玩转SpringSecurity之二读取存储密文重写规则校验登录
上一篇文章已经说过,自定义内存方式是极少使用的,更多则是数据库存储,然后自定义校验规则等,而且现在对于密码的要求很高一定会采取加密方式存储,那么我们就来看看SpringSecurity提供了些什么吧。
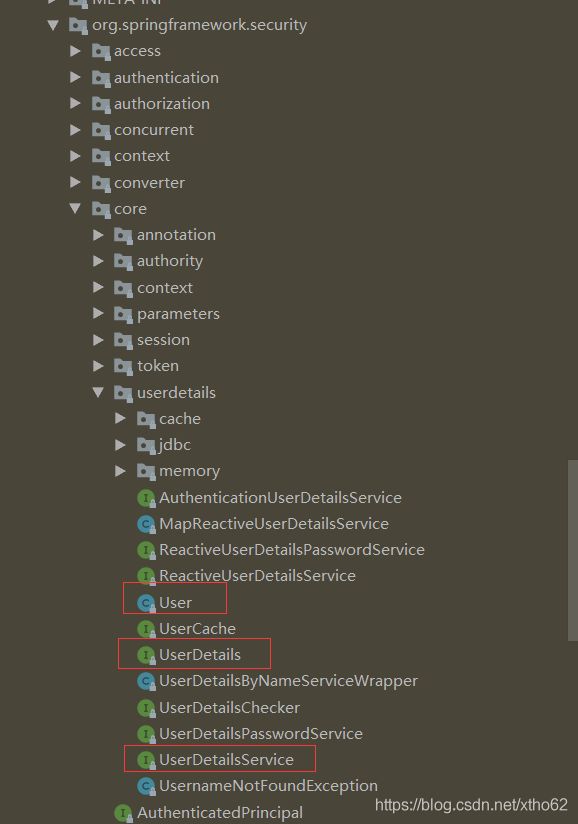
UserDetailsService
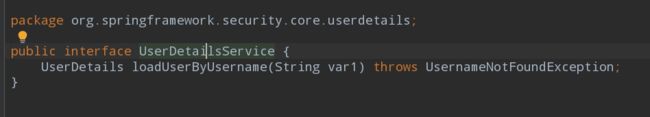
只有一个方法就是通过用户名重载用户,其实就是通过用户名查找用户,然后校验。用户的登录是访问这个接口的唯一方法loadUserByUsername的,这个方法接收一个参数,就是用户名,如果没有,会抛异常。如果有,返回UserDetails。
UserDetails也是Spring Security提供的一个接口,源码如下:
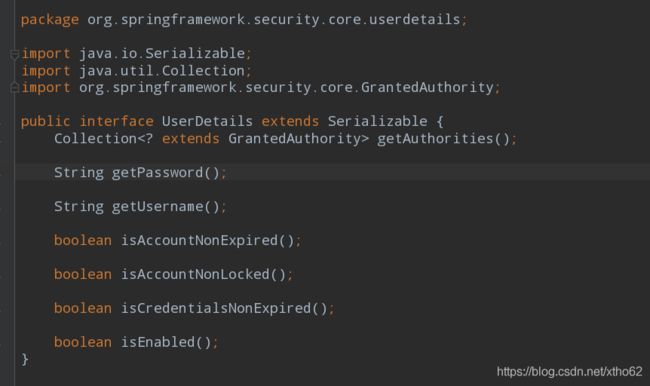
这个接口有7个抽象方法,值得注意的前3个方法,第1个方法是获取权限的,第2个方法获取密码,第3个方法获取用户名。
后面的分别是判断
- isAccountNonExpired 用户账户未过期
- isAccountNonLocked 账户未被锁定
- isCredentialsNonExpired 凭证未过期
- isEnabled 是否可用
这些规则呢在SpringSecurity有个实现类User其实现了登录详情以及权限相关,如果我们要自定义自己的规则,可以参考它编写
package org.springframework.security.core.userdetails;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.SortedSet;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.security.core.CredentialsContainer;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.AuthorityUtils;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.factory.PasswordEncoderFactories;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
public class User implements UserDetails, CredentialsContainer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 540L;
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(User.class);
private String password;
private final String username;
private final Set<GrantedAuthority> authorities;
private final boolean accountNonExpired;
private final boolean accountNonLocked;
private final boolean credentialsNonExpired;
private final boolean enabled;
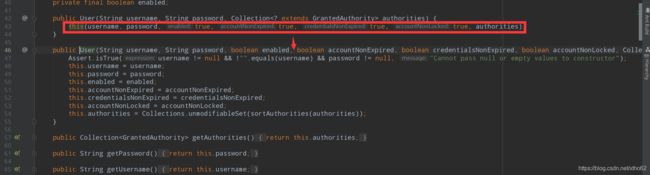
public User(String username, String password, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
this(username, password, true, true, true, true, authorities);
}
public User(String username, String password, boolean enabled, boolean accountNonExpired, boolean credentialsNonExpired, boolean accountNonLocked, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
Assert.isTrue(username != null && !"".equals(username) && password != null, "Cannot pass null or empty values to constructor");
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.enabled = enabled;
this.accountNonExpired = accountNonExpired;
this.credentialsNonExpired = credentialsNonExpired;
this.accountNonLocked = accountNonLocked;
this.authorities = Collections.unmodifiableSet(sortAuthorities(authorities));
}
public Collection<GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return this.authorities;
}
public String getPassword() {
return this.password;
}
public String getUsername() {
return this.username;
}
public boolean isEnabled() {
return this.enabled;
}
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return this.accountNonExpired;
}
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return this.accountNonLocked;
}
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return this.credentialsNonExpired;
}
public void eraseCredentials() {
this.password = null;
}
private static SortedSet<GrantedAuthority> sortAuthorities(Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
Assert.notNull(authorities, "Cannot pass a null GrantedAuthority collection");
SortedSet<GrantedAuthority> sortedAuthorities = new TreeSet(new User.AuthorityComparator());
Iterator var2 = authorities.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
GrantedAuthority grantedAuthority = (GrantedAuthority)var2.next();
Assert.notNull(grantedAuthority, "GrantedAuthority list cannot contain any null elements");
sortedAuthorities.add(grantedAuthority);
}
return sortedAuthorities;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return obj instanceof User ? this.username.equals(((User)obj).username) : false;
}
public int hashCode() {
return this.username.hashCode();
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(this.getClass().getName()).append(" [");
sb.append("Username=").append(this.username).append(", ");
sb.append("Password=[PROTECTED], ");
sb.append("Enabled=").append(this.enabled).append(", ");
sb.append("AccountNonExpired=").append(this.accountNonExpired).append(", ");
sb.append("credentialsNonExpired=").append(this.credentialsNonExpired).append(", ");
sb.append("AccountNonLocked=").append(this.accountNonLocked).append(", ");
sb.append("Granted Authorities=").append(this.authorities).append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
public static User.UserBuilder withUsername(String username) {
return builder().username(username);
}
public static User.UserBuilder builder() {
return new User.UserBuilder();
}
/** @deprecated */
@Deprecated
public static User.UserBuilder withDefaultPasswordEncoder() {
logger.warn("User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder() is considered unsafe for production and is only intended for sample applications.");
PasswordEncoder encoder = PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
User.UserBuilder var10000 = builder();
encoder.getClass();
return var10000.passwordEncoder(encoder::encode);
}
public static User.UserBuilder withUserDetails(UserDetails userDetails) {
return withUsername(userDetails.getUsername()).password(userDetails.getPassword()).accountExpired(!userDetails.isAccountNonExpired()).accountLocked(!userDetails.isAccountNonLocked()).authorities(userDetails.getAuthorities()).credentialsExpired(!userDetails.isCredentialsNonExpired()).disabled(!userDetails.isEnabled());
}
public static final class UserBuilder {
private String username;
private String password;
private List<GrantedAuthority> authorities;
private boolean accountExpired;
private boolean accountLocked;
private boolean credentialsExpired;
private boolean disabled;
private Function<String, String> passwordEncoder;
private UserBuilder() {
this.passwordEncoder = (password) -> {
return password;
};
}
public User.UserBuilder username(String username) {
Assert.notNull(username, "username cannot be null");
this.username = username;
return this;
}
public User.UserBuilder password(String password) {
Assert.notNull(password, "password cannot be null");
this.password = password;
return this;
}
public User.UserBuilder passwordEncoder(Function<String, String> encoder) {
Assert.notNull(encoder, "encoder cannot be null");
this.passwordEncoder = encoder;
return this;
}
public User.UserBuilder roles(String... roles) {
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList(roles.length);
String[] var3 = roles;
int var4 = roles.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
String role = var3[var5];
Assert.isTrue(!role.startsWith("ROLE_"), () -> {
return role + " cannot start with ROLE_ (it is automatically added)";
});
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_" + role));
}
return this.authorities((Collection)authorities);
}
public User.UserBuilder authorities(GrantedAuthority... authorities) {
return this.authorities((Collection)Arrays.asList(authorities));
}
public User.UserBuilder authorities(Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
this.authorities = new ArrayList(authorities);
return this;
}
public User.UserBuilder authorities(String... authorities) {
return this.authorities((Collection)AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList(authorities));
}
public User.UserBuilder accountExpired(boolean accountExpired) {
this.accountExpired = accountExpired;
return this;
}
public User.UserBuilder accountLocked(boolean accountLocked) {
this.accountLocked = accountLocked;
return this;
}
public User.UserBuilder credentialsExpired(boolean credentialsExpired) {
this.credentialsExpired = credentialsExpired;
return this;
}
public User.UserBuilder disabled(boolean disabled) {
this.disabled = disabled;
return this;
}
public UserDetails build() {
String encodedPassword = (String)this.passwordEncoder.apply(this.password);
return new User(this.username, encodedPassword, !this.disabled, !this.accountExpired, !this.credentialsExpired, !this.accountLocked, this.authorities);
}
}
private static class AuthorityComparator implements Comparator<GrantedAuthority>, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 540L;
private AuthorityComparator() {
}
public int compare(GrantedAuthority g1, GrantedAuthority g2) {
if (g2.getAuthority() == null) {
return -1;
} else {
return g1.getAuthority() == null ? 1 : g1.getAuthority().compareTo(g2.getAuthority());
}
}
}
}
安全问题是现在计算机设计中尤为重要的一环,所以密码自然一定是加密的
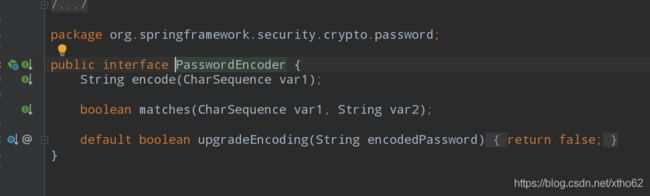
第一个方法是加密编码,第二个是使用序列化字符和密文进行比较
PasswordEncoder接口有很多实现类,其中最主要的是官方推荐的BCryptPasswordEncoder类,平时使用的最多的就是这个密码解析器。BCryptPasswordEncoder是对bcrypt强散列方法的具体实现,是基于hash算法的单向加密。可以通过strength来控制强度,默认是
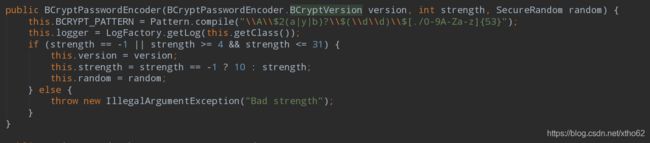
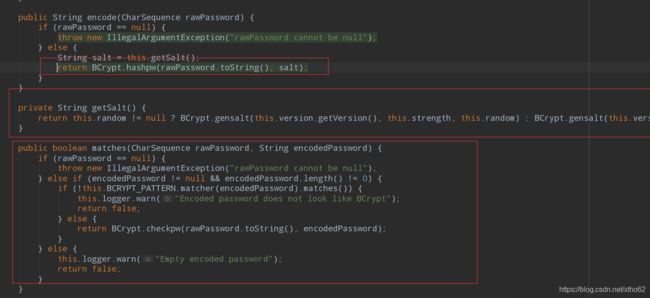
一些具体的实现调用的是BCrypt
public static String hashpw(String password, String salt) {
byte[] passwordb = password.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
return hashpw(passwordb, salt);
}
public static String hashpw(byte[] passwordb, String salt) {
char minor = 0;
StringBuilder rs = new StringBuilder();
if (salt == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("salt cannot be null");
} else {
int saltLength = salt.length();
if (saltLength < 28) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid salt");
} else if (salt.charAt(0) == '$' && salt.charAt(1) == '2') {
byte off;
if (salt.charAt(2) == '$') {
off = 3;
} else {
minor = salt.charAt(2);
if (minor != 'a' && minor != 'x' && minor != 'y' && minor != 'b' || salt.charAt(3) != '$') {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid salt revision");
}
off = 4;
}
if (salt.charAt(off + 2) > '$') {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Missing salt rounds");
} else if (off == 4 && saltLength < 29) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid salt");
} else {
int rounds = Integer.parseInt(salt.substring(off, off + 2));
String real_salt = salt.substring(off + 3, off + 25);
byte[] saltb = decode_base64(real_salt, 16);
if (minor >= 'a') {
passwordb = Arrays.copyOf(passwordb, passwordb.length + 1);
}
BCrypt B = new BCrypt();
byte[] hashed = B.crypt_raw(passwordb, saltb, rounds, minor == 'x', minor == 'a' ? 65536 : 0);
rs.append("$2");
if (minor >= 'a') {
rs.append(minor);
}
rs.append("$");
if (rounds < 10) {
rs.append("0");
}
rs.append(rounds);
rs.append("$");
encode_base64(saltb, saltb.length, rs);
encode_base64(hashed, bf_crypt_ciphertext.length * 4 - 1, rs);
return rs.toString();
}
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid salt version");
}
}
}
ok测试一下,使用的实用性:
@Test
public void test1() {
String password = "123456";// 密码
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
// 加密明文密码,返回密文
String encoder = passwordEncoder.encode(password);
// 明文和密文进行匹配
boolean bool = passwordEncoder.matches(password, encoder);
System.out.println(encoder + ":是否匹配?" + bool);
}
}
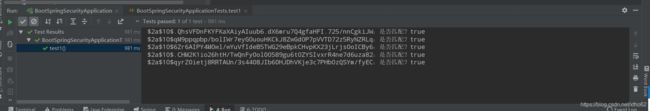
哪怕是123456都不会是规定的密文,所以官网也推荐使用BCryptPasswordEncoder,很好!!这样存储如数据库也相对安全,如果是使用直接MD5加密,这个123456很轻松就被破解了。
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig {
/**向容器中注入PasswordEncoder实例*/
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder getPasswordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
package com.tho.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.AuthorityUtils;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
/**
* 重写loadUserByUsername方法
*/
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username)
throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//实际是根据用户名去数据库查,这里就直接用静态数据了
if(!username.equals("calmtho")) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户名不存在!");
}
//比较密码,匹配成功会返回UserDetails,实际上也会去数据库查
String password = passwordEncoder.encode("tho123456");
User user = new User(username,password, AuthorityUtils.
commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("calmtho,admin"));
return user;
}
}