边框回归的损失函数_目标检测回归损失函数——IOU、GIOU、DIOU、CIOU
一、IOU Loss
上一篇文章提到L1,L2及其变种只将Bounding box的四个角点分别求loss然后相加,没有引入box四个顶点之间的相关性并且模型在训练过程中更偏向于尺寸更大的物体。在此基础上旷视在2016文章《UnitBox: An Advanced Object Detection Network》中提出了IOU Loss将4个点构成的box看成一个整体做回归。
文章链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.01471.pdf
1. 函数特性
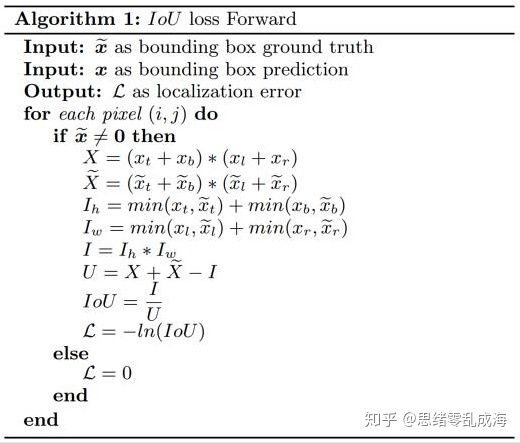
IOU Loss的定义是先求出预测框和真实框之间的交集和并集之比,再求负对数,但是在实际使用中我们常常将IOU Loss写成1-IOU。如果两个框重合则交并比等于1,Loss为0说明重合度非常高。
IOU满足非负性、同一性、对称性、三角不等性,相比于L1/L2等损失函数还具有尺度不变性,不论box的尺度大小,输出的iou损失总是在0-1之间。所以能够较好的反映预测框与真实框的检测效果。
伪代码如下:
其中,
box位置的修正是通过对loss的反向传播迭代计算的。关于IOU Loss的反向传播具体推到过程可以移步到论文中,这里摘出结论部分如下:
其中:
从这个公式可以看出惩罚来自两个部分,预测框四个变量和预测框和真实框相交区域:
1 .损失函数和
2 .同时损失函数和
根据求导公式为了减小IOU Loss,会尽可能增大相交面积同时预测更小的框。
Python实现如下:
def calculate_iou(box_1, box_2):
"""
calculate iou
:param box_1: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:param box_2: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:return: value of iou
"""
# calculate area of each box
area_1 = (box_1[2] - box_1[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
area_2 = (box_2[2] - box_2[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
# find the edge of intersect box
top = max(box_1[0], box_2[0])
left = max(box_1[1], box_2[1])
bottom = min(box_1[3], box_2[3])
right = min(box_1[2], box_2[2])
# if there is an intersect area
if left >= right or top >= bottom:
return 0
# calculate the intersect area
area_intersection = (right - left) * (bottom - top)
# calculate the union area
area_union = area_1 + area_2 - area_intersection
iou = float(area_intersection) / area_union
return iou2. 存在的问题
IOU Loss虽然解决了Smooth L1系列变量相互独立和不具有尺度不变性的两大问题,但是它也存在两个问题:
- 预测框和真实框不相交时,不能反映出两个框的距离的远近。根据IOU定义loss等于0,没有梯度的回传无法进一步学习训练。
- 预测框和真实框无法反映重合度大小。借用一张图来说,三者具有相同的IOU,但是不能反映两个框是如何相交的,从直观上感觉第三种重合方式是最差的。
二、GIOU Loss
上面指出IOU Loss的两大缺点:无法优化两个框不相交的情况;无法反映两个框如何相交的。针对此类问题斯坦福学者在2019年的文章《Generalized Intersection over Union: A Metric and A Loss for Bounding Box Regression》中提出了GIOU Loss,在IOU的基础上引入了预测框和真实框的最小外接矩形。
文章链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.01471.pdf
1.函数特性
GIOU作为IOU的升级版,保持了 IOU 的主要性质并避免了 IOU 的缺点,首先计算预测框
伪代码如下:
从GIOU的原理可以看出:
-
与
类似采用距离度量损失函数,并且对尺度不敏感
-
,而
,所以
-
不仅关注重叠区域,还关注其他的非重合区域,能更好的反映两者的重合度
- 当预测框和真实框完全重合时,
- 当预测框和真实框不重合时,不重合度越高,GIOU越趋近于-1
- 特别是预测框和真实框不相交时,由于引入了预测框和真实框的最小外接矩形
最大化GIOU就是促使
最小两个框
和
不断靠近。
Python实现如下:
def calculate_giou(box_1, box_2):
"""
calculate giou
:param box_1: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:param box_2: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:return: value of giou
"""
# calculate area of each box
area_1 = (box_1[2] - box_1[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
area_2 = (box_2[2] - box_2[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
# calculate minimum external frame
area_c = (max(box_1[2], box_2[2]) - min(box_1[0], box_2[0])) * (max(box_1[3], box_2[3]) - min(box_1[1], box_2[1]))
# find the edge of intersect box
top = max(box_1[0], box_2[0])
left = max(box_1[1], box_2[1])
bottom = min(box_1[3], box_2[3])
right = min(box_1[2], box_2[2])
# calculate the intersect area
area_intersection = (right - left) * (bottom - top)
# calculate the union area
area_union = area_1 + area_2 - area_intersection
# calculate iou
iou = float(area_intersection) / area_union
# calculate giou(iou - (area_c - area_union)/area_c)
giou = iou - float((area_c - area_union)) / area_c
return giou2. 存在的问题
在预测框和真实框没有很好地对齐时,会导致最小外接框C的面积增大,从而使GIOU的值变小,而两个矩形框不重合时,也可以计算GIOU。GIOU Loss虽然解决了IOU的上述两个问题,但是当两个框属于包含关系时,借用下图来说:GIOU会退化成IOU,无法区分其相对位置关系。
由于GIOU仍然严重依赖IOU,因此在两个垂直方向,误差很大,基本很难收敛,这就是GIoU不稳定的原因。借用下图来说:红框内部分:C为两个框的最小外接矩形,此部分表征除去两个框的其余面积,预测框和真实框在相同距离的情况下,水平垂直方向时,此部分面积最小,对loss的贡献也就越小,从而导致在垂直水平方向上回归效果较差。
三、DIOU Loss
针对上述GIOU的两个问题(预测框和真实框是包含关系的情况或者处于水平/垂直方向上,GIOU损失几乎已退化为IOU损失,即
文章地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.08287.pdf
1. 函数特性
DIOU损失函数公式如下:
其中,
DIOU Loss的惩罚项能够直接最小化中心点间的距离,而GIOU Loss旨在减少外界包围框的面积,所以DIOU Loss具有以下特性:
- DIOU与IOU、GIOU一样具有尺度不变性;
- DIOU与GIOU一样在与目标框不重叠时,仍然可以为边界框提供移动方向;
- DIOU可以直接最小化两个目标框的距离,因此比GIOU Loss收敛快得多;
- DIOU在包含两个框水平/垂直方向上的情况回归很快,而GIOU几乎退化为IOU;
- 当预测框和真实框完全重合时,
;
- 当预测框和真实框不相交时,
;
Python实现如下:
def calculate_diou(box_1, box_2):
"""
calculate diou
:param box_1: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:param box_2: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:return: value of diou
"""
# calculate area of each box
area_1 = (box_1[2] - box_1[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
area_2 = (box_2[2] - box_2[0]) * (box_1[3] - box_1[1])
# calculate center point of each box
center_x1 = (box_1[2] - box_1[0]) / 2
center_y1 = (box_1[3] - box_1[1]) / 2
center_x2 = (box_2[2] - box_2[0]) / 2
center_y2 = (box_2[3] - box_2[1]) / 2
# calculate square of center point distance
p2 = (center_x2 - center_x1) ** 2 + (center_y2 - center_y1) ** 2
# calculate square of the diagonal length
width_c = max(box_1[2], box_2[2]) - min(box_1[0], box_2[0])
height_c = max(box_1[3], box_2[3]) - min(box_1[1], box_2[1])
c2 = width_c ** 2 + height_c ** 2
# find the edge of intersect box
top = max(box_1[0], box_2[0])
left = max(box_1[1], box_2[1])
bottom = min(box_1[3], box_2[3])
right = min(box_1[2], box_2[2])
# calculate the intersect area
area_intersection = (right - left) * (bottom - top)
# calculate the union area
area_union = area_1 + area_2 - area_intersection
# calculate iou
iou = float(area_intersection) / area_union
# calculate diou(iou - p2/c2)
diou = iou - float(p2) / c2
return diou2. 存在的问题
虽然DIOU能够直接最小化预测框和真实框的中心点距离加速收敛,但是Bounding box的回归还有一个重要的因素纵横比暂未考虑。
四、CIOU Loss
CIOU Loss 和 DIOU Loss出自于2020年同一篇文章,CIOU在DIOU的基础上将Bounding box的纵横比考虑进损失函数中,进一步提升了回归精度。
1. 函数特性
CIOU的惩罚项是在DIOU的惩罚项基础上加了一个影响因子
其中
完整的CIOU损失函数的公式如下:
CIOU Loss的梯度在长宽
Python实现如下:
def calculate_ciou(box_1, box_2):
"""
calculate ciou
:param box_1: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:param box_2: (x0, y0, x1, y1)
:return: value of ciou
"""
# calculate area of each box
width_1 = box_1[2] - box_1[0]
height_1 = box_1[3] - box_1[1]
area_1 = width_1 * height_1
width_2 = box_2[2] - box_2[0]
height_2 = box_2[3] - box_2[1]
area_2 = width_2 * height_2
# calculate center point of each box
center_x1 = (box_1[2] - box_1[0]) / 2
center_y1 = (box_1[3] - box_1[1]) / 2
center_x2 = (box_2[2] - box_2[0]) / 2
center_y2 = (box_2[3] - box_2[1]) / 2
# calculate square of center point distance
p2 = (center_x2 - center_x1) ** 2 + (center_y2 - center_y1) ** 2
# calculate square of the diagonal length
width_c = max(box_1[2], box_2[2]) - min(box_1[0], box_2[0])
height_c = max(box_1[3], box_2[3]) - min(box_1[1], box_2[1])
c2 = width_c ** 2 + height_c ** 2
# find the edge of intersect box
left = max(box_1[0], box_2[0])
top = max(box_1[1], box_2[1])
bottom = min(box_1[3], box_2[3])
right = min(box_1[2], box_2[2])
# calculate the intersect area
area_intersection = (right - left) * (bottom - top)
# calculate the union area
area_union = area_1 + area_2 - area_intersection
# calculate iou
iou = float(area_intersection) / area_union
# calculate v
arctan = math.atan(float(width_2) / height_2) - math.atan(float(width_1) / height_1)
v = (4.0 / math.pi ** 2) * (arctan ** 2)
# calculate alpha
alpha = float(v) / (1 - iou + v)
# calculate ciou(iou - p2 / c2 - alpha * v)
ciou = iou - float(p2) / c2 - alpha * v
return ciou2. 存在的问题
纵横比权重的设计还不太明白,是否有更好的设计方式有待更新。
五、IOU、GIOU、DIOU、CIOU对比
边界框回归的三大几何因素:重叠面积、中心点距离、纵横比
- IOU Loss:考虑了重叠面积,归一化坐标尺度;
- GIOU Loss:考虑了重叠面积,基于IOU解决边界框不相交时loss等于0的问题;
- DIOU Loss:考虑了重叠面积和中心点距离,基于IOU解决GIOU收敛慢的问题;
- CIOU Loss:考虑了重叠面积、中心点距离、纵横比,基于DIOU提升回归精确度;
| IOU Loss | GIOU Loss | DIOU Loss | CIOU Loss | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优点 | IOU算法是目标检测中最常用的指标,具有尺度不变性,满足非负性;同一性;对称性;三角不等性等特点。 | GIOU在基于IOU特性的基础上引入最小外接框解决检测框和真实框没有重叠时loss等于0问题。 | DIOU在基于IOU特性的基础上考虑到GIOU的缺点,直接回归两个框中心点的欧式距离,加速收敛。 | CIoU就是在DIoU的基础上增加了检测框尺度的loss,增加了长和宽的loss,这样预测框就会更加的符合真实框。 |
| 缺点 | 1.如果两个框不相交,不能反映两个框距离远近2.无法精确的反映两个框的重合度大小 | 1.当检测框和真实框出现包含现象的时候GIOU退化成IOU2.两个框相交时,在水平和垂直方向上收敛慢 | 回归过程中未考虑Bounding box的纵横比,精确度上尚有进一步提升的空间 | 待定 |