欢迎访问我的GitHub
https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java、Docker、Kubernetes、DevOPS等;
关于《JUnit5学习》系列
《JUnit5学习》系列旨在通过实战提升SpringBoot环境下的单元测试技能,一共八篇文章,链接如下:
- 基本操作
- Assumptions类
- Assertions类
- 按条件执行
- 标签(Tag)和自定义注解
- 参数化测试(Parameterized Tests)基础
- 参数化测试(Parameterized Tests)进阶
- 综合进阶(终篇)
本篇概览
本文是《JUnit5学习》系列的第一篇,通过实战学习在SpringBoot框架下JUnit5的基本功能,全篇章节如下:
- JUnit5简介
- SpringBoot对JUnit5的依赖
- 常用注解简介
- 5版本已废弃的注解介绍
- 进入实战环节,先介绍版本和环境信息
- 创建《JUnit5学习》系列源码的父工程
- 创建子工程,编码体验常用注解
关于JUnit5
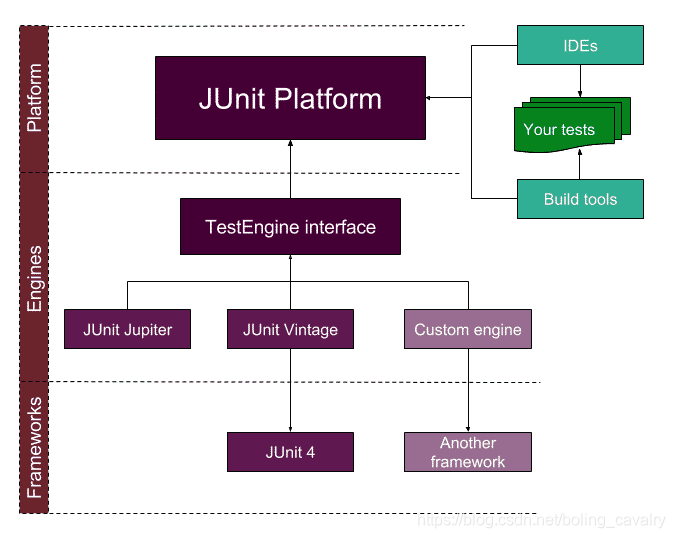
- JUnit是常用的java单元测试框架,5是当前最新版本,其整体架构如下(图片来自网络):
- 从上图可见,整个JUnit5可以划分成三层:顶层框架(Framework)、中间的引擎(Engine),底层的平台(Platform);
- 官方定义JUnit5由三部分组成:Platform、Jupiter、Vintage,功能如下;
- Platform:位于架构的最底层,是JVM上执行单元测试的基础平台,还对接了各种IDE(例如IDEA、eclipse),并且还与引擎层对接,定义了引擎层对接的API;
- Jupiter:位于引擎层,支持5版本的编程模型、扩展模型;
- Vintage:位于引擎层,用于执行低版本的测试用例;
- 可见整个Junit Platform是开放的,通过引擎API各种测试框架都可以接入;
SpringBoot对JUnit5的依赖
- 这里使用SpringBoot版本为2.3.4.RELEASE,在项目的pom.xml中依赖JUnit5的方法如下:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
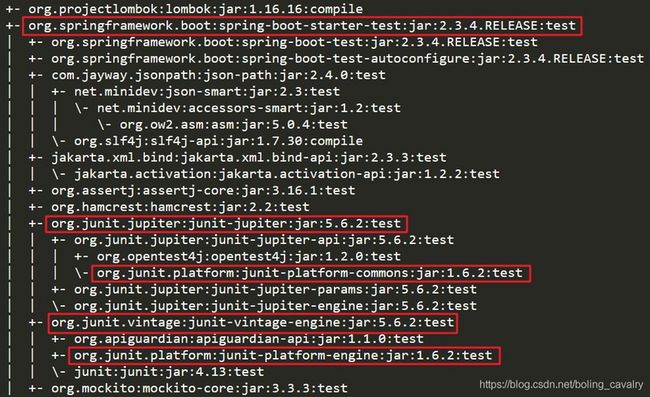
- 如下图红框,可见JUnit5的jar都被spring-boot-starter-test间接依赖进来了:
曾经的RunWith注解
- 在使用JUnit4的时候,咱们经常这么写单元测试类:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
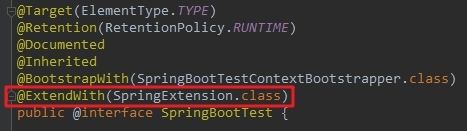
public class XXXTest {- 对于上面的RunWith注解,JUnit5官方文档的说法如下图红框所示,已经被ExtendWith取代:
- 咱们再来看看SpringBootTest注解,如下图,可见已经包含了ExtendWith:
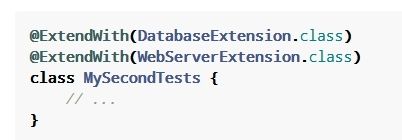
- 综上所述,SpringBoot+JUnit5时,RunWith注解已经不需要了,正常情况下仅SpringBootTest注解即可,如果对扩展性有更多需求,可以添加ExtendWith注解,如下图:
常用的JUnit5注解(SpringBoot环境)
注意,接下来提到的测试方法,是指当前class中所有被@Test、@RepeatedTest、@ParameterizedTest、@TestFactory修饰的方法;
- ExtendWith:这是用来取代旧版本中的RunWith注解,不过在SpringBoot环境如果没有特别要求无需额外配置,因为SpringBootTest中已经有了;
- Test:被该注解修饰的就是测试方法;
- BeforeAll:被该注解修饰的必须是静态方法,会在所有测试方法之前执行,会被子类继承,取代低版本的BeforeClass;
- AfterAll:被该注解修饰的必须是静态方法,会在所有测试方法执行之后才被执行,会被子类继承,取代低版本的AfterClass;
- BeforeEach:被该注解修饰的方法会在每个测试方法执行前被执行一次,会被子类继承,取代低版本的Before;
- AfterEach:被该注解修饰的方法会在每个测试方法执行后被执行一次,会被子类继承,取代低版本的Before;
- DisplayName:测试方法的展现名称,在测试框架中展示,支持emoji;
- Timeout:超时时长,被修饰的方法如果超时则会导致测试不通过;
- Disabled:不执行的测试方法;
5版本已废弃的注解
以下的注解都是在5之前的版本使用的,现在已经被废弃:
| 被废弃的注解 | 新的继任者 |
|---|---|
| Before | BeforeEach |
| After | AfterEach |
| BeforeClass | BeforeAll |
| AfterClass | AfterAll |
| Category | Tag |
| RunWith | ExtendWith |
| Rule | ExtendWith |
| ClassRule | RegisterExtension |
版本和环境信息
整个系列的编码和执行在以下环境进行,供您参考:
- 硬件配置:处理器i5-8400,内存32G,硬盘128G SSD + 500G HDD
- 操作系统:Windows10家庭中文版
- IDEA:2020.2.2 (Ultimate Edition)
- JDK:1.8.0_181
- SpringBoot:2.3.4.RELEASE
- JUnit Jupiter:5.6.2
接下来开始实战,咱们先建好SpringBoot项目;
关于lombok
为了简化代码,项目中使用了lombok,请您在IDEA中安装lombok插件;
源码下载
- 如果您不想编码,可以在GitHub下载所有源码,地址和链接信息如下表所示(https://github.com/zq2599/blo...:
| 名称 | 链接 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 项目主页 | https://github.com/zq2599/blo... | 该项目在GitHub上的主页 |
| git仓库地址(https) | https://github.com/zq2599/blo... | 该项目源码的仓库地址,https协议 |
| git仓库地址(ssh) | [email protected]:zq2599/blog_demos.git | 该项目源码的仓库地址,ssh协议 |
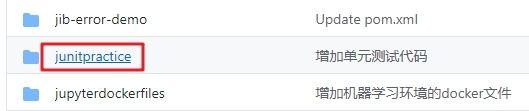
- 这个git项目中有多个文件夹,本章的应用在junitpractice文件夹下,如下图红框所示:
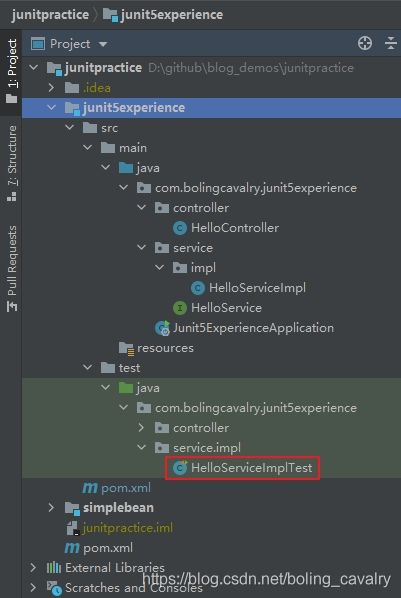
- junitpractice是父子结构的工程,本篇的代码在junit5experience子工程中,如下图:
创建Maven父工程
- 为了便于管理整个系列的源码,在此建立名为junitpractice的maven工程,后续所有实战的源码都作为junitpractice的子工程;
- junitpractice的pom.xml如下,可见是以SpringBoot的2.3.4.RELEASE版本作为其父工程:
4.0.0
simplebean
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.3.4.RELEASE
com.bolingcavalry
junitpractice
1.0-SNAPSHOT
pom
UTF-8
UTF-8
1.8
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.16.16
本篇的源码工程
接下来咱们准备一个简单的SpringBoot工程用于做单元测试,该工程有service和controller层,包含一些简单的接口和类;
- 创建名为junit5experience的子工程,pom.xml如下,注意单元测试要依赖spring-boot-starter-test:
4.0.0
com.bolingcavalry
junitpractice
1.0-SNAPSHOT
../pom.xml
com.bolingcavalry
junit5experience
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
junit5experience
Demo project for simplebean in Spring Boot junit5
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.projectlombok
lombok
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-webflux
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
- 写一些最简单的业务代码,首先是service层的接口HelloService.java:
package com.bolingcavalry.junit5experience.service;
public interface HelloService {
String hello(String name);
int increase(int value);
/**
* 该方法会等待1秒后返回true,这是在模拟一个耗时的远程调用
* @return
*/
boolean remoteRequest();
}- 上述接口对应的实现类如下,hello和increase方法分别返回String型和int型,remoteRequest故意sleep了1秒钟,用来测试Timeout注解的效果:
package com.bolingcavalry.junit5experience.service.impl;
import com.bolingcavalry.junit5experience.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service()
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String hello(String name) {
return "Hello " + name;
}
@Override
public int increase(int value) {
return value + 1;
}
@Override
public boolean remoteRequest() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException interruptedException) {
interruptedException.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
}- 添加一个简单的controller:
package com.bolingcavalry.junit5experience.controller;
import com.bolingcavalry.junit5experience.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private HelloService helloService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/{name}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String hello(@PathVariable String name){
return helloService.hello(name);
}
}- 启动类:
package com.bolingcavalry.junit5experience;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Junit5ExperienceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Junit5ExperienceApplication.class, args);
}
}- 以上就是一个典型的web工程,接下来一起为该工程编写单元测试用例;
编写测试代码
- 在下图红框位置新增单元测试类:
- 测试类的内容如下,涵盖了刚才提到的常用注解,请注意每个方法的注释说明:
package com.bolingcavalry.junit5experience.service.impl;
import com.bolingcavalry.junit5experience.service.HelloService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class HelloServiceImplTest {
private static final String NAME = "Tom";
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
/**
* 在所有测试方法执行前被执行
*/
@BeforeAll
static void beforeAll() {
log.info("execute beforeAll");
}
/**
* 在所有测试方法执行后被执行
*/
@AfterAll
static void afterAll() {
log.info("execute afterAll");
}
/**
* 每个测试方法执行前都会执行一次
*/
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
log.info("execute beforeEach");
}
/**
* 每个测试方法执行后都会执行一次
*/
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
log.info("execute afterEach");
}
@Test
@DisplayName("测试service层的hello方法")
void hello() {
log.info("execute hello");
assertThat(helloService.hello(NAME)).isEqualTo("Hello " + NAME);
}
/**
* DisplayName中带有emoji,在测试框架中能够展示
*/
@Test
@DisplayName("测试service层的increase方法\uD83D\uDE31")
void increase() {
log.info("execute increase");
assertThat(helloService.increase(1)).isEqualByComparingTo(2);
}
/**
* 不会被执行的测试方法
*/
@Test
@Disabled
void neverExecute() {
log.info("execute neverExecute");
}
/**
* 调用一个耗时1秒的方法,用Timeout设置超时时间是500毫秒,
* 因此该用例会测试失败
*/
@Test
@Timeout(unit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, value = 500)
@Disabled
void remoteRequest() {
assertThat(helloService.remoteRequest()).isEqualTo(true);
}
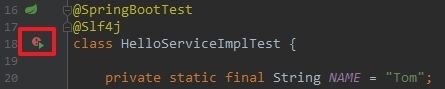
}- 接下来执行测试用例试试,点击下图红框中的按钮:
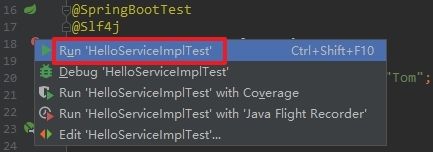
- 如下图,在弹出的菜单中,点击红框位置:
- 执行结果如下,可见Displayname注解的值作为测试结果的方法名展示,超时的方法会被判定为测试不通过,Disable注解修饰的方法则被标记为跳过不执行:
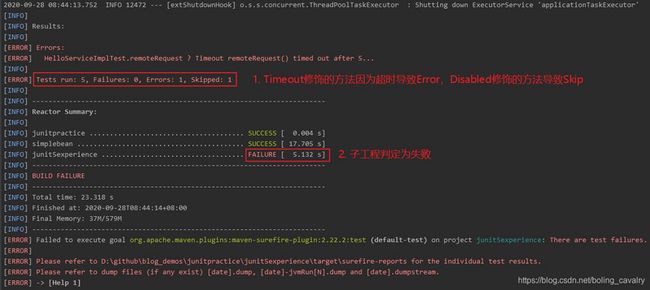
- 在父工程junitpractice的pom.xml文件所在目录,执行mvn test命令,可以看到maven执行单元测试的效果:
- 至此,咱们对SpringBoot环境下的JUnit5有了最基本的了解,接下来的章节会展开更多知识点和细节,对单元测试做更深入的学习。
你不孤单,欣宸原创一路相伴
欢迎关注公众号:程序员欣宸
微信搜索「程序员欣宸」,我是欣宸,期待与您一同畅游Java世界...
https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos