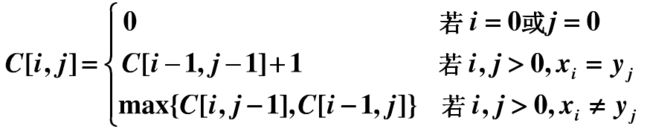算法图解 学习笔记
1.快速排序
import random
def quick_sort(ary):
#基线条件:为空或者只包含一个元素的数组是"有序"的
if len(ary)<2:
return ary
else:
print "in...",ary
pivot=ary[0] #基准值
less=[] #所有小于基准值的数值放这
greater=[] #所有大于基准值的数值放这
for i in ary[1:]:
if i<=pivot:
less.append(i)
else:
greater.append(i)
print "pivot=",pivot,"less",less,"greater",greater
print "out...",less+[pivot]+greater
return quick_sort(less)+[pivot]+quick_sort(greater)
xList=[]
for i in range(0,10):
xList.append(random.randint(1,100))
quick_sort(xList) in... [44, 35, 79, 61, 37, 68, 64, 7, 89, 79]
pivot= 44 less [35, 37, 7] greater [79, 61, 68, 64, 89, 79]
out... [35, 37, 7, 44, 79, 61, 68, 64, 89, 79]
in... [35, 37, 7]
pivot= 35 less [7] greater [37]
out... [7, 35, 37]
in... [79, 61, 68, 64, 89, 79]
pivot= 79 less [61, 68, 64, 79] greater [89]
out... [61, 68, 64, 79, 79, 89]
in... [61, 68, 64, 79]
pivot= 61 less [] greater [68, 64, 79]
out... [61, 68, 64, 79]
in... [68, 64, 79]
pivot= 68 less [64] greater [79]
out... [64, 68, 79]2.广度优先算法
广度优先算法可回答两类问题:
1.从节点A触发,有前往节点B的路径吗?
2.从节点A出发,前往节点B的那条路径最短?
例子1:需找芒果销售商
from collections import deque
def person_is_seller(name):
return name[-1]=='m'
def test_1():
graph={}
graph["you"]=["alice","bob","claire"]
graph["bob"]=["anuj","peggy"]
graph["alice"]=["peggy"]
graph["claire"]=["thom","jonny"]
graph["anuj"]=[]
graph["peggy"]=[]
graph["thom"]=[]
graph["jonny"]=[]
search_queue=deque()
search_queue+=graph["you"]
while search_queue: #只要队列不为空
person=search_queue.popleft() #就取出其中的第一个人
if person_is_seller(person): #检查这个人是否是芒果销售商
print person+"is a mango seller!";#是芒果销售商
return True;
else:
search_queue+=graph[person] #不是芒果销售商。将这个人的朋友都加入搜索列表
return False #如果到了这里,就说明队伍中没有芒果销售商
test_1()例子1中有人("peggy")检查了两次,做了无用功。因此应该优化一下:
from collections import deque
def person_is_seller(name):
return name[-1]=='m'
def test_1():
graph={}
graph["you"]=["alice","bob","claire"]
graph["bob"]=["anuj","peggy"]
graph["alice"]=["peggy"]
graph["claire"]=["thom","jonny"]
graph["anuj"]=[]
graph["peggy"]=[]
graph["thom"]=[]
graph["jonny"]=[]
search_queue=deque()
search_queue+=graph["you"]
while search_queue: #只要队列不为空
person=search_queue.popleft() #就取出其中的第一个人
if person_is_seller(person): #检查这个人是否是芒果销售商
print person+"is a mango seller!";#是芒果销售商
return True;
else:
search_queue+=graph[person] #不是芒果销售商。将这个人的朋友都加入搜索列表
return False #如果到了这里,就说明队伍中没有芒果销售商
def test_2():
graph={}
graph["you"]=["alice","bob","claire"]
graph["bob"]=["anuj","peggy"]
graph["alice"]=["peggy"]
graph["claire"]=["thom","jonny"]
graph["anuj"]=[]
graph["peggy"]=[]
graph["thom"]=[]
graph["jonny"]=[]
search_queue=deque()
search_queue+=graph["you"]
searched=[] #这个数组用于检测记录过的人
while search_queue: #只要队列不为空
person=search_queue.popleft() #就取出其中的第一个人
if not person in searched: #仅当这个人没检查过才检查
if person_is_seller(person): #检查这个人是否是芒果销售商
print person+"is a mango seller!";#是芒果销售商
return True;
else:
searched.append(person) #标记检查过的人
search_queue+=graph[person] #不是芒果销售商。将这个人的朋友都加入搜索列表
return False #如果到了这里,就说明队伍中没有芒果销售商
test_2()3.狄克斯特拉算法
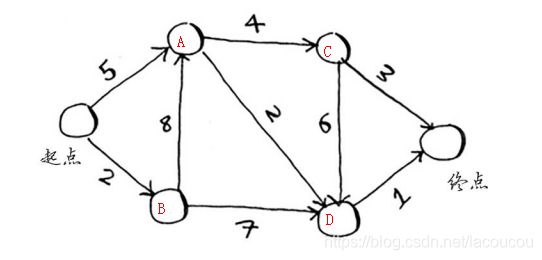
下图中,从起点到终点的最短路径的总权重分别是多少?
processed=[] #这个数组用于检测记录过的人
def find_lowest_cost_node(costs):
lowest_cost=float("inf")
lowest_cost_node=None
for node in costs:
cost=costs[node]
if costnew_cost:
costs[n]=new_cost
parents[n]=node
processed.append(node)
node=find_lowest_cost_node(costs)
print "graph",graph
print "costs",costs
print "parents",parents
test_3() //开始
graph {'a': {'c': 4, 'd': 2}, 'c': {'fin': 3, 'd': 6}, 'b': {'a': 8, 'd': 7}, 'd': {'fin': 1}, 'start': {'a': 5, 'b': 2}, 'fin': {}}
costs {'a': 5, 'c': inf, 'b': 2, 'fin': inf, 'd': inf}
parents {'a': 'start', 'c': None, 'b': 'start', 'fin': None, 'd': None}//运行结束
graph {'a': {'c': 4, 'd': 2}, 'c': {'fin': 3, 'd': 6}, 'b': {'a': 8, 'd': 7}, 'd': {'fin': 1}, 'start': {'a': 5, 'b': 2}, 'fin': {}}
costs {'a': 5, 'c': 9, 'b': 2, 'fin': 8, 'd': 7}
parents {'a': 'start', 'c': 'a', 'b': 'start', 'fin': 'd', 'd': 'a'}path= fin -> d -> a -> start
cost: 8
4.贪婪算法 广播台
states_needed=set(["mt","wa","or","id","nv","ut","ca","az"])
stations={}
stations["kone"]=set(["id","nv","ut"])
stations["ktwo"]=set(["wa","id","mt"])
stations["kthree"]=set(["or","nv","ca"])
stations["kfour"]=set(["nv","ut"])
stations["kfive"]=set(["ca","az"])
final_stations=set()
best_station=None
states_covered=set()
#第一步,找到最好的
for station,states_for_station in stations.items():
covered=states_needed & states_for_station
#print station
if len(covered) > len(states_covered):
best_station=station
states_covered=covered
#print best_station,states_covered
#字典是无序的,遍历顺序为 kfive ktwo kthree kone kfour
#所以结果是:ktwo set(['mt', 'id', 'wa'])
print "best_station=",best_station,"states_covered=",states_covered
#第二部,找到全覆盖的
final_stations.add(best_station)
states_needed-=states_covered
while states_needed:
best_station=None
states_covered=set()
for station,states in stations.items():
covered=states_needed & states
if len(covered) > len(states_covered):
best_station=station
states_covered=covered
states_needed-=states_covered
final_stations.add(best_station)
print final_stations
5.动态规划
python二维数组:参考https://www.cnblogs.com/woshare/p/5823303.html
方法1 直接定义
matrix = [[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]]
方法2 间接定义
matrix = [[0 for i in range(3)] for i in range(3)]
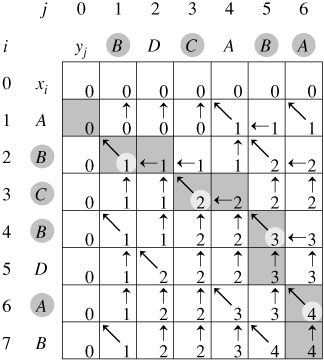
最长公共子序列:
https://www.cnblogs.com/Lee-yl/p/9975827.html
创建 DP数组C[i][j]:表示子字符串L【:i】和子字符串S【:j】的最长公共子序列个数。
def LCS(L,S):
if not L or not S:
return ""
dp = [[0] * (len(L)+1) for i in range(len(S)+1)]
for i in range(len(S)+1):
for j in range(len(L)+1):
if i == 0 or j == 0:
dp[i][j] = 0
else:
if L[j-1] == S[i-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1])
return dp[-1][-1]
L = 'BDCABA'
S = 'ABCBDAB'
LCS(L,S)
def LCS(L,S):
if not L or not S:
return ""
res = ''
dp = [[0] * (len(L)+1) for i in range(len(S)+1)]
flag = [['left'] * (len(L)+1) for i in range(len(S)+1)]
for i in range(len(S)+1):
for j in range(len(L)+1):
if i == 0 or j == 0:
dp[i][j] = 0
flag [i][j] = '0'
else:
if L[j-1] == S[i-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
flag[i][j] = 'ok'
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1])
flag[i][j] = 'up' if dp[i][j] == dp[i-1][j] else 'left'
return dp[-1][-1],flag
def printres(flag,L,S):
m = len(flag)
n = len(flag[0])
res = ''
i , j = m-1 , n-1
while i > 0 and j > 0:
if flag[i][j] == 'ok':
res += L[j-1]
i -= 1
j -= 1
elif flag[i][j] == 'left':
j -= 1
elif flag[i][j] == 'up':
i -= 1
return res[::-1]
L = 'BDCABA'
S = 'ABCBDAB'
num,flag = LCS(L,S)
res = printres(flag,L,S)