简单的A*算法寻路的 lua实现
简单的A*算法寻路实现
- 基本描述
-
- 实现思路
- 参考图
- 代码实现
- 结果
基本描述
常用的路径寻找算法,确定由计算机控制的物体从A到B的最佳路径。实际使用中有很多可以优化可以做,同时也有很多针对性的处理需要做,这里只是做了一个基础版的demo。
实现思路
将地图划分成规则的格子,已知起始点(当前节点)和目标点,同时已知墙节点列表
定义一个开放列表和一个闭合列表
确定 当前节点 相邻的所有 非墙体节点,将它们加入到一个 开放列表 ;设定当前节点作为它们的 父节点
将当前节点从开放列表移除,添加到闭合列表
至此,完成了第一次操作
接下来开始循环
便利所有开放列表中的所有节点,找到参考值 F值(G值+H值)最小的节点
从开放列表中删除该节点,将其添加到闭合列表中,设为当前节点
检索当前节点的所有可用的相邻节点,如果节点在开放列表中,检测G值,如果比开放列表中节点的G值小,就改变它的父节点
直到当前节点为目标节点就结束循环
遍历闭合列表,从目标节点开始,父节点组成的链表就是我们要找的路径
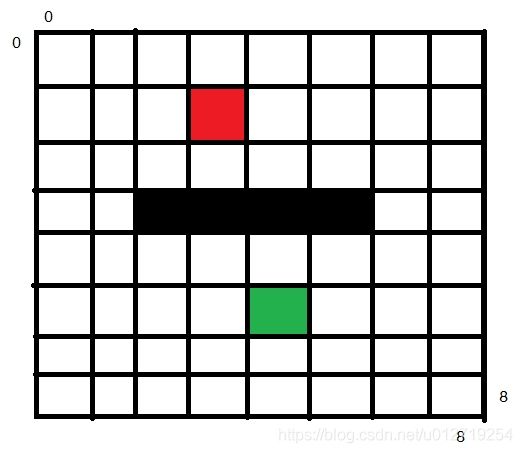
参考图
代码实现
local world = {
}--地图格子列表
local open = {
}--开放列表
local closed = {
}--闭合列表
local path = {
}--路径列表
local maxX = 8--地图最大范围
local maxY = 8--地图最大范围
local closedIndex = 0--闭合列表的下标
local targetX = 0--目标节点的坐标
local targetY = 0--目标节点的坐标
local maxCheckTime = 1000--最大检索步数
-------------------------
--先确定所有的区域格子
for i=1,8 do
world[i] = {
}
for j=1,8 do
--定义区域
world[i][j] = 0
end
end
--不可行走区域
world[1][4] = 1
world[2][4] = 1
world[3][4] = 1
world[4][4] = 1
world[5][4] = 1
world[6][4] = 1
world[7][4] = 1
-------------------------
function DefineStart( x,y )
--定义起点信息
open[1] = {
}
open[1].x = x
open[1].y = y
open[1].parent = 0
open[1].g = 0--从初始节点到当前节点的移动距离
open[1].h = 0--从这个节点到目标节点的预测距离
end
function FindLowestF( nodeTable )
--从开放列表里寻找F(参考值)最小的节点
local count = #(nodeTable)
local minF = 1000000
local minFIndex = 0
if count > 0 then
for index = 1,count do
local curF = nodeTable[index].g + nodeTable[index].h
if curF <= minF then
minF = curF
minFIndex = index
end
end
end
return minFIndex
end
function FindH( curX,curY,tarX,tarY )
--计算H值(两坐标之间的 曼哈顿距离 )
return 10*(math.abs(curX-tarX) + math.abs(curY-tarY))
end
function FindG( nodeTable,node )
--G的计算是将父节点的G值与当前节点到父节点的距离相加,这里只做简单计算,水平或者垂直相邻的话单位距离为10,斜线的话单位距离为14
--从初始节点到当前节点的移动距离
local parentG = closed[nodeTable[node].parent].g
local curValue = 0
if (nodeTable[node].x == closed[nodeTable[node].parent].x) or (nodeTable[node].y == closed[nodeTable[node].parent].y) then
curValue = 10
else
curValue = 14
end
return parentG + curValue
end
function NewOpenEntry( newX,newY )
--添加节点到开放列表
local myIndex = #(open) + 1
open[myIndex] = {
}
open[myIndex].x = newX
open[myIndex].y = newY
open[myIndex].parent = closedIndex
open[myIndex].g = FindG(open,myIndex)
open[myIndex].h = FindH(open[myIndex].x,open[myIndex].y,targetX,targetY)
end
function AlreadyExists( newX,newY )
--检测节点是否存在于开放列表
for k,v in pairs(open) do
if v.x == newX and v.y == newY then
return k
end
end
return -1
end
function ProcessNode( newX,newY )
--对节点进行检查
targetFound = false
exists = AlreadyExists(newX,newY)--检测节点是否存在于开放列表
if exists == -1 then
--不在开放列表中
if (newX == targetX) and (newY == targetY) then
--找到目标点
targetFound = true
else
--填入开放列表
NewOpenEntry(newX,newY)
end
else
--在开放列表中,那么重新定义父节点
existingG = open[exists].g
curValue = 0
parentG = closed[closedIndex].g
if (open[exists].x == closed[closedIndex].X) or open[exists].y == closed[closedIndex].y then
curValue = 10
else
curValue = 14
end
newG = parentG + curValue
if newG < existingG then
open[exists].parent = closedIndex
end
end
return targetFound
end
function FindPath( )
--针对当前位置进行检索周边处理
targetFound = false
local openIndex = FindLowestF(open)
closedIndex = #(closed) + 1
closed[closedIndex] = {
}
closed[closedIndex].x = open[openIndex].x
closed[closedIndex].y = open[openIndex].y
closed[closedIndex].parent = open[openIndex].parent
closed[closedIndex].g = open[openIndex].g
closed[closedIndex].h = open[openIndex].h
local curX = closed[closedIndex].x
local curY = closed[closedIndex].y
local math_list = {
--遍历周边8个格子,试图寻找目标节点
[1] = {
-1,-1},
[2] = {
-1,0},
[3] = {
-1,1},
[4] = {
0,-1},
[5] = {
0,1},
[6] = {
1,-1},
[7] = {
1,0},
[8] = {
1,1},
}
for k,v in pairs(math_list) do
if not targetFound then
myX = curX + v[1]
myY = curY + v[2]
if (myX > 0) and (myY > 0) and world[myX] and world[myX][myY] and (world[myX][myY])~=1 then
ProcessNode(myX,myY)
end
else
break
end
end
table.remove(open,openIndex)
return targetFound
end
function BuildPath( )
--节点检索结束后,构建路径列表
count = 1
path[count] = {
}
path[count].x = targetX
path[count].y = targetY
count = count + 1
path[count] = {
}
pathIndex = #(closed)
path[count].x = closed[pathIndex].x
path[count].y = closed[pathIndex].y
newPathIndex = closed[pathIndex].parent
while newPathIndex ~= 1 do
count = count + 1
path[count] = {
}
path[count].x = closed[newPathIndex].x
path[count].y = closed[newPathIndex].y
oldPathIndex = newPathIndex
newPathIndex = closed[oldPathIndex].parent
end
path = ReverseTable(path)--得到倒序表需要反序
return path
end
function ReverseTable( data )
--表反序
local temp = {
}
local endCount = #(data)
for index = 1,#(data) do
temp[index] = data[endCount]
endCount = endCount - 1
end
return temp
end
function PlaceTarget( myX,myY )
--选中目标点后执行
DefineStart(4,2)
--确定目标点
targetX = myX
targetY = myY
if (myX < maxX-1) and (myX > 1) and (myY < maxY-1) and (myY > 1) then
if world[myX][myY] ~= 1 then
local time = 0
repeat
targetFound = FindPath()
time = time + 1
until (targetFound or time >= maxCheckTime)
--获得路线图
if targetFound then
local path = BuildPath()
-- PrintTable(path)
else
print("没有找到路径")
end
--得到路径后的操作
-- DoSomeThing(path)
end
end
end
--执行函数
PlaceTarget(5,6)
结果
上面代码执行后得到的路径
{
[1] = {5,3},
[2] = {6,3},
[3] = {7,3},
[4] = {8,4},
[5] = {7,5},
[6] = {6,6},
[7] = {5,6},
}