概述
在日常开发的过程中,同学们都遇到过需要RecyclerView无限循环的需求,但是在官方提供的几种LayoutManager中并未支持无限循环。
遇到此种问题,通常的解决方案是:
1、在adapter返回Integer.MAX_VALUE并让RecyclerView滑动到某个足够大的位置。
2、选择自定义LayoutManager,实现循环的RecyclerView。
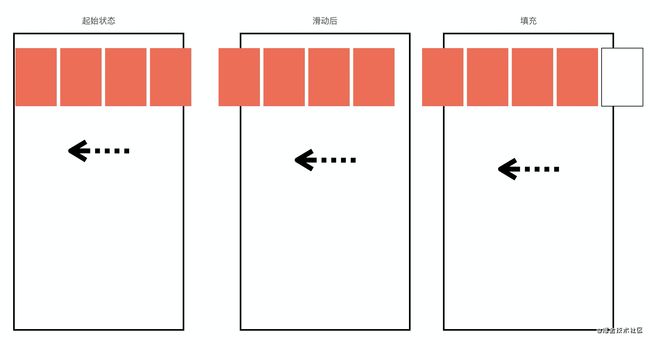
自定义LayoutManager的难度较高,本文将带大家一起实现这个自定义LayoutManager,效果如下图所示。同时,在熟悉了在自定义LayoutManager后,还可以根据需要调整RecyclerView的展示效果。
初探LayoutManager
自定义ViewGroup类似,自定义LayoutManager所要做的就是ItemView的「添加(add)」、「测量(measure)」、「布局(layout)」。
但是自定义ViewGroup相比,LayoutManager多了一个「回收(recycle)」工作。
在自定义LayoutManager之前,需要对其提供的「测量」、「布局」以及「回收」相关的API进行了解。
measure
首先介绍测量方法,与自定义ViewGroup类似,测量通常是固定的逻辑不需要自己实现,开发者无需复写测量方法,只需要在布局之前调用测量函数来获取将要布局的「View的宽度」即可。
LayoutManager提供了两个用来测量子View的方法:
//测量子View
public void measureChild(@NonNull View child, int widthUsed, int heightUsed)
//测量子View,并将子View的Margin也考虑进来,通常使用此函数
public void measureChildWithMargins(@NonNull View child, int widthUsed, int heightUsed)
测量完成后,便可以使用getMeasuredWidth()、getMeasuredHeight()直接获取View的宽高,但是在自定义LayoutManager中需要考虑ItemDecoration,所以需要通过如下两个API获取测量后的View大小:
//获取child的宽度,并将ItemDecoration考虑进来
public int getDecoratedMeasuredWidth(@NonNull View child) {
final Rect insets = ((LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams()).mDecorInsets;
return child.getMeasuredWidth() + insets.left + insets.right;
}
//获取child的高度,并将ItemDecoration考虑进来
public int getDecoratedMeasuredHeight(@NonNull View child) {
final Rect insets = ((LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams()).mDecorInsets;
return child.getMeasuredHeight() + insets.top + insets.bottom;
}
layout
然后介绍layout方法,和自定义ViewGroup一样,LayoutManager完成ItemView的测量后就是布局了。
在LayoutManager中,并非靠直接调用ItemView的layout函数进行子View的布局,而是使用layoutDecorated与layoutDecoratedWithMargins, 两者的区别是后者考虑了Margins:
public void layoutDecorated(@NonNull View child, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
final Rect insets = ((LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams()).mDecorInsets;
child.layout(left + insets.left, top + insets.top, right - insets.right,
bottom - insets.bottom);
}
public void layoutDecoratedWithMargins(@NonNull View child, int left, int top, int right,
int bottom) {
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final Rect insets = lp.mDecorInsets;
child.layout(left + insets.left + lp.leftMargin, top + insets.top + lp.topMargin,
right - insets.right - lp.rightMargin,
bottom - insets.bottom - lp.bottomMargin);
}
recycle
回收是RecyclerView的灵魂,也是RecyclerView与普通ViewGroup的区别。众所周知,RecyclerView中含有四类缓存,在布局过程中它们各自有各自的用途:
1、AttachedScrap: 存放可见、不需要重新绑定的ViewHolder
2、CachedViews: 存放不可见、不需要重新绑定的ViewHoler
3、ViewCacheExtension: 自定义缓存(存放不可见、不需要重新绑定)
4、RecyclerPool: 存放不可见、需要重新绑定的ViewHolder
在LayoutManager中提供了多个回收方法:
//将指定的View直接回收加至ecyclerPool
public void removeAndRecycleView(@NonNull View child, @NonNull Recycler recycler) {
removeView(child);
recycler.recycleView(child);
}
//将指定位置的View直接回收加至ecyclerPool
public void removeAndRecycleViewAt(int index, @NonNull Recycler recycler) {
final View view = getChildAt(index);
removeViewAt(index);
recycler.recycleView(view);
}
LayoutManager创建
1、实现抽抽象方法,并让RecyclerView可横向滑动
public class RepeatLayoutManager extends RecyclerView.LayoutManager {
@Override
public RecyclerView.LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new RecyclerView.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
@Override
public boolean canScrollHorizontally() {
return true;
}
}
2、定义初始布局
在onLayoutChildren(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state)方法中对ItemView进行添加、测量、布局。
具体步骤如下:
- 使用
recycler.getViewForPosition(int pos)从缓存中获取子View - 当可布局区域有多余的空间时,通过
addView(View view)将对子View进行添加,通过在RecyclerView中添加子View,并对子View进行测量与布局,直至子View超出RecyclerView的可布局宽度。
@Override
public void onLayoutChildren(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state) {
if (getItemCount() <= 0) {
return;
}
if (state.isPreLayout()) {
return;
}
//将所有Item分离至scrap
detachAndScrapAttachedViews(recycler);
int itemLeft = getPaddingLeft();
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
if (itemLeft >= getWidth() - getPaddingRight()) {
break;
}
View itemView = recycler.getViewForPosition(i % getItemCount());
//添加子View
addView(itemView);
//测量子View
measureChildWithMargins(itemView, 0, 0);
int right = itemLeft + getDecoratedMeasuredWidth(itemView);
int top = getPaddingTop();
int bottom = top + getDecoratedMeasuredHeight(itemView) - getPaddingBottom();
//对子View进行布局
layoutDecorated(itemView, itemLeft, top, right, bottom);
itemLeft = right;
}
}
3、滑动与填充
offsetChildrenHorizontal(int x)用作对RecyclerView中的子View进行整体左右移动。
为了在滑动RecyclerView时有子View移动的效果,需要复写scrollHorizontallyBy函数,并在其中调用offsetChildrenHorizontal(int x)。
当左滑后子View被左移动时,RecyclerView的右侧会出现可见的未填充区域,这时需要在RecyclerView右侧添加并布局好新的子View,直到没有可见的未填充区域为止。
同样,在右滑后需要对左侧的未填充区域进行填充。
具体代码如下:
@Override
public int scrollHorizontallyBy(int dx, RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state) {
fill(recycler, dx > 0);
offsetChildrenHorizontal(-dx);
return dx;
}
/**
* 滑动的时候,填充可见的未填充区域
*/
private void fill(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, boolean fillEnd) {
if (getChildCount() == 0) return;
if (fillEnd) {
//填充尾部
View anchorView = getChildAt(getChildCount() - 1);
int anchorPosition = getPosition(anchorView);
for (; anchorView.getRight() < getWidth() - getPaddingRight(); ) {
int position = (anchorPosition + 1) % getItemCount();
if (position < 0) position += getItemCount();
View scrapItem = recycler.getViewForPosition(position);
addView(scrapItem);
measureChildWithMargins(scrapItem, 0, 0);
int left = anchorView.getRight();
int top = getPaddingTop();
int right = left + getDecoratedMeasuredWidth(scrapItem);
int bottom = top + getDecoratedMeasuredHeight(scrapItem) - getPaddingBottom();
layoutDecorated(scrapItem, left, top, right, bottom);
anchorView = scrapItem;
}
} else {
//填充首部
View anchorView = getChildAt(0);
int anchorPosition = getPosition(anchorView);
for (; anchorView.getLeft() > getPaddingLeft(); ) {
int position = (anchorPosition - 1) % getItemCount();
if (position < 0) position += getItemCount();
View scrapItem = recycler.getViewForPosition(position);
addView(scrapItem, 0);
measureChildWithMargins(scrapItem, 0, 0);
int right = anchorView.getLeft();
int top = getPaddingTop();
int left = right - getDecoratedMeasuredWidth(scrapItem);
int bottom = top + getDecoratedMeasuredHeight(scrapItem) - getPaddingBottom();
layoutDecorated(scrapItem, left, top,
right, bottom);
anchorView = scrapItem;
}
}
return;
}
回收
前面讲到,当对RecyclerView进行滑动时,需要对可见的未填充区域进行填充。然而一直填充不做回收Item,那就和普通的ViewGroup没有太多的区别了。
在RecyclerView中,需要在滑动、填充可见区域的同时,对不可见区域的子View进行回收,这样才能体现出RecyclerView的优势。
回收的方向与填充的方向恰好相反。那回收的代码具体如何实现呢?代码如下:
@Override
public int scrollHorizontallyBy(int dx, RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state) {
fill(recycler, dx > 0);
offsetChildrenHorizontal(-dx);
recyclerChildView(dx > 0, recycler);
return dx;
}
/**
* 回收不可见的子View
*/
private void recyclerChildView(boolean fillEnd, RecyclerView.Recycler recycler) {
if (fillEnd) {
//回收头部
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
boolean needRecycler = view != null && view.getRight() < getPaddingLeft();
if (needRecycler) {
removeAndRecycleView(view, recycler);
} else {
return;
}
}
} else {
//回收尾部
for (int i = getChildCount() - 1; ; i--) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
boolean needRecycler = view != null && view.getLeft() > getWidth() - getPaddingRight();
if (needRecycler) {
removeAndRecycleView(view, recycler);
} else {
return;
}
}
}
}
使用
- 添加依赖
implementation 'cn.student0.manager:repeatmanager:1.0.2'
- 在代码中使用
RecyclerView recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.rv_demo);
recyclerView.setAdapter(new DemoAdapter());
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new RepeatLayoutManager
结语
到此,无限循环的LayoutManager的实现已经完成。文章的不足还请指出,谢谢大家。
Github地址:https://github.com/jiarWang/RepeatLayoutManager, 欢迎大家Star。
感谢HenCoder团队
参考
Android自定义LayoutManager第十一式之飞龙在天
【Android】掌握自定义LayoutManager(一) 系列开篇 常见误区、问题、注意事项,常用API