python--Matplotlib学习总结
目录
一、Matplotlib常见用法
1. 绘制简单图像
2. 添加常用元素
3. 绘制多曲线
4. 认识figure(画布)
5. 绘制多图像
6. 绘制常用图
7. 参数简写
7.1 c代表color(颜色)
7.2 ls代表linestyle(线条样式)
7.3 marker(记号样式)
7.4 其他缩写
二、Matplotlib进阶用法
1. 添加文本注释
2. 绘制3D图像
3. 导入图像(加州房价)
4. 绘制等高线
绘制动画
Matplotlib 是建立在NumPy基础之上的Python绘图库,是在机器学习中用于数据可视化的工具
Matplotlib具有很强的工具属性,也就是说它只是为我所用的,我们不必花太多的精力去精进它。
我们只需要知道它可以做哪些事,可以绘制哪些图形,有一个印象就足够了。
我们在实际使用中用什么拿什么,我们用到了自然就熟练了。
一、Matplotlib常见用法
1. 绘制简单图像
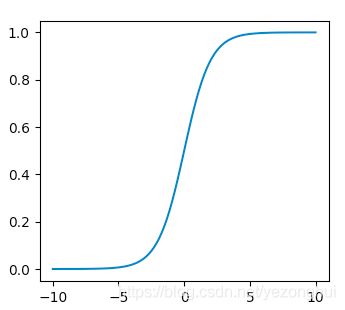
我们以机器学习中最常见的激活函数sigmoid举例,我们来绘制它。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(-10,10,1000)
y = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()
其中sigmoid的公式为:
plot()方法展示变量间的趋势,show()方法展示图像。
我们得到如图所示图像:
2. 添加常用元素
我们添加一些参考元素,各函数的解释我在代码中进行了详细的标注。
x = np.linspace(-10,10,1000)
#写入公式
y = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
#x轴范围限制
plt.xlim(-5,5)
#y轴范围限制
plt.ylim(-0.2,1.2)
#x轴添加标签
plt.xlabel("X axis")
#y轴添加标签
plt.ylabel("Y axis")
#标题
plt.title("sigmoid function")
#设置网格,途中红色虚线
plt.grid(linestyle=":", color ="red")
#设置水平参考线
plt.axhline(y=0.5, color="green", linestyle="--", linewidth=2)
#设置垂直参考线
plt.axvline(x=0.0, color="green", linestyle="--", linewidth=2)
#绘制曲线
plt.plot(x,y)
#保存图像
plt.savefig("./sigmoid.png",format='png', dpi=300)
以上代码包含了限制X、Y轴范围,添加标题和标签,设置网格,添加参考线,保存图像等内容。
绘制图像如下:
3. 绘制多曲线
#生成均匀分布的1000个数值
x = np.linspace(-10,10,1000)
#写入sigmoid公式
y = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
z = x**2
plt.xlim(-2,2)
plt.ylim(0,1)
#绘制sigmoid
plt.plot(x,y,color='#E0BF1D',linestyle='-', label ="sigmoid")
#绘制y=x*x
plt.plot(x,z,color='purple',linestyle='-.', label = "y=x*x")
#绘制legend,即下图角落的图例
plt.legend(loc="upper left")
#展示
plt.show()
绘制多图像直接调用多个plot()即可。
注意:如果不调用legend()方法,不会绘制左上角的legend(图例)。其中color参数支持hex表示。
4. 认识figure(画布)
首先我们认识figure(画布),比如legend我们在上文中提到过,是线条标签的展示。
grid所圈住的虚线是网格参考线。Title/x axislabel等文本标签。这张图有助于我们对figure有一个直观的理解。
5. 绘制多图像
一个figure是可以对应多个plot的,现在我们试着在一个figure上绘制多图像。
x = np.linspace(-2*np.pi, 2*np.pi, 400)
y = np.sin(x**2)
z = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
a = np.random.randint(0,100,400)
b = np.maximum(x,0.1*x)
#创建两行两列的子图像
fig, ax_list = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2)
# 'r-'其中r表示color=red,-表示linestyle='-'
ax_list[0][0].plot(x,y,'r-')
ax_list[0][0].title.set_text('sin')
ax_list[0][1].scatter(x,a,s=1)
ax_list[0][1].title.set_text('scatter')
ax_list[1][0].plot(x,b,'b-.')
ax_list[1][0].title.set_text('leaky relu')
ax_list[1][1].plot(x,z,'g')
ax_list[1][1].title.set_text('sigmoid')
#调整子图像的布局
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.9,hspace=0.5)
fig.suptitle("Figure graphs",fontsize=16)
plt.show()
其中,最关键的是subplots方法,生成2行2列的子图像,然后我们调用ax_list中的各绘图方法。
其中'r-','b-.'参数为绘图的缩写写法,本文后续参数缩写段落会单独讲解。
6. 绘制常用图
我们常用图来表示数据之间的关系,常见的图包括直方图、柱状图、饼图、散点图等等。
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# import numpy as np
# x = np.linspace(-10,10,100)
# y = 1 / (1+np.exp(-x))
# plt.plot(x,y);
# plt.show()
#添加一些参考元素
# import numpy as np
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# x = np.linspace(-10,10,1000)
# y = 1/ (1+np.exp(-x))
# #x轴范围限制
# plt.xlim(-5,5)
# #y轴范围限制
# plt.ylim(-0.2,1.2)
# # x轴添加标签
# plt.xlabel("X axis")
# #y轴添加标签
# plt.ylabel("Y axis")
# #标题
# plt.title("Sigmoid function")
#
# # 设置网格,途中红色虚线
# plt.grid(linestyle = ":",color = "red")
#
# # 设置水平参考线
# plt.axhline(y=0.5,color="green",linestyle="--",linewidth=2)
# #设置垂直参考线
# plt.axvline(x =0.0,color="green",linestyle="--",linewidth=2)
# #绘制曲线
# plt.plot(x,y)
# plt.show()
# #保存图像
# # plt.savefig("./sigmod.png",format="png",dpi=300)
#
#绘制多曲线
# import numpy as np
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# #生成均匀分布的1000个数值
# x = np.linspace(-10,10,1000)
# y = 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
# z = x**2;
# plt.xlim(-2,2)
# plt.ylim(0,1)
# #绘制sigmod
# plt.plot(x,y,color="red",linestyle="-",label="sigmod")
# #绘制y = x**2
# plt.plot(x,z,color="purple",linestyle="-.",label="y=x**2")
# plt.legend(loc="upper left") #左上方角落的图例。
# plt.show()
# 绘制多图像
#一个figure是可以对应多个plot的
# import numpy as np
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# x = np.linspace(-2*np.pi,2*np.pi,400)
# y = np.sin(x**2)
# z = 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
# a = np.random.randint(0,100,400)
# b = np.maximum(x,0.1*x)
# #创建两行两列的子对象
# fig ,ax_list = plt.subplots(nrows =2,ncols =2)
# # r-中r表示color = red. - 表示linestyle ='-'
# ax_list[0][0].plot(x,y,"r-")
# ax_list[0][0].title.set_text("scatter")
#
# ax_list[0][1].scatter(x,a,s=1)
# ax_list[0][1].title.set_text('scatter')
#
# ax_list[1][0].plot(x,b,'b-.')
# ax_list[1][0].title.set_text('leaky relu')
#
# ax_list[1][1].plot(x,z,'g')
# ax_list[1][1].title.set_text('sigmoid')
#
# fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.9,hspace=0.5)
# fig.suptitle("Figure graphs",fontsize = 16)
# fig.show()
# plt.show()
#
#
# 绘制常用图
#直方图,柱状图,饼图,散点图等
# 使绘图支持中文
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Arial Unicode MS']
#plt.rcParams["font.sans_serif"]=["Microsoft YaHei"]
#创建两行两列的子对象
fig,[[ax1,ax2],[ax3,ax4],[ax5,ax6]]=plt.subplots(nrows=3,ncols=2,figsize=(8,8))
#绘制柱状图
value = (2,3,4,1,2)
index = np.arange(5)
ax1.bar(index,value,alpha = 0.4,color="b")
ax1.set_xlabel("Group")
ax1.set_ylabel("Scores")
ax1.set_title("柱状图")
#绘制直方图
h = 100 + 15*np.random.randn(437)
ax2.hist(h,bins=50)
ax2.title.set_text("直方图")
#绘制饼图pie
labels = "Frogs","CAT","yongji","Logs"
sizes =[15,30,45,10]
explode =(0,0.1,0,0)
ax3.pie(sizes,explode = explode,labels=labels,autopct='%1.1f%%',
shadow = True,startangle = 90)
ax3.axis("equal")
ax3.title.set_text("饼图")
# 绘制棉棒图
x = np.linspace(0.5,2*np.pi,20)
y = np.random.randn(20)
ax4.stem(x,y,linefmt="-",markerfmt ="o",basefmt='-')
ax4.title.set_text("棉棒图")
#绘制气泡图scatter
a = np.random.randn(100)
b = np.random.randn(100)
ax5.scatter(a,b,s=np.power(2*a+4*b,2),c = np.random.rand(100),cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu,marker='o')
#绘制极线图polar
fig.delaxes(ax6)
ax6 = fig.add_subplot(236,projection='polar')
r = np.arange(0,2,0.01)
theta = 2*np.pi*r
ax6.plot(theta,r)
ax6.set_rmax(2)
ax6.set_rticks([0.5,1,1.5,2])
ax6.set_rlabel_position(-22.5)
ax6.grid(True)
#调整子图像的布局
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=1,hspace=1.2)
fig.suptitle("图形绘制", fontsize=16)
plt.show()
绘制图像如下:
7. 参数简写
因为matplotlib支持参数的缩写,所以我认为有必要单独拿出来讲一讲各参数缩写的表示。
x = np.linspace(-10,10,20)
y = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
plt.plot(x,y,c='k',ls='-',lw=5, label ="sigmoid", marker="o", ms=15, mfc='r')
plt.legend()
plt.show()绘制图像如下:
7.1 c代表color(颜色)
| 字符 | 颜色 |
|---|---|
| ‘b’ | blue |
| ‘g’ | green |
| ‘r’ | red |
| ‘c’ | cyan |
| ‘m’ | magenta |
| ‘y’ | yellow |
| ‘k’ | black |
| ‘w’ | white |
7.2 ls代表linestyle(线条样式)
| 字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| '-' | solid line style |
| '--' | dashed line style |
| '-.' | dash-dot line style |
| ':' | dotted line style |
| '.' | point marker |
| ',' | pixel marker |
| 'o' | circle marker |
| 'v' | triangle_down marker |
| '^' | triangle_up marker |
| '<' | triangle_left marker |
| '>' | triangle_right marker |
| '1' | tri_down marker |
| '2' | tri_up marker |
| '3' | tri_left marker |
| '4' | tri_right marker |
| 's' | square marker |
| 'p' | pentagon marker |
| '*' | star marker |
| 'h' | hexagon1 marker |
| 'H' | hexagon2 marker |
| '+' | plus marker |
| 'x' | x marker |
| 'D' | diamond marker |
| 'd' | thin_diamond marker |
| '|' | vline marker |
| '_' | hline marker |
7.3 marker(记号样式)
7.4 其他缩写
-
lw代表linewidth(线条宽度),如:lw=2.5 -
ms代表markersize(记号尺寸),如:ms=5 -
mfc代表markerfacecolor(记号颜色),如:mfc='red'
二、Matplotlib进阶用法
1. 添加文本注释
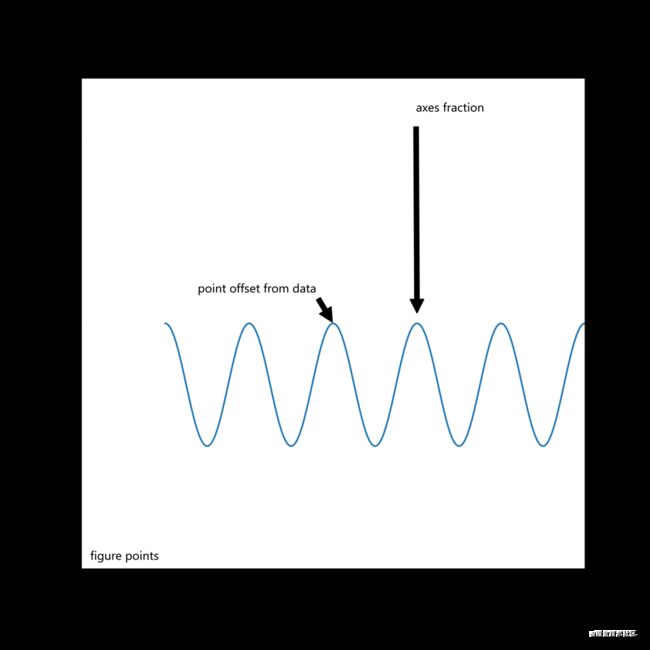
我们可以在画布(figure)上添加文本、箭头等标注,来让图像表述更清晰准确。
我们通过调用annotate方法来绘制注释。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
t = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.01)
s = np.cos(2*np.pi*t)
# 绘制一条曲线
line, = ax.plot(t, s)
#添加注释
ax.annotate('figure pixels',
xy=(10, 10), xycoords='figure pixels')
ax.annotate('figure points',
xy=(80, 80), xycoords='figure points')
ax.annotate('figure fraction',
xy=(.025, .975), xycoords='figure fraction',
horizontalalignment='left', verticalalignment='top',
fontsize=20)
#第一个箭头
ax.annotate('point offset from data',
xy=(2, 1), xycoords='data',
xytext=(-15, 25), textcoords='offset points',
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),
horizontalalignment='right', verticalalignment='bottom')
#第二个箭头
ax.annotate('axes fraction',
xy=(3, 1), xycoords='data',
xytext=(0.8, 0.95), textcoords='axes fraction',
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),
horizontalalignment='right', verticalalignment='top')
ax.set(xlim=(-1, 5), ylim=(-3, 5))
绘制图像如下:
2. 绘制3D图像
绘制3D图像需要导入Axes3D库。
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from matplotlib.ticker import LinearLocator, FormatStrFormatter
import numpy as np
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
# Make data.
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R)
# Plot the surface.
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap=cm.coolwarm,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
# Customize the z axis.
ax.set_zlim(-1.01, 1.01)
ax.zaxis.set_major_locator(LinearLocator(10))
ax.zaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%.02f'))
# Add a color bar which maps values to colors.
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
其中cmap意为colormap,用来绘制颜色分布、渐变色等。cmap通常配合colorbar使用,来绘制图像的颜色栏。
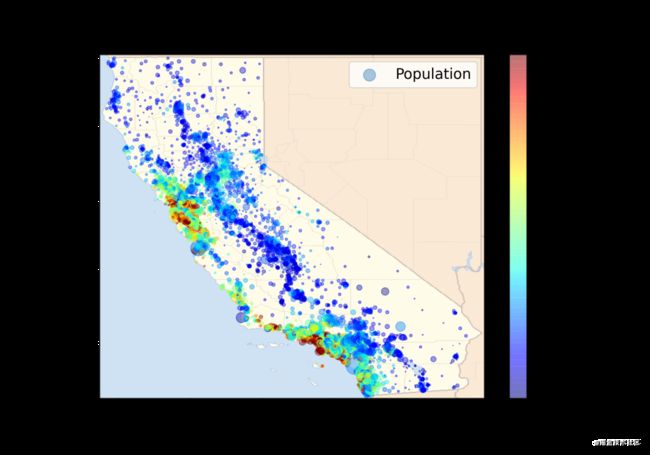
3. 导入图像(加州房价)
引入mpimg库,来导入图像。
我们以美国加州房价数据为例,导入加州房价数据绘制散点图,同时导入加州地图图片,查看地图经纬度对应房价的数据。同时使用颜色栏,绘制热度图像。
代码如下:
import os
import urllib
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
#加州房价数据(大家不用在意域名)
housing = pd.read_csv("http://blog.caiyongji.com/assets/housing.csv")
#加州地图
url = "http://blog.caiyongji.com/assets/california.png"
urllib.request.urlretrieve("http://blog.caiyongji.com/assets/california.png", os.path.join("./", "california.png"))
california_img=mpimg.imread(os.path.join("./", "california.png"))
#根据经纬度绘制房价散点图
ax = housing.plot(kind="scatter", x="longitude", y="latitude", figsize=(10,7),
s=housing['population']/100, label="Population",
c="median_house_value", cmap=plt.get_cmap("jet"),
colorbar=False, alpha=0.4,
)
plt.imshow(california_img, extent=[-124.55, -113.80, 32.45, 42.05], alpha=0.5,
cmap=plt.get_cmap("jet"))
plt.ylabel("Latitude", fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel("Longitude", fontsize=14)
prices = housing["median_house_value"]
tick_values = np.linspace(prices.min(), prices.max(), 11)
#颜色栏,热度地图
cbar = plt.colorbar(ticks=tick_values/prices.max())
cbar.ax.set_yticklabels(["$%dk"%(round(v/1000)) for v in tick_values], fontsize=14)
cbar.set_label('Median House Value', fontsize=16)
v
plt.legend(fontsize=16)
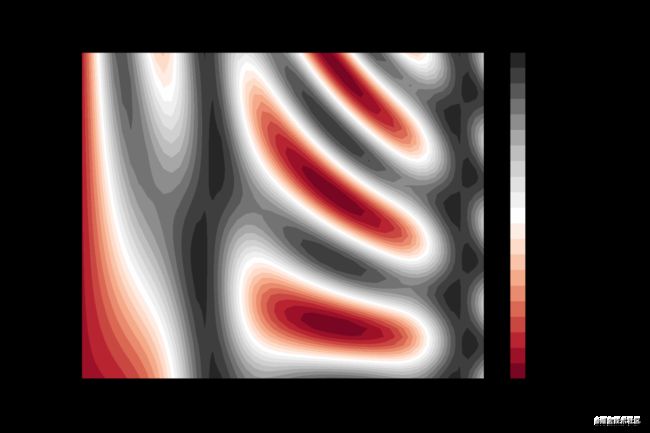
4. 绘制等高线
等高线对于在二维空间内绘制三维图像很有用。
def f(x, y):
return np.sin(x) ** 10 + np.cos(10 + y * x) * np.cos(x)
x = np.linspace(0, 5, 50)
y = np.linspace(0, 5, 40)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
Z = f(X, Y)
plt.contourf(X, Y, Z, 20, cmap='RdGy')
plt.colorbar()
绘制图像如下:
黑色地方是峰,红色地方是谷。
绘制动画
绘制动画需要引入animation库,通过调用FuncAnimation方法来实现绘制动画。
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import animation
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(xlim=(0, 2), ylim=(-2, 2))
line, = ax.plot([], [], lw=2)
# 初始化方法
def init():
line.set_data([], [])
return line,
# 数据更新方法,周期性调用
def animate(i):
x = np.linspace(0, 2, 1000)
y = np.sin(2 * np.pi * (x - 0.01 * i))
line.set_data(x, y)
return line,
#绘制动画,frames帧数,interval周期行调用animate方法
anim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init,
frames=200, interval=20, blit=True)
anim.save('ccccc.gif', fps=30)
plt.show()
上述代码中anim.save()方法支持保存mp4格式文件。
绘制动图如下: