Tree 定义
简化定义Scala Tree结构,包含两个部分: Branch和Tree。为了简化数据结构,Branch只包含 Tree类型的 左节点 和 右节点, Leaf包含具体 Value
sealed trait Tree[+A]
case class Leaf[A](value: A) extends Tree[A]
case class Branch[A](left: Tree[A], right: Tree[A]) extends Tree[A]深度优先遍历 DFS
树的遍历右两种方式:
- 深度优先
- 广度优先
这里用DFS 实现,深度优先搜索属于图算法的一种,英文缩写为DFS即Depth First Search,其过程简要来说是对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止,而且每个节点只能访问一次。
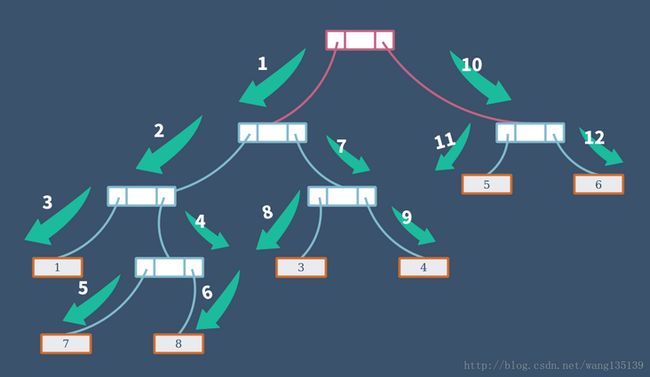
具体搜索顺序可以参考附图
- 搜索根节点 左子树
- 搜索当前树的左子树
- 搜索当前树的左子树
- 返回父节点,搜索父节点 右子树
- 搜索当前树的左子树
- 返回父节点,搜索父节点 右子树
- 返回父节点, 返回父节点,返回父节点,搜索右子树
- ….
我们从一道题来熟悉Scala遍历操作,求Scala树中节点总数
按照DFS 思想实现代码如下
def countNodes[A](tree: Tree[A]): Int = {
def go[A](tree: Tree[A], sum: Int): Int = tree match {
case Leaf(v) => sum + 1 //叶子节点 sum+1
case Branch(left, right) => sum + 1 + go(left, 0) + go(right, 0) //分支节点 sum = sum + 1 + 左子树节点总数 + 右子树节点总数
case _ => 0
}
go(tree, 0) //递归
}结合【Scala笔记——道】Scala List HOF foldLeft / foldRight 中讲到的List fold思想
我们将countNode 方法的遍历进行抽象化
,首先一个函数最重要的就是输入 / 输出,参考List fold,不难理解对Tree的函数操作必然是将Tree[A]转化为 [B],我们这里实现的简化树模型中,Value的具体存储都在叶子节点中,因此
def deepFirstSearch[A, B](tree: Tree[A])(f: A => B)... = tree match {
case Leaf(value) => f(value)
...
}其次,将DFS 搜索的过程进行抽象。对每一个 枝点,首先搜索 枝点的左节点,得到左节点执行结果以后,再搜索右节点,得到右节点执行结果以后,执行 对左右子树 函数结果的 函数操作,因此
def deepFirstSearch[A, B](tree: Tree[A])(f: A => B)(g: (B, B) => B) : B = tree match {
case Leaf(value) => f(value)
case Branch(l, r) => g( deepFirstSearch(l), deepFirstSearch(r) )
}使用
通过几个小例子来实践deepFirstSearch
获取Tree[Int]中最大值
def maximum(tree: Tree[Int]): Int =
deepFirstSearch(tree)(l => l)(_ max _)求树的最大深度
def depth[A](tree: Tree[A]): Int =
deepFirstSearch(tree)(_ => 1)(_.max(_) + 1)MAP函数 将A 转化为B
def map[A, B](tree: Tree[A])(f: A => B): Tree[B] = {
deepFirstSearch(tree)( x => (Leaf(f(x)): Tree[B]))( (a, b) => Branch(a, b))测试如下
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val tree = Branch(
Branch(
Branch
(Leaf(1),
Branch(
Leaf(7),
Branch(
Leaf(8),
Leaf(9)
))),
Branch(
Leaf(34), Leaf(4))),
Branch(
Leaf(5), Leaf(6)))
println("Max value :" + maximum(tree))
println("Depth :" + depth(tree))
println("Map :" + map(tree)(x => if(x%2 == 0) Branch(Leaf(1), Leaf(2)) else x))
}结果如下
Max value :34
Depth :6
Map :Branch(Branch(Branch(Leaf(1),Branch(Leaf(7),Branch(Leaf(Branch(Leaf(1),Leaf(2))),Leaf(9)))),Branch(Leaf(Branch(Leaf(1),Leaf(2))),Leaf(Branch(Leaf(1),Leaf(2))))),Branch(Leaf(5),Leaf(Branch(Leaf(1),Leaf(2)))))