【项目杂记】JWT(中):项目中使用 JWT 时用到的工具类
在上一篇我们介绍了 JWT 是什么,本篇就来看看在项目使用 JWT 时需要用到哪些工具类。
1.RsaUtils
RsaUtils:生成公钥和私钥,并写入指定文件
注:公钥和私钥是生成签名和验证签名的依据。
public class RsaUtils {
/**
* 根据密文,生成rsa公钥和私钥,并写入指定文件
*
* @param publicKeyFilename 公钥文件路径
* @param privateKeyFilename 私钥文件路径
* @param secret 生成密钥的密文
* @throws IOException
* @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException
*/
public static void generateKey(String publicKeyFilename, String privateKeyFilename, String secret) throws Exception {
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom(secret.getBytes());
keyPairGenerator.initialize(1024, secureRandom);
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.genKeyPair();
// 获取公钥并写出
byte[] publicKeyBytes = keyPair.getPublic().getEncoded();
writeFile(publicKeyFilename, publicKeyBytes);
// 获取私钥并写出
byte[] privateKeyBytes = keyPair.getPrivate().getEncoded();
writeFile(privateKeyFilename, privateKeyBytes);
}
private static byte[] readFile(String fileName) throws Exception {
return Files.readAllBytes(new File(fileName).toPath());
}
private static void writeFile(String destPath, byte[] bytes) throws IOException {
File dest = new File(destPath);
if (!dest.exists()) {
dest.createNewFile();
}
Files.write(dest.toPath(), bytes);
}
/**
* 从文件中读取公钥
*
* @param filename 公钥保存路径,相对于classpath
* @return 公钥对象
* @throws Exception
*/
public static PublicKey getPublicKey(String filename) throws Exception {
byte[] bytes = readFile(filename);
return getPublicKey(bytes);
}
/**
* 获取公钥
*
* @param bytes 公钥的字节形式
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static PublicKey getPublicKey(byte[] bytes) throws Exception {
X509EncodedKeySpec spec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(bytes);
KeyFactory factory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return factory.generatePublic(spec);
}
/**
* 从文件中读取密钥
*
* @param filename 私钥保存路径,相对于classpath
* @return 私钥对象
* @throws Exception
*/
public static PrivateKey getPrivateKey(String filename) throws Exception {
byte[] bytes = readFile(filename);
return getPrivateKey(bytes);
}
/**
* 获取密钥
*
* @param bytes 私钥的字节形式
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static PrivateKey getPrivateKey(byte[] bytes) throws Exception {
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec spec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(bytes);
KeyFactory factory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return factory.generatePrivate(spec);
}
}
2.JwtUtils
JwtUtils:生成 token;解析 token 并获取信息
public class JwtUtils {
/**
* 生成 token
*
* @param userInfo 载荷中的数据来源(需自己修改)
* @param privateKey 生成签名的私钥
* @param expireMinutes 过期时间,单位秒
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static String generateToken(UserInfo userInfo, PrivateKey privateKey, int expireMinutes) throws Exception {
return Jwts.builder()
// 在 payload 中设置自定义信息(需要自己修改)
.claim(JwtConstans.JWT_KEY_ID, userInfo.getId())
// 在 payload 中设置过期时间
.setExpiration(DateTime.now().plusMinutes(expireMinutes).toDate())
// 设置生成签名的算法为 RS256,并传入生成签名的私钥
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.RS256, privateKey)
.compact();
}
/**
* 获取 token 中的用户信息
*
* @param token 用户请求中的令牌
* @param publicKey 公钥
* @return 用户信息(需自己修改)
* @throws Exception
*/
public static UserInfo getInfoFromToken(String token, PublicKey publicKey) throws Exception {
Jws<Claims> claimsJws = parserToken(token, publicKey);
Claims body = claimsJws.getBody();
// 构建用户信息(需自己修改)
return new UserInfo(
// 从jwt解析得到的数据是Object类型,为防止转换时出现空指针,这里封装了一个工具类
ObjectUtils.toLong(body.get(JwtConstans.JWT_KEY_ID))
);
}
/**
* 公钥验证 token
*
* @param token 用户请求中的token
* @param publicKey 公钥
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private static Jws<Claims> parserToken(String token, PublicKey publicKey) {
return Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(publicKey).parseClaimsJws(token);
}
}
这里说明两点:
1)其中 JwtConstans 存放的是 Jwt payload 中用户自定义信息的 Key
PS:Jwt 是 JSON 结构,所以也是 key-value 形式。
public abstract class JwtConstans {
public static final String JWT_KEY_ID = "id";
}
2)在生成 jwt 设置过期时间 setExpiration(DateTime.now().plusMinutes(expireMinutes).toDate()) 时,DateTime 需要引入 joda-time 的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-timegroupId>
<artifactId>joda-timeartifactId>
dependency>
3.ObjectUtils
ObjectUtils:从jwt解析得到的数据是Object类型,转换为具体类型可能出现空指针, 这个工具类进行了一些转换
public class ObjectUtils {
public static String toString(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return null;
}
return obj.toString();
}
public static Long toLong(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return 0L;
}
if (obj instanceof Double || obj instanceof Float) {
return Long.valueOf(StringUtils.substringBefore(obj.toString(), "."));
}
if (obj instanceof Number) {
return Long.valueOf(obj.toString());
}
if (obj instanceof String) {
return Long.valueOf(obj.toString());
} else {
return 0L;
}
}
public static Integer toInt(Object obj) {
return toLong(obj).intValue();
}
}
4.CookieUtils
CookieUtils:构建 cookie,因为 Jwt 是通过 cookie 发送到客户端的
public class CookieUtils {
@Value("${domain}")
private static String domain; // 从配置文件 application.yml 中读取 domain 域
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CookieUtils.class);
/**
* 发送 cookie 到用户端
* @param request {@link HttpServletRequest}
* @param response {@link HttpServletResponse}
* @param cookieName cookie名
* @param cookieValue cookie 要保存的值
* @param cookieMaxAge cookie 的存活时间
*/
public static void setCookie(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,String cookieName,String cookieValue,Integer cookieMaxAge){
setCookie(request,response,cookieName,cookieValue,cookieMaxAge,domain,null,null);
}
private static final void setCookie(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String cookieName, String cookieValue, Integer cookieMaxAge,String domain, String encodeString, Boolean httpOnly) {
try {
if(StringUtils.isBlank(encodeString)) {
encodeString = "utf-8";
}
if (cookieValue == null) {
cookieValue = "";
} else {
cookieValue = URLEncoder.encode(cookieValue, encodeString);
}
Cookie cookie = new Cookie(cookieName, cookieValue);
if (cookieMaxAge != null && cookieMaxAge > 0)
cookie.setMaxAge(cookieMaxAge);
if (null != request) // 设置域名的cookie
cookie.setDomain(domain);
cookie.setPath("/");
if(httpOnly != null) {
cookie.setHttpOnly(httpOnly);
}
// 发送 cookie 到客户端
response.addCookie(cookie);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Cookie Encode Error.", e);
}
}
/**
* 得到Cookie的值, 不编码
*
* @param request
* @param cookieName
* @return
*/
public static String getCookieValue(HttpServletRequest request, String cookieName) {
return getCookieValue(request, cookieName, false);
}
/**
* 得到Cookie的值,
*
* @param request
* @param cookieName
* @return
*/
public static String getCookieValue(HttpServletRequest request, String cookieName, boolean isDecoder) {
Cookie[] cookieList = request.getCookies();
if (cookieList == null || cookieName == null){
return null;
}
String retValue = null;
try {
for (int i = 0; i < cookieList.length; i++) {
if (cookieList[i].getName().equals(cookieName)) {
if (isDecoder) {
retValue = URLDecoder.decode(cookieList[i].getValue(), "UTF-8");
} else {
retValue = cookieList[i].getValue();
}
break;
}
}
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
logger.error("Cookie Decode Error.", e);
}
return retValue;
}
}
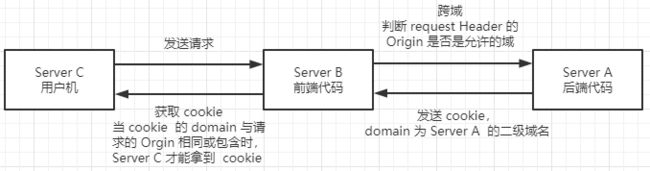
关于 CookieUtils,这里说一下为什么要从配置文件中读取 domain 。
domain 是指定什么域可以拿到该 cookie,默认是后端服务器的二级域名。
-
问题:前后端对接时,后端代码部署到了测试服务器上(比如 43.107.136.112),那么,后端发送的 cookie 的 domain 域将是 107.136.112;而web页面依然在前端人员的本机(localhost),所以,导致的结果就是客户端根本无法拿到 cookie,更别说在请求时携带 cookie 中的 jwt
-
解决(两种方案):
-
注意:在前端也部署到服务器后,一般不存在这个问题,比如后端代码在 aaa.jd.com,而前端页面在 bbb.jd.com,即两者的二级域名相同(domain(jd.com) 包含 web 页面的请求域(bbb.jd.com))。
另外,在 Chrome 的控制台的 Application 可以看到本机存储了当前网站的什么 cookie,及 cookie 的 name、value、domain、expires 等。
关于使用 JWT 鉴权的具体逻辑请看下一篇…