操作系统原理实验 :C语言创建进程,操作文件修改文本文件某一行指定位置文字
本文章仅供本人作为学习笔记,也很荣幸能给大家参考学习
问题实现:
在Windows环境下,利用高级语言编程环境(限定为VS环境或VC环境)调用相关的系统调用(CreateProccess,即系统API)实现一个包括“进程创建,文件读写”功能的应用程序。有一个文本文件CommandList.txt,第一行是说明性文字:本文件最后一次打开和运行日期是20200224。第二行开始每行是一个可执行程序的名称(含路径)。编写一个应用程序能打开该文件,顺序执行其中的每个程序,并将文件第一行中的日期更新为当前日期。
例如:运行程序前: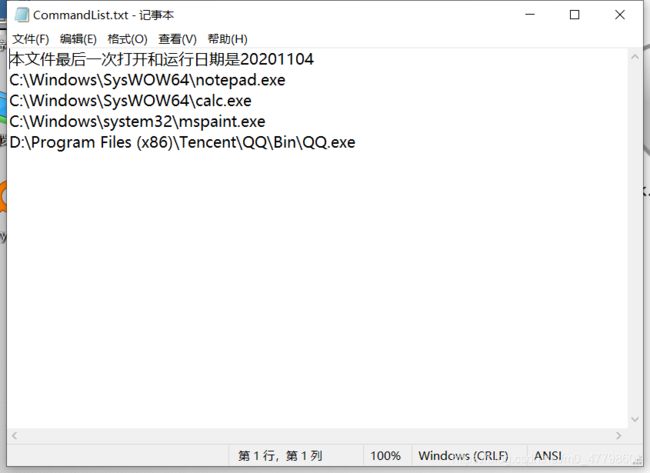
运行程序后: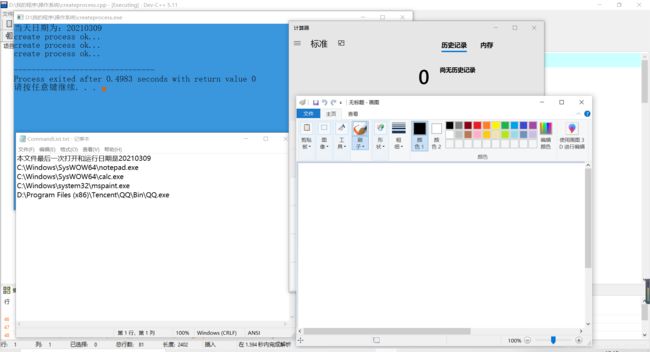
可以看到记事本文件第一行日期已经自动更新了
重点:获取系统日期,并将该日期先转换为字符串,再写入CommandList.txt文件,更新日期
下面为获取系统日期代码:
//获取系统日期
time_t timep;
struct tm *p;
time (&timep);
p=gmtime(&timep);
int number1=1900+p->tm_year;//年份
int number2=1+p->tm_mon;//月份
int number3=p->tm_mday ;
将三个整数转换为字符串并合并在一起:
//将日期转换为字符串开始代码
char string1[4] = {0};
char string2[4] = {0};
char string3[4] = {0};
itoa(number1,string1,10); //itoa:将整数转换为字符串
itoa(number2,string2,10);
itoa(number3,string3,10);
if(number2<10){
strcat(string1,"0");//例:将3月改为03月
}
strcat(string1,string2);//连接字符串
if(number3<10){
strcat(string1,"0");
}
strcat(string1,string3); //将日期转换为字符串截至代码
printf("当天日期为:");
puts(string1);
操作CommandList.txt文件:
//文件操作开始代码
FILE *fp;
fp=fopen("CommandList.txt","rt+");
char *pt;
fseek(fp,30L,0);//定位第一行文字的日期位置 ,30L表示日期前面15个汉字占用的字节数
pt=string1; //从第16个文字开始修改日期为系统日期(修改字符串)
fputs(pt,fp); //写入文件
接下来是完整程序代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
//获取系统日期
time_t timep;
struct tm *p;
time (&timep);
p=gmtime(&timep);
int number1=1900+p->tm_year;//年份
int number2=1+p->tm_mon;//月份
int number3=p->tm_mday ;//获取日期截至代码
//将日期转换为字符串开始代码
char string1[4] = {0};
char string2[4] = {0};
char string3[4] = {0};
itoa(number1,string1,10); //itoa:将整数转换为字符串
itoa(number2,string2,10);
itoa(number3,string3,10);
if(number2<10){
strcat(string1,"0");//例:将3月改为03月
}
strcat(string1,string2);//连接字符串
if(number3<10){
strcat(string1,"0");
}
strcat(string1,string3); //将日期转换为字符串截至代码
printf("当天日期为:");
puts(string1);
//文件操作开始代码
FILE *fp;
fp=fopen("CommandList.txt","rt+");
char *pt;
fseek(fp,30L,0);//定位第一行文字的日期位置 ,30L表示日期前面15个汉字占用的字节数
pt=string1; //从第16个文字开始修改日期为系统日期(修改字符串)
fputs(pt,fp); //写入文件
//创建进程模块
PROCESS_INFORMATION processInfo;
STARTUPINFOA startupInfo;
ZeroMemory(&processInfo, sizeof(processInfo));
ZeroMemory(&startupInfo, sizeof(startupInfo));
startupInfo.cb = sizeof(startupInfo);
char *zw="C:\\Windows\\SysWOW64\\notepad.exe";
char *zw1="C:\\Windows\\SysWOW64\\calc.exe";
char *zw2="C:\\Windows\\system32\\mspaint.exe";
//char *zw3="D:\\Program Files (x86)\\Tencent\\QQ\\Bin\\QQ.exe";
char *commandtext=" CommandList.txt";
BOOL ret = CreateProcess(zw,commandtext,NULL, NULL, false,
0, NULL, NULL, &startupInfo, &processInfo);
BOOL ret1 = CreateProcess(zw1,NULL,NULL, NULL, false,
0, NULL, NULL, &startupInfo, &processInfo);
BOOL ret2 = CreateProcess(zw2,NULL,NULL, NULL, false,
0, NULL, NULL, &startupInfo, &processInfo);
//BOOL ret3 = CreateProcess(zw3,NULL,NULL, NULL, false,
//0, NULL, NULL, &startupInfo, &processInfo);
//判断进程是否创建成功
if(ret)
printf("create process ok...\n");
else
{
printf("create process failed...\n");
printf("error is %d", GetLastError());
}
if(ret1)
printf("create process ok...\n");
else
{
printf("create process failed...\n");
printf("error is %d", GetLastError());
}
if(ret2)
printf("create process ok...\n");
else
{
printf("create process failed...\n");
printf("error is %d", GetLastError());
}
return 0;
}
该文章仅供学习参考,如有部分不懂,可自行去查阅资料