前言
React 是一个十分庞大的库,由于要同时考虑 ReactDom 和 ReactNative ,还有服务器渲染等,导致其代码抽象化程度很高,嵌套层级非常深,阅读其源码是一个非常艰辛的过程。在学习 React 源码的过程中,给我帮助最大的就是这个系列文章,于是决定基于这个系列文章谈一下自己的理解。本文会大量用到原文中的例子,想体会原汁原味的感觉,推荐阅读原文。
本系列文章基于 React 15.4.2 ,以下是本系列其它文章的传送门:
React 源码深度解读(一):首次 DOM 元素渲染 - Part 1
React 源码深度解读(二):首次 DOM 元素渲染 - Part 2
React 源码深度解读(三):首次 DOM 元素渲染 - Part 3
React 源码深度解读(四):首次自定义组件渲染 - Part 1
React 源码深度解读(五):首次自定义组件渲染 - Part 2
React 源码深度解读(六):依赖注入
React 源码深度解读(七):事务 - Part 1
React 源码深度解读(八):事务 - Part 2
React 源码深度解读(九):单个元素更新
React 源码深度解读(十):Diff 算法详解
正文
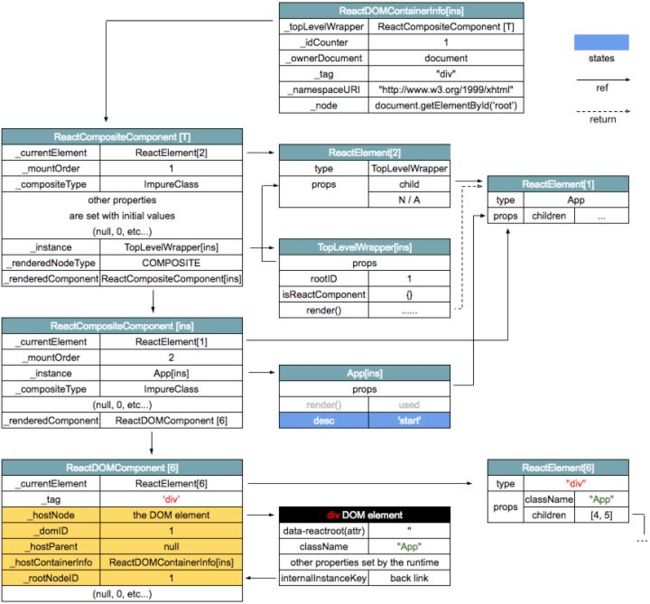
上一篇文章中,我们讲解到ReactCompositeComponent[ins]被初始化后,App[ins]的 render 方法被调用,生成 ReactElement 树,然后对应的ReactDOMComponent[6]被返回。下面我们来看看这个ReactDOMComponent[6]是如何转化为 DOM 树的。
performInitialMount: function (renderedElement, hostParent,
hostContainerInfo, transaction, context) {
...
// 这里会调用 App 实例的 render 方法,而 render 的返回值是 React.createElement 的嵌套调用。
if (renderedElement === undefined) {
renderedElement = this._renderValidatedComponent();
}
...
// 上回讲到这里
// 返回 ReactDOMComponent[6]
var child = this._instantiateReactComponent(
renderedElement,
nodeType !== ReactNodeTypes.EMPTY /* shouldHaveDebugID */
);
this._renderedComponent = child;
// 今天讲这部分
var markup = ReactReconciler.mountComponent(
child,
transaction,
hostParent,
hostContainerInfo,
this._processChildContext(context),
debugID
);
return markup;
},ReactDOMComponent[6].mountComponent
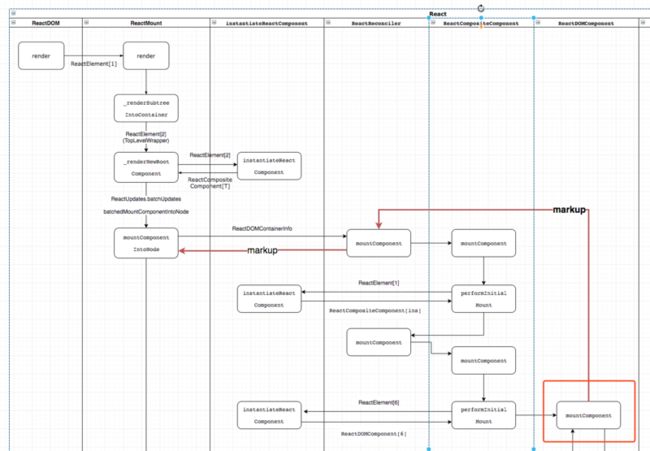
ReactReconciler.mountComponent 会触发ReactDOMComponent[6]的 mountComponent 方法,调用栈如下:
...
|~mountComponentIntoNode() |
|-ReactReconciler.mountComponent() |
|-ReactCompositeComponent[T].mountComponent() |
|-ReactCompositeComponent[T].performInitialMount() upper half
|-ReactReconciler.mountComponent() |
|-ReactCompositeComponent[ins].mountComponent() |
|-this.performInitialMount() |
|-this._renderValidatedComponent() |
|-instantiateReactComponent() _|_
(we are here) |
|-ReactDOMComponent[6].mountComponent( |
transaction, // scr: -----> not of interest |
hostParent, // scr: -----> null |
hostContainerInfo,// scr:---------------------> ReactDOMContainerInfo[ins] lower half
context // scr: -----> not of interest |
) |
...mountComponent: function (
transaction,
hostParent,
hostContainerInfo,
context
) {
...
var mountImage;
if (transaction.useCreateElement) {
var ownerDocument = hostContainerInfo._ownerDocument;
...
// 创建 div 元素
el = ownerDocument.createElement(this._currentElement.type);
...
// 设置 attributes
if (!this._hostParent) {
DOMPropertyOperations.setAttributeForRoot(el);
}
// 设置 properties
this._updateDOMProperties(null, props, transaction);
// 构造 DOM 树
var lazyTree = DOMLazyTree(el);
// 遍历子节点并创建 DOM 结点
this._createInitialChildren(transaction, props, context, lazyTree);
mountImage = lazyTree;
}
...
return mountImage;
}这里主要做的事情有3部分:
- 创建 DOM 元素
- 设置 attributes 和 properties
- 遍历子元素并重复上述过程
流程图:
_createInitialChildren 遍历子节点并创建 DOM 结点
下面来看一下 _createInitialChildren 的细节:
_createInitialChildren: function (transaction, props, context, lazyTree) {
// Intentional use of != to avoid catching zero/false.
var innerHTML = props.dangerouslySetInnerHTML;
if (innerHTML != null) {
if (innerHTML.__html != null) {
DOMLazyTree.queueHTML(lazyTree, innerHTML.__html);
}
} else {
// 如果是 string 或者 number,返回 true
var contentToUse =
CONTENT_TYPES[typeof props.children] ? props.children :
null;
var childrenToUse = contentToUse != null ? null : props.children;
// 直接渲染字符串
if (contentToUse != null) {
// Avoid setting textContent when the text is empty. In IE11 setting
// textContent on a text area will cause the placeholder to not
// show within the textarea until it has been focused and blurred again.
// https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/6731#issuecomment-254874553
if (contentToUse !== '') {
DOMLazyTree.queueText(lazyTree, contentToUse);
}
}
// 渲染子节点
else if (childrenToUse != null) {
var mountImages = this.mountChildren(
childrenToUse,
transaction,
context
);
for (var i = 0; i < mountImages.length; i++) {
DOMLazyTree.queueChild(lazyTree, mountImages[i]);
}
}
}
},这部分代码十分好懂,就 3 条分支:
- 设置了 dangerouslySetInnerHTML 属性,直接渲染 HTML
- 子节点类型为 string 或 number,渲染字符
- 其它情况就需要将 ReactElement 转换成 ReactDOMComponent 或 ReactCompositeComponent 作进一步的渲染。
DOMLazyTree 的 queueText 和 queueChild 真正有效的都各只有一行代码:
function queueText(tree, text) {
if (enableLazy) { // scr: NO, I mean, false
...
} else {
setTextContent(tree.node, text);
}
}
var setTextContent = function (node, text) {
if (text) {
var firstChild = node.firstChild;
if (firstChild && firstChild === node.lastChild && firstChild.nodeType === 3) { // scr: false
...
}
}
node.textContent = text; // scr: the only effective line
};
function queueChild(parentTree, childTree) {
if (enableLazy) { // scr: again, false
...
} else {
parentTree.node.appendChild(childTree.node);
}
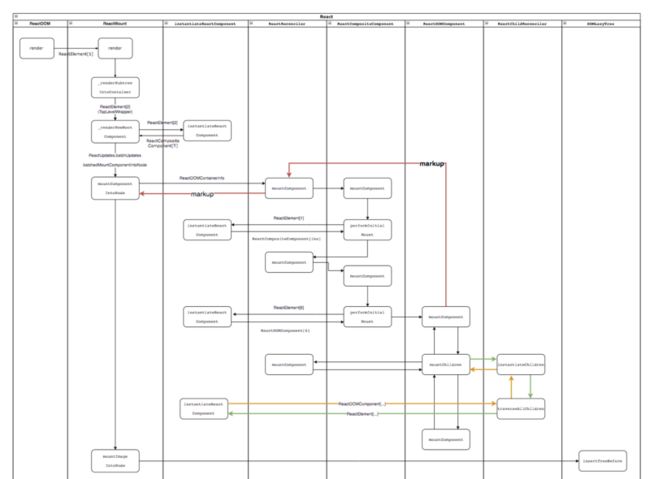
}mountChildren 的调用栈如下:
ReactDOMComponent[6].mountComponent() <-------------------------|
(we are here) |
|-this._createInitialChildren() |
?{1} |
|-DOMLazyTree.queueText() |
?{2} |
|-this.mountChildren() // scr: ---------------> 1)(a) |
|-this._reconcilerInstantiateChildren() |
|-ReactChildReconciler.instantiateChildren() |
|-traverseAllChildren() |
|-traverseAllChildrenImpl() <------|inner |
|↻traverseAllChildrenImpl() ------|recursion |
|-instantiateChild() |
|-instantiateReactComponent() |
|↻ReactDOMComponent.mountComponent() // scr: -> 1)(b)---|
|↻DOMLazyTree.queueChild() // scr: ---------------> 2)这中间的函数调用逻辑很清晰,最终会走到 traverseAllChildrenImpl 这里:
function traverseAllChildrenImpl(
children,
nameSoFar,
callback,
traverseContext
) {
var type = typeof children;
if (type === 'undefined' || type === 'boolean') {
// All of the above are perceived as null.
children = null;
}
if (children === null ||
type === 'string' ||
type === 'number' ||
// The following is inlined from ReactElement. This means we can optimize
// some checks. React Fiber also inlines this logic for similar purposes.
(type === 'object' && children.$$typeof === REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE)) {
callback(
traverseContext,
children,
// If it's the only child, treat the name as if it was wrapped in an array
// so that it's consistent if the number of children grows.
nameSoFar === '' ? SEPARATOR + getComponentKey(children, 0) :
nameSoFar
);
return 1;
}
var child;
var nextName;
var subtreeCount = 0; // Count of children found in the current subtree.
var nextNamePrefix = nameSoFar === '' ? SEPARATOR : nameSoFar +
SUBSEPARATOR;
if (Array.isArray(children)) {
for (var i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
child = children[i];
nextName = nextNamePrefix + getComponentKey(child, i);
subtreeCount += traverseAllChildrenImpl(
child,
nextName,
callback,
traverseContext
);
}
} else {
...
}
return subtreeCount;
}这里的逻辑很简单,如果 children 不是数组,则调用回调函数;如果是数组,则继续调用自身,相当于深度优先遍历。这里的回调函数就是 ReactChildReconciler 中的 instantiateChild:
function instantiateChild(childInstances, child, name, selfDebugID) {
...
if (child != null && keyUnique) {
childInstances[name] = instantiateReactComponent(child, true);
}
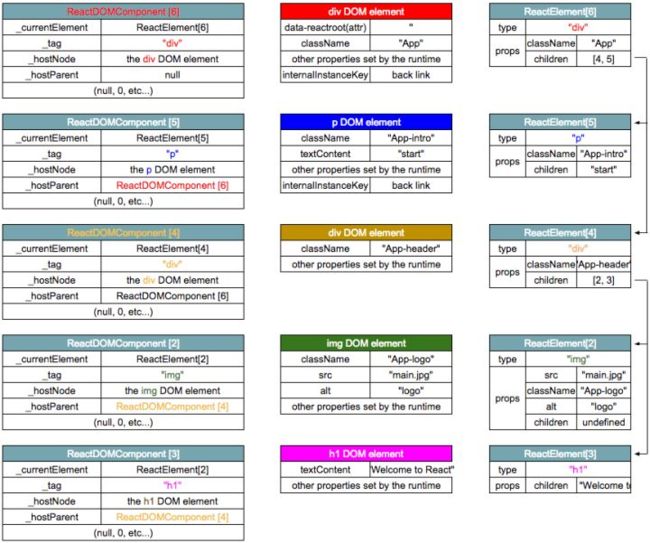
}这里直接调用 instantiateReactComponent,创建ReactDOMComponent。所有的ReactDOMComponent的创建顺序如下:
ReactDOMComponent[6].mountComponent()
|-this._createInitialChildren()
|-this.mountChildren()
... |↻instantiateReactComponent()[4,5]
|-ReactDOMComponent[5].mountComponent()
|-this._createInitialChildren()
|-node.textContent = text; // scr: [5] done
|-ReactDOMComponent[4].mountComponent()
|-this._createInitialChildren()
|-this.mountChildren()
... |↻instantiateReactComponent()[2,3]
|-ReactDOMComponent[2].mountComponent() // scr: [2] done
|-ReactDOMComponent[3].mountComponent()
|-this._createInitialChildren()
|-node.textContent = text; // scr: [3] done
|↻node[4].appendChild()[2,3] // scr: [4] done
|↻node[6].appendChild()[4,5] // scr: [6] done完成的流程图: