Java双端队列
本教程详细介绍了Java中的双端队列或“双端队列”。您将了解Deque接口,API方法,实现等:
Java中的Deque或“双端队列”是一种数据结构,我们可以在其中插入或删除两端的元素。双端队列是Java中属于java.util包的接口,它实现了java.queue接口。
我们可以将双端队列实现为堆栈(后进先出)结构或队列(先进先出)。双端队列比Stack和/或LinkedList快。与“扑克牌”一样,双双被称为“扑克牌”。
Java双端队列
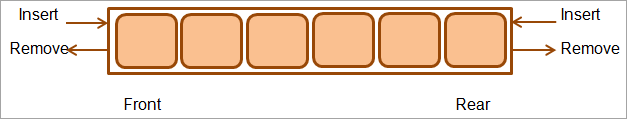
典型的双端队列收集如下所示:
Deque主要用于实现堆栈,队列或列表数据结构。它也可以用于实现优先级队列。可以使用双端队列来实现Web浏览器中主要存在的撤消或历史记录功能。
Java Deque接口
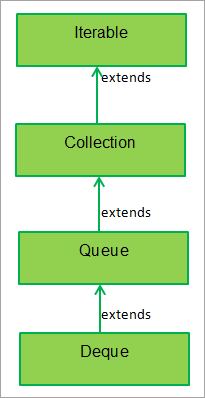
下图显示了双端队列或双端队列的层次结构。如下图所示,Deque接口扩展到Queue接口,而Queue接口又扩展了Collection接口。
要在我们的程序中使用双端队列接口,我们必须使用import语句导入包含双端队列功能的软件包,如下所示。
导入java.util.deque;
或者
导入java.util。*;
由于双端队列是一个接口,因此我们需要具体的类来实现双端队列接口的功能。
下面的两个类实现了双端队列接口。
- ArrayDeque
- 链表
因此,我们可以使用这两个类创建双端队列对象,如下所示:
Deque numdeque =新的ArrayDeque <>();
Deque strDeque =新的LinkedList <>();
因此,一旦成功创建了上述双端队列对象,它们就可以使用双端队列接口的功能。
以下是有关双端队列的一些重要注意事项:
- Deque接口支持可调整大小的数组,该数组可以根据需要增长。
- 数组双端队列不允许使用Null值。
- Deque不支持通过多个线程进行并发访问。
- 除非提供外部同步,否则双端队列不是线程安全的。
Java中的ArrayDeque
ArrayDeque属于java.util包。它实现了双端队列接口。在内部,ArrayDeque类使用可动态调整大小的数组,该数组随着元素数量的增加而增长。
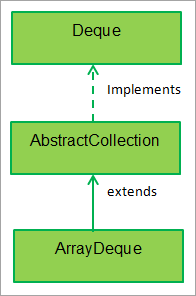
下图显示了ArrayDeque类的层次结构:
如图所示,ArrayDeque类继承了AbstractCollection类并实现了Deque接口。
我们可以使用ArrayDeque类创建一个双端队列对象,如下所示:
Deque deque_obj =新的ArrayDeque();
双端队列示例
以下Java程序演示了一个简单的示例,以更好地了解双端队列。在这里,我们使用ArrayDeque类实例化了双端队列接口。我们刚刚向双端队列对象添加了一些元素,然后使用forEach循环将它们打印出来。
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Creat a Deque and add elements
Dequenew ArrayDeque
cities_deque.add("Delhi");
cities_deque.add("Mumbai");
cities_deque.add("Bangaluru");
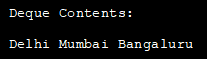
System.out.println("Deque Contents:");
//Traverse the Deque
for (String str : cities_deque) {
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
}
}
|
输出:
Java中的双端队列API方法
由于双端队列接口实现了队列接口,因此它支持队列接口的所有方法。此外,双端队列接口提供了以下方法,可用于对双端队列对象执行各种操作。
让我们在下表中总结这些方法。
| Method | Method Prototype | Description |
|---|---|---|
| add | boolean add(E e) | Adds given element e into the deque (at the tail) without violating capacity restrictions and returns true if success. Throws IllegalStateException if no space available in the deque. |
| addFirst | void addFirst(E e) | Adds given element e to the front of the queue without violating capacity restrictions. |
| addLast | void addLast(E e) | Adds element e to the last of the deque without violating capacity restrictions. |
| contains | boolean contains(Object o) | Checks if the deque contains given element o. Returns true if yes. |
| descendingIterator | Iterator < E > descendingIterator() | This method returns reverse order iterator for the deque. |
| element | E element() | Returns the first element or head of the deque. Note that it does not delete the element. |
| getFirst | E getFirst() | Retrieve the first element of the deque without removing it. |
| getLast | E getLast() | Gets the last element of the deque without removing it. |
| iterator | Iterator< E > iterator() | Returns a standard iterator over the elements of the deque. |
| offer | boolean offer(E e) | Adds given element e to the deque (as a tail) without violating capacity restrictions. Returns true on success and false on failure. |
| offerFirst | boolean offerFirst(E e) | Insert the given element e to the front of the deque without violating capacity restrictions. |
| offerLast | boolean offerLast(E e) | Insert the given element e at the end of the deque without violating capacity restrictions. |
| peek | E peek() | Returns head of the deque (first element) or null if a queue is empty. ** does not delete the head |
| peekFirst | E peekFirst() | Returns the first element in the deque without deleting it. Returns null if the deque is empty. |
| peekLast | E peekLast() | Retrieves the last element in the deque without removing it. Returns null if the deque is empty. |
| poll | E poll() | Deletes and returns the head of the deque. Returns null if the deque is empty. |
| pollFirst | E pollFirst() | Returns and removes the first element of the deque. Returns null if the deque is empty. |
| pollLast | E pollLast() | Returns and removes the last element of the deque. Returns null if the deque is empty. |
| pop | E pop() | Pop the element from the stack that is represented using deque. |
| push | void push(E e) | Push given element e on to the stack represented using deque without violating the capacity restrictions. Returns true on success or IllegalStateException if no space is available on deque. |
| remove | E remove() | Remove and return the head of the deque. |
| remove | boolean remove(Object o) | Remove the first occurrence of the given element o from the deque. |
| removeFirst | E removeFirst() | Remove and return the first element of the deque. |
| removeFirstOccurrence | boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) | Removes the first occurrence of the given element o from the deque. |
| removeLast | E removeLast() | Retrieves and deletes the last element in the deque. |
| removeLastOccurrence | boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) | Deletes the last occurrence of a given element o from the deque. |
| size | int size() | Returns the size or number of elements in the deque. |
Java中的双端队列实现
现在让我们实现一个Java程序来演示上面讨论的一些主要的双端队列方法。
在此程序中,我们使用String类型的双端队列,然后使用各种方法(例如add,addFirst,addLast,push,offer,offerFirst等)向此双端队列添加元素。然后显示双端队列。接下来,我们为双端队列定义标准迭代器和反向迭代器,并遍历双端队列以打印元素。
我们还使用其他方法,例如contains,pop,push,peek,poll,remove等。
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Declare Deque object
Dequenew LinkedList
// add elements to the queue using various methods
deque.add("One"); //add ()
deque.addFirst("Two"); //addFirst ()
deque.addLast("Three"); //addLast ()
deque.push("Four"); //push ()
deque.offer("Five"); //offer ()
deque.offerFirst("Six"); //offerFirst ()
deque.offerLast("Seven"); //offerLast ()
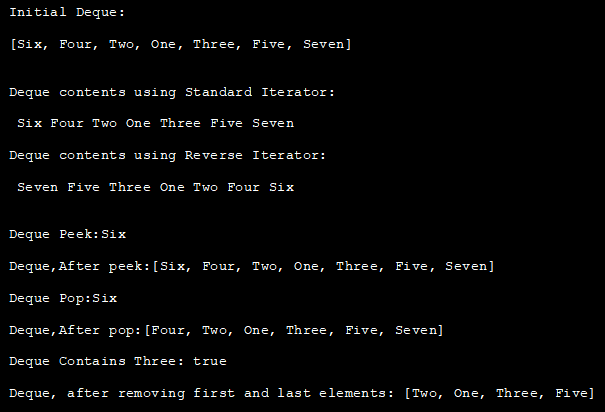
System.out.println("Initial Deque:");
System.out.print(deque + " ");
// Iterate using standard iterator
System.out.println("\n\nDeque contents using Standard Iterator:");
Iterator iterator = deque.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext())
System.out.print(" " + iterator.next());
// Iterate using Reverse order iterator
Iterator reverse = deque.descendingIterator();
System.out.println("\n\nDeque contents using Reverse Iterator:");
while (reverse.hasNext())
System.out.print(" " + reverse.next());
// Peek () method
System.out.println("\n\nDeque Peek:" + deque.peek());
System.out.println("\nDeque,After peek:" + deque);
// Pop () method
System.out.println("\nDeque Pop:" + deque.pop());
System.out.println("\nDeque,After pop:" + deque);
// contains () method
System.out.println("\nDeque Contains Three: " + deque.contains("Three"));
deque.removeFirst(); //removeFirst ()
deque.removeLast(); //removeLast ()
System.out.println("\nDeque, after removing " + "first and last elements: " + deque);
}
}
|
输出:
经常问的问题
Q#1)Deque是线程安全的Java吗?
答: ArrayDeque不是线程安全的。但是java.util.concurrent类中的BlockingDeque接口表示双端队列。此双端队列是线程安全的。
Q#2)为什么双端队列比堆栈快?
答案:实现双端队列接口的ArrayDeque接口具有存储效率,因为它不需要跟踪上一个或下一个节点。同样,它是可调整大小的实现。因此,双端队列比堆栈快。
Q#3)Deque是堆栈吗?
答:双端队列是双端队列。它允许LIFO行为,因此尽管它不是堆栈,也可以实现为堆栈。
问#4)在何处使用Deque?
答:双端队列主要用于实现撤消和历史记录等功能。
问#5)双端队列是否为圆形?
答:是的,Deque是圆形的。
结论
至此,我们完成了有关Java中Deque接口的教程。双端队列接口由双端队列数据结构实现,双端队列数据结构是一个可以在两端插入和删除元素的集合。
ArrayDeque和LinkedList这两个类实现了双端队列接口。我们可以使用这些类来实现双端队列接口的功能。