Python 内置数据结构字符串(创建及特性,内建方法,string模块)
字符串
-
- 1.字符串的创建和赋值
- 2.字符串的基本特性
- 2.1 连接操作符和重复操作符
- 2.2 成员操作符
- 2.3 正向索引和反向索引
- 2.4 切片
- 5. for循环访问
- test1: 判断一串字符是否为回文字符串
- 3.字符串的内建方法
- 3.1.字符串的判断与转换项目
- 判断
- 转换
- test2:需求: 用户输入Y或者y都继续继续代码(yum install )时候选择y|n
- 3.2 字符串的开头与结尾匹配
- startswith
- endswith:
-
- 3.3 字符串的位置调整
- 3.4字符串的数据清洗
- 3.5 字符串的搜索与统计
- 3.6字符串的分离与拼接
- test3: 判断ip合法性
- 4.拓展:string模块
- 5.小学生计算能力测试系统
1.字符串的创建和赋值
字符串或串(String)是由数字、字母、下划线组成的一串字符。Python 里面最常见的类型。 可以简单地通过在引号间(单引号,双引号和三引号)包含字符的方式创建它。
第一种方式:
str1 = ‘our company is westos’
第二种方式:
str2 = “our company is westos”
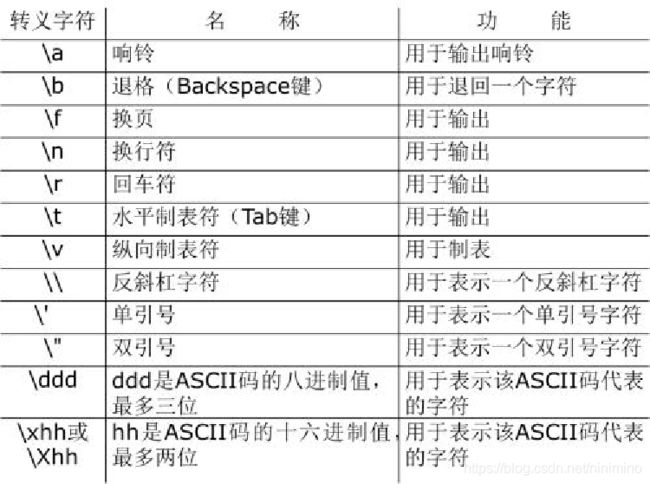
字符串是不可变的,只能通过赋一个空字符串或者使用 del 语句来清空或者删除一个字符串
但是没有必要显式的删除字符串。定义这个字符串的代码结束时会自动释放这些字符串
2.字符串的基本特性
2.1 连接操作符和重复操作符
##>>> name = 'westos'
>>> print('hello' + name)
hellowestos
符号可以用乘号形式让其重复出现
>>> print("*" * 30 + '学生管理系统' + '*' * 30)
******************************学生管理系统******************************
>>>
2.2 成员操作符
判断字符是否在字符串中
>>> s = 'hello westos'
>>> print('westos' in s)
True
>>> print('westos' not in s)
False
>>> print('x' in s)
False
>>>
2.3 正向索引和反向索引
索引从0开始
>>> s = 'WESTOS'
>>> print(s[0]) ##0号索引对应的字符是
W
>>> print(s[-3]) ##倒数第三个字符是
T
>>>
2.4 切片
切片如同前面的range模块的使用
range(3):[0, 1, 2]
range(1, 4): [1, 2, 3]
range(1, 6, 2): [1, 3, 5]
切片: 切除一部分的内容
s[start:end:step]
s[:end]:
s[start:]:
s[:n] |
: 拿出前n个元素 |
|---|---|
s[n:] |
: 除了前n个元素, 其他元素保留 |
s[:] |
:从头开始访问一直到字符串结束的位置 |
s[::-1] |
: 倒序输出 |
>>> s = 'hello ll'
>>> print(s[:])
hello ll
>>> print(s[::-1]) ##倒叙输出
ll olleh
>>> print(s[1:]) #除第一个元素外都保留
ello ll
>>> print(s[:5])##拿出字符串的前5个字符
hello
>>> print(s[1:3]) ##拿出第一个索引和第二个索引的字符
el
5. for循环访问
s = 'westos'
count = 0
for item in s:
count += 1
print(f"第{count}个字符:{item}")
test1: 判断一串字符是否为回文字符串
#回文字符串: 顺序和倒叙读取是一样的
简单判断
s1 = input("输入所要判断的字符:")
s2 = s1[::-1]
if s1 == s2:
print(f"{s1}是回文字符串" )
else:
print(f"{s1}不是回文字符串")
2
#只考虑字母和数字字符。可以忽略字母的大小写
解题思路:
考虑到字母又大小写问题,先把器其全部转换为小写
print(‘Hello’.lower())
s1 = (input("输入所要判断的字符:").lower())
s2 = s1[::-1]
if s1 == s2:
print(f"{s1}是回文字符串" )
else:
print(f"{s1}不是回文字符串")
3.字符串的内建方法
3.1.字符串的判断与转换项目
判断
| isalnum | 是否为字母或数字 |
|---|---|
| isalpha | 是否为字母 |
| isdigit | 是否数字 |
| islower | 是否小写字母 |
| isspace | 是否空格 |
| istitle | 是否为标题eg: Hello Eww |
| isupper | 是否为大写字母 |
| isdecimal | 是否为十进制字符 |
s = 'HelloWESTOS'
print(s.isalnum()) # True
print(s.isdigit()) # Flase
print(s.isupper()) # False
转换
常用转换
print('hello'.upper()) |
转换为大写字母 |
|---|---|
| print(‘HellO’.lower()) | 转换为小写 |
| print(‘hello ww’.title()) | 转换为标题Hello Ww |
print('HellO WOrld'.capitalize()) |
首字母为大写,其余为小写Hello world |
print('HellO WOrld'.swapcase()) |
大写转换为小写,小写转换为大写hELLo woRLD |
test2:需求: 用户输入Y或者y都继续继续代码(yum install )时候选择y|n
3.2 字符串的开头与结尾匹配
startswith
一些网址的开头是http,用来判断网址的正确性
url = 'http://www.baidu.com'
if url.startswith('http'):
# 具体实现爬虫,感兴趣的话可以看request模块。
print(f'{url}是一个正确的网址,可以爬取网站的代码')
endswith:
== 常用的场景: 判断文件的类型==
filename = 'hello.png'
if filename.endswith('.png'):
print(f'{filename} 是图片文件')
elif filename.endswith('mp3'):
print(f'{filename}是音乐文件')
else:
print(f'{filename}是未知文件')
3.3 字符串的位置调整
| center(width) | 字符串居中且长度为指定宽度 |
|---|---|
| ljust(width) | 字符串左对齐且长度为指定宽度 |
| rjust(width) | 字符串右对齐且长度为指定宽度 |
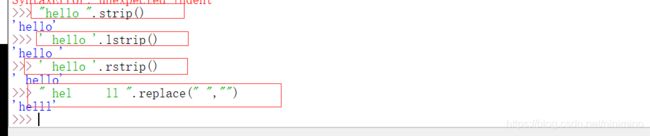
3.4字符串的数据清洗
| 数据清洗的思路 | : |
|---|---|
| lstrip | : 删除字符串左边的空格(指广义的空格: \n, \t, ’ ') |
| rstrip | : 删除字符串右边的空格(指广义的空格: \n, \t, ’ ') |
| strip | : 删除字符串左边和右边的空格(指广义的空格: \n, \t, ’ ') |
| replace | : 替换函数, 删除中间的空格, 将空格替换为空。replace(" ", ) |
3.5 字符串的搜索与统计
| find(str,beg,end) | 检测str是否包含string中,返回索引否则返回-1 |
|---|---|
| index(str,beg,end) | 检测str是否包含在string 中,返回索引,否则抛出异常 |
| count(str,start,end) | 检测str在string中出现的次数、 |
>>> s = "hello westos"
>>> s.find("llo") #llo字符是从第二个索引开始的
2
>>> s.index("llo")
2
>>> s.find("xxx") ##find查找的结果不存在,返回-1
-1
>>> s.count("xxx") ##统计字符出现的个数
0
>>> s.count("l")
2
>>> s.count("o")
2
3.6字符串的分离与拼接
| split(str=’ ') | 以str为分隔符切片string,默认是空格 |
|---|---|
| splitlines() | 以 为分隔符切片string |
| join | 以什么为连接将多个字符串拼接成一个字符串 |
test3: 判断ip合法性
ip = “172.25.254.100”
需求:IP地址的合法性-将ip的每一位数字拿出, 判断每位数字是否在0-255之间。
>>> ip.split('.')
['172', '25', '254', '100']
>>> items = ip.split('.')
>>> items
['172', '25', '254', '100']
拼接
>>> items
['172', '25', '254', '100']
>>> # 需求: 将四个数字用'-'拼接起来
>>> "-".join(items)
'172-25-254-100'
>>>
ip = input("输入想要检测的ip:")
items = ip.split('.') #是列表的形式,需要进行转换
true = 0
for n in {0,1,2,3}:
m = int(items[n]) #数字循环起来
first = int(items[n][0])
if first == 0 or m<0 or m>255:
print(f"{ip} is false")
else:
true +=1
if true == 4:
print(f"{ip} is true")
4.拓展:string模块
需求:随机生成6位验证码: 两个数字加4个字母的组合
import random
random模块虽然也可以随机生成数字,但较为繁琐random.choice(“0123456789”)
‘6’random.choice(“0123456789”) + random.choice(‘0123456789’)
‘84’random.choice(“0123456789”) + random.choice(‘0123456789’) + random.choice(‘abcdef’)
‘16b’
>>> import string
>>> string.digits ##string 模块中有随机生成数字和字母的模块
'0123456789'
>>> string.ascii_letters
'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
>>> random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4)
['z', 'N', 'u', 't']
>>> random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4)
['c', 'q', 'X', 'f']
>>> random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4)
['D', 'b', 'e', 'A']
>>> "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4))
'aMUF'
>>> "".join(random.sample(string.digits, 2)) + "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4))
'95sGFj'
>>> "".join(random.sample(string.digits, 2)) + "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4))
'17TlIb'
>>> "".join(random.sample(string.digits, 2)) + "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4))
'50uvqM'
>>> "".join(random.sample(string.digits, 2)) + "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4))
'09MCDW'
>>> "".join(random.sample(string.digits, 2)) + "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4))
'83Wntf'
for i in range(100):
print("".join(random.sample(string.digits, 2)) + "".join(random.sample(string.ascii_letters, 4)))
53SJbP
83dRcm
5.小学生计算能力测试系统
“”"
设计一个程序,用来实现帮助小学生进行算术运算练习,
它具有以下功能:
提供基本算术运算(加减乘)的题目,每道题中的操作数是随机产生的,
练习者根据显示的题目输入自己的答案,程序自动判断输入的答案是否正确
并显示出相应的信息。最后显示正确率。
1+2=?
3*6=?
import random
count = 10
right_count = 0
for i in range(count):
num1 = random.randint(1, 10)
num2 = random.randint(1, 10)
symbol = random.choice(["+", "-", "*"])
if symbol == "+":
result = num1 + num2
elif symbol == "-":
result = num1 - num2
elif symbol == "*":
result = num1 * num2
question = f"{num1} {symbol} {num2} = ?"
print(question)
user_answer = int(input("Answer:"))
if user_answer == result:
print("Right")
right_count += 1
else:
print("Error")
print("Right percent: %.2f%%" %(right_count/count*100))
import random
count = 10
right_count = 0
for i in range(count):
num1 = random.randint(1, 10)
num2 = random.randint(1, 10)
symbol = random.choice(["+", "-", "*"])
result = eval(f"{num1}{symbol}{num2}")
question = f"{num1} {symbol} {num2} = ?"
print(question)
user_answer = int(input("Answer:"))
if user_answer == result:
print("Right")
right_count += 1
else:
print("Error")
print("Right percent: %.2f%%" %(right_count/count*100))