机器学习之监督学习--(回归)多元线性回归
注:数据集放在文章末尾
(1)多元线性回归 —— 梯度下降法
port numpy as np
from numpy import genfromtxt
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
# 读入数据
data = genfromtxt(r"Delivery.csv",delimiter=',')
# 切分数据
x_data = data[:,:-1]
y_data = data[:,-1]
# 学习率learning rate
lr = 0.0001
# 参数
theta0 = 0
theta1 = 0
theta2 = 0
# 最大迭代次数
epochs = 1000
# 最小二乘法
def compute_error(theta0, theta1, theta2, x_data, y_data):
totalError = 0
for i in range(0, len(x_data)):
totalError += (y_data[i] - (theta1 * x_data[i,0] + theta2*x_data[i,1] + theta0)) ** 2
return totalError / float(len(x_data))
def gradient_descent_runner(x_data, y_data, theta0, theta1, theta2, lr, epochs):
# 计算总数据量
m = float(len(x_data))
# 循环epochs次
for i in range(epochs):
theta0_grad = 0
theta1_grad = 0
theta2_grad = 0
# 计算梯度的总和再求平均
for j in range(0, len(x_data)):
theta0_grad += (1/m) * ((theta1 * x_data[j,0] + theta2*x_data[j,1] + theta0) - y_data[j])
theta1_grad += (1/m) * x_data[j,0] * ((theta1 * x_data[j,0] + theta2*x_data[j,1] + theta0) - y_data[j])
theta2_grad += (1/m) * x_data[j,1] * ((theta1 * x_data[j,0] + theta2*x_data[j,1] + theta0) - y_data[j])
# 更新b和k
theta0 = theta0 - (lr*theta0_grad)
theta1 = theta1 - (lr*theta1_grad)
theta2 = theta2 - (lr*theta2_grad)
return theta0, theta1, theta2
print("Starting theta0 = {0}, theta1 = {1}, theta2 = {2}, error = {3}".
format(theta0, theta1, theta2, compute_error(theta0, theta1, theta2, x_data, y_data)))
print("Running...")
theta0, theta1, theta2 = gradient_descent_runner(x_data, y_data, theta0, theta1, theta2, lr, epochs)
print("After {0} iterations theta0 = {1}, theta1 = {2}, theta2 = {3}, error = {4}".
format(epochs, theta0, theta1, theta2, compute_error(theta0, theta1, theta2, x_data, y_data)))
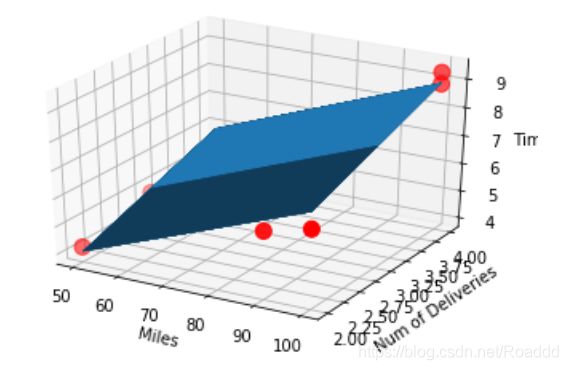
# 画图
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection = '3d')
ax.scatter(x_data[:,0], x_data[:,1], y_data, c = 'r', marker = 'o', s = 100) #点为红色三角形
x0 = x_data[:,0]
x1 = x_data[:,1]
# 生成网格矩阵
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(x0, x1)
z = theta0 + x0*theta1 + x1*theta2
# 画3D图
ax.plot_surface(x0, x1, z)
#设置坐标轴
ax.set_xlabel('Miles')
ax.set_ylabel('Num of Deliveries')
ax.set_zlabel('Time')
#显示图像
plt.show()
(2)多元线性回归 —— sklearn
import numpy as np
from numpy import genfromtxt
from sklearn import linear_model
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
# 读入数据
data = genfromtxt(r"Delivery.csv",delimiter=',')
# 切分数据
x_data = data[:,:-1]
y_data = data[:,-1]
# 创建模型
model = linear_model.LinearRegression()
model.fit(x_data, y_data)
# 系数
print("coefficients:",model.coef_)
# 截距
print("intercept:",model.intercept_)
# 测试
x_test = [[102,4]]
predict = model.predict(x_test)
print("predict:",predict)
# 画图
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection = '3d')
ax.scatter(x_data[:,0], x_data[:,1], y_data, c = 'r', marker = 'o', s = 100) #点为红色三角形
x0 = x_data[:,0]
x1 = x_data[:,1]
# 生成网格矩阵
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(x0, x1)
z = model.intercept_ + x0*model.coef_[0] + x1*model.coef_[1]
# 画3D图
ax.plot_surface(x0, x1, z)
#设置坐标轴
ax.set_xlabel('Miles')
ax.set_ylabel('Num of Deliveries')
ax.set_zlabel('Time')
#显示图像
plt.show()
100,4,9.3
50,3,4.8
100,4,8.9
100,2,6.5
50,2,4.2
80,2,6.2
75,3,7.4
65,4,6
90,3,7.6
90,2,6.1