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)), initial_theta, options);
% =========================================================================
end
Part 3: Predict for One-Vs-All
predictOneVsAll.m
使用得到的10400参数对数据进行预测(用训练集预测哈哈哈)
首先得到all_p为500010的矩阵,包含0、1,得到5000个数据的预测分类
找到每一行的1值序号,得到p为5000*1的向量,是每一个数据的预测分类。
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label for a trained one-vs-all classifier. The labels
%are in the range 1..K, where K = size(all_theta, 1).
% p = PREDICTONEVSALL(all_theta, X) will return a vector of predictions
% for each example in the matrix X. Note that X contains the examples in
% rows. all_theta is a matrix where the i-th row is a trained logistic
% regression theta vector for the i-th class. You should set p to a vector
% of values from 1..K (e.g., p = [1; 3; 1; 2] predicts classes 1, 3, 1, 2
% for 4 examples)
m = size(X, 1);%5000
num_labels = size(all_theta, 1);%10
% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1);%5000*1
% Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters (one-vs-all).
% You should set p to a vector of predictions (from 1 to
% num_labels).
%
% Hint: This code can be done all vectorized using the max function.
% In particular, the max function can also return the index of the
% max element, for more information see 'help max'. If your examples
% are in rows, then, you can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max
% for each row.
%
all_p = floor(sigmoid(X * (all_theta)') / 0.5);
[val, p] = max(all_p, [], 2);
% =========================================================================
end
运行结果
Training Set Accuracy: 89.160000
主函数
ex3.m
%% Machine Learning Online Class - Exercise 3 | Part 1: One-vs-all
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the
% linear exercise. You will need to complete the following functions
% in this exericse:
%
% lrCostFunction.m (logistic regression cost function)
% oneVsAll.m
% predictOneVsAll.m
% predict.m
%
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
%
%% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc
%% Setup the parameters you will use for this part of the exercise
input_layer_size = 400; % 20x20 Input Images of Digits
num_labels = 10; % 10 labels, from 1 to 10
% (note that we have mapped "0" to label 10)
%% =========== Part 1: Loading and Visualizing Data =============
% We start the exercise by first loading and visualizing the dataset.
% You will be working with a dataset that contains handwritten digits.
%
% Load Training Data
fprintf('Loading and Visualizing Data ...\n')
load('ex3data1.mat'); % training data stored in arrays X, y
m = size(X, 1);
% Randomly select 100 data points to display
rand_indices = randperm(m);
sel = X(rand_indices(1:100), :);
displayData(sel);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============ Part 2a: Vectorize Logistic Regression ============
% In this part of the exercise, you will reuse your logistic regression
% code from the last exercise. You task here is to make sure that your
% regularized logistic regression implementation is vectorized. After
% that, you will implement one-vs-all classification for the handwritten
% digit dataset.
%
% Test case for lrCostFunction
fprintf('\nTesting lrCostFunction() with regularization');
theta_t = [-2; -1; 1; 2];
X_t = [ones(5,1) reshape(1:15,5,3)/10];
y_t = ([1;0;1;0;1] >= 0.5);
lambda_t = 3;
[J grad] = lrCostFunction(theta_t, X_t, y_t, lambda_t);
fprintf('\nCost: %f\n', J);
fprintf('Expected cost: 2.534819\n');
fprintf('Gradients:\n');
fprintf(' %f \n', grad);
fprintf('Expected gradients:\n');
fprintf(' 0.146561\n -0.548558\n 0.724722\n 1.398003\n');
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============ Part 2b: One-vs-All Training ============
fprintf('\nTraining One-vs-All Logistic Regression...\n')
lambda = 0.1;
[all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ================ Part 3: Predict for One-Vs-All ================
pred = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X);
fprintf('\nTraining Set Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(pred == y)) * 100);
Neural Networks
Part 1: Loading and Visualizing Data
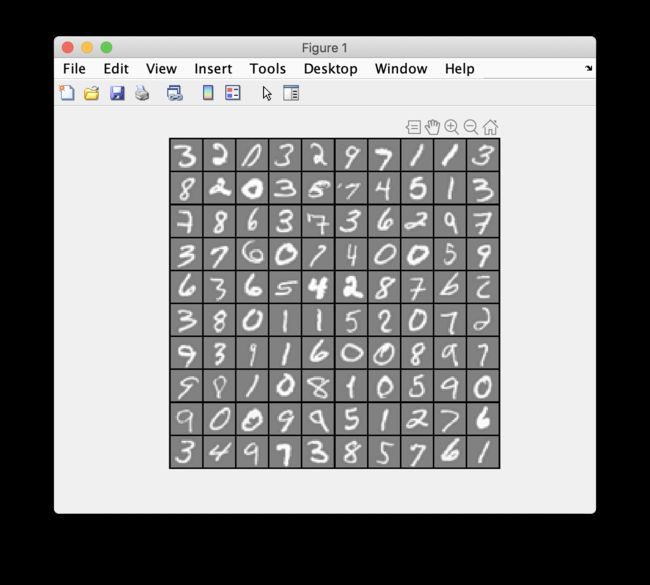
Part 2: Loading Pameters
Part 3: Implement Predict
predict.m
function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label of an input given a trained neural network
% p = PREDICT(Theta1, Theta2, X) outputs the predicted label of X given the
% trained weights of a neural network (Theta1, Theta2)
% Useful values
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(Theta2, 1);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned neural network. You should set p to a
% vector containing labels between 1 to num_labels.
%
% Hint: The max function might come in useful. In particular, the max
% function can also return the index of the max element, for more
% information see 'help max'. If your examples are in rows, then, you
% can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max for each row.
%
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
all_p = floor(sigmoid(X * (Theta1)') / 0.5);
all_p = [ones(m, 1) all_p];
all_p = floor(sigmoid(all_p * (Theta2)') / 0.5);
[val, p] = max(all_p, [], 2);
% =========================================================================
end
实验结果
Loading and Visualizing Data ...
Program paused. Press enter to continue.
Loading Saved Neural Network Parameters ...
Training Set Accuracy: 95.400000
Program paused. Press enter to continue.
Displaying Example Image
Neural Network Prediction: 8 (digit 8)
Paused - press enter to continue, q to exit:
Displaying Example Image
Neural Network Prediction: 2 (digit 2)
Paused - press enter to continue, q to exit:


主函数
ex3_nn.m
%% Machine Learning Online Class - Exercise 3 | Part 2: Neural Networks
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the
% linear exercise. You will need to complete the following functions
% in this exericse:
%
% lrCostFunction.m (logistic regression cost function)
% oneVsAll.m
% predictOneVsAll.m
% predict.m
%
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
%
%% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc
%% Setup the parameters you will use for this exercise
input_layer_size = 400; % 20x20 Input Images of Digits
hidden_layer_size = 25; % 25 hidden units
num_labels = 10; % 10 labels, from 1 to 10
% (note that we have mapped "0" to label 10)
%% =========== Part 1: Loading and Visualizing Data =============
% We start the exercise by first loading and visualizing the dataset.
% You will be working with a dataset that contains handwritten digits.
%
% Load Training Data
fprintf('Loading and Visualizing Data ...\n')
load('ex3data1.mat');
m = size(X, 1);%5000
% Randomly select 100 data points to display
sel = randperm(size(X, 1));
sel = sel(1:100);
displayData(X(sel, :));
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ================ Part 2: Loading Pameters ================
% In this part of the exercise, we load some pre-initialized
% neural network parameters.
fprintf('\nLoading Saved Neural Network Parameters ...\n')
% Load the weights into variables Theta1 and Theta2
load('ex3weights.mat');%Theta1 25*401,Theta2 10*26
%% ================= Part 3: Implement Predict =================
% After training the neural network, we would like to use it to predict
% the labels. You will now implement the "predict" function to use the
% neural network to predict the labels of the training set. This lets
% you compute the training set accuracy.
pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X);
fprintf('\nTraining Set Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(pred == y)) * 100);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
% To give you an idea of the network's output, you can also run
% through the examples one at the a time to see what it is predicting.
% Randomly permute examples
rp = randperm(m);
for i = 1:m
% Display
fprintf('\nDisplaying Example Image\n');
displayData(X(rp(i), :));
pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X(rp(i),:));
fprintf('\nNeural Network Prediction: %d (digit %d)\n', pred, mod(pred, 10));
% Pause with quit option
s = input('Paused - press enter to continue, q to exit:','s');
if s == 'q'
break
end
end
实验三完成