写在前面
seata是阿里巴巴开源,用于解决分布式事务的中间件,目前拥有四种解决分布式事务的模式:AT、TCC、XA、SAGA。由于SAGA模式与状态机、正向补偿类似,并且使用方式上比较陡峭,所以我只会分析前三种模式的源码。
在看此系列源码解析之前,希望你:
1.阅读过seata官方的文档:http://seata.io/zh-cn/docs/overview/what-is-seata.html
2.阅读过seata相关的理论文章,比如这篇说明seata各种模式的优劣与分布式事务中的“CAP”:https://www.jianshu.com/p/917cb4bdaa03
3.将seata源码拉下来,git clone https://github.com/seata/seata.git
4.准备开启你的源码解析之旅
AT-TM端分析
@Bean
@DependsOn({BEAN_NAME_SPRING_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_PROVIDER, BEAN_NAME_FAILURE_HANDLER})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(GlobalTransactionScanner.class)
public GlobalTransactionScanner globalTransactionScanner(SeataProperties seataProperties, FailureHandler failureHandler) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Automatically configure Seata");
}
return new GlobalTransactionScanner(seataProperties.getApplicationId(), seataProperties.getTxServiceGroup(), failureHandler);
}
一看SeataAutoConfiguration就会觉得非常熟悉,就是利用了spring自动注入的特点,为某个方法打上@Bean注解,完成了对GlobalTransactionScanner的生成。
接下来我们进入GlobalTransactionScanner,它实现了spring的InitializingBean接口,因此利用spring的特性,当bean实现时会调用afterPropertiesSet方法进行初始化。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)this);
if (disableGlobalTransaction) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Global transaction is disabled.");
}
return;
}
if (initialized.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
initClient();
}
}
private void initClient() {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Initializing Global Transaction Clients ... ");
}
if (StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(applicationId) || StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(txServiceGroup)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("applicationId: %s, txServiceGroup: %s", applicationId, txServiceGroup));
}
//init TM
TMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup, accessKey, secretKey);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Transaction Manager Client is initialized. applicationId[{}] txServiceGroup[{}]", applicationId, txServiceGroup);
}
//init RM
RMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Resource Manager is initialized. applicationId[{}] txServiceGroup[{}]", applicationId, txServiceGroup);
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Global Transaction Clients are initialized. ");
}
registerSpringShutdownHook();
}
GlobalTransactionScanner的afterPropertiesSet方法中,对TM、RM的client进行初始化,对关闭钩子的注册。
同时,GlobalTransactionScanner也实现了AbstractAutoProxyCreator方法,会对所有由spring生成的bean进行wrapIfNecessary的二次处理,正是由此方法,为打上@GlobalTransaction注解的bean进行动态代理,由GlobalTransactionalInterceptor进行代理。
@Override
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
try {
synchronized (PROXYED_SET) {
if (PROXYED_SET.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
interceptor = null;
//check TCC proxy
if (TCCBeanParserUtils.isTccAutoProxy(bean, beanName, applicationContext)) {
//TCC interceptor, proxy bean of sofa:reference/dubbo:reference, and LocalTCC
interceptor = new TccActionInterceptor(TCCBeanParserUtils.getRemotingDesc(beanName));
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)interceptor);
} else {
Class serviceInterface = SpringProxyUtils.findTargetClass(bean);
Class[] interfacesIfJdk = SpringProxyUtils.findInterfaces(bean);
if (!existsAnnotation(new Class[]{serviceInterface})
&& !existsAnnotation(interfacesIfJdk)) {
return bean;
}
if (interceptor == null) {
if (globalTransactionalInterceptor == null) {
globalTransactionalInterceptor = new GlobalTransactionalInterceptor(failureHandlerHook);
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(
ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)globalTransactionalInterceptor);
}
interceptor = globalTransactionalInterceptor;
}
}
LOGGER.info("Bean[{}] with name [{}] would use interceptor [{}]", bean.getClass().getName(), beanName, interceptor.getClass().getName());
if (!AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean)) {
bean = super.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
} else {
AdvisedSupport advised = SpringProxyUtils.getAdvisedSupport(bean);
Advisor[] advisor = buildAdvisors(beanName, getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(null, null, null));
for (Advisor avr : advisor) {
advised.addAdvisor(0, avr);
}
}
PROXYED_SET.add(beanName);
return bean;
}
} catch (Exception exx) {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}
由GlobalTransactionalInterceptor接管后,调用将经过它的invoke方法,再经过handleGlobalTransaction或者handleGlobalLock进行处理,这是看方法上的注解是@GlobalTransactional或者@GlobalLock决定的。
@Override
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
Class targetClass =
methodInvocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(methodInvocation.getThis()) : null;
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
if (specificMethod != null && !specificMethod.getDeclaringClass().equals(Object.class)) {
final Method method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
final GlobalTransactional globalTransactionalAnnotation =
getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalTransactional.class);
final GlobalLock globalLockAnnotation = getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalLock.class);
boolean localDisable = disable || (degradeCheck && degradeNum >= degradeCheckAllowTimes);
if (!localDisable) {
if (globalTransactionalAnnotation != null) {
return handleGlobalTransaction(methodInvocation, globalTransactionalAnnotation);
} else if (globalLockAnnotation != null) {
return handleGlobalLock(methodInvocation, globalLockAnnotation);
}
}
}
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
handleGlobalLock其实是handleGlobalTransaction的子集,接下来只分析handleGlobalTransaction方法,handleGlobalTransaction比较简单,直接调用事务模板类TransactionalTemplate的execute方法继续进行,报错则调用错误处理器进行处理,最后发送消息到事务总线。execute入参是TransactionalExecutor,封装了对原方法的调用、名称、事务配置的获取。
Object handleGlobalTransaction(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation,
final GlobalTransactional globalTrxAnno) throws Throwable {
boolean succeed = true;
try {
return transactionalTemplate.execute(new TransactionalExecutor() {
@Override
public Object execute() throws Throwable {
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
public String name() {
String name = globalTrxAnno.name();
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(name)) {
return name;
}
return formatMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod());
}
@Override
public TransactionInfo getTransactionInfo() {
// reset the value of timeout
int timeout = globalTrxAnno.timeoutMills();
if (timeout <= 0 || timeout == DEFAULT_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION_TIMEOUT) {
timeout = defaultGlobalTransactionTimeout;
}
TransactionInfo transactionInfo = new TransactionInfo();
transactionInfo.setTimeOut(timeout);
transactionInfo.setName(name());
transactionInfo.setPropagation(globalTrxAnno.propagation());
transactionInfo.setLockRetryInternal(globalTrxAnno.lockRetryInternal());
transactionInfo.setLockRetryTimes(globalTrxAnno.lockRetryTimes());
Set rollbackRules = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (Class rbRule : globalTrxAnno.rollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : globalTrxAnno.rollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (Class rbRule : globalTrxAnno.noRollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : globalTrxAnno.noRollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
transactionInfo.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return transactionInfo;
}
});
} catch (TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException e) {
TransactionalExecutor.Code code = e.getCode();
switch (code) {
case RollbackDone:
throw e.getOriginalException();
case BeginFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onBeginFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case CommitFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onCommitFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case RollbackFailure:
failureHandler.onRollbackFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
case RollbackRetrying:
failureHandler.onRollbackRetrying(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
default:
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException(String.format("Unknown TransactionalExecutor.Code: %s", code));
}
} finally {
if (degradeCheck) {
EVENT_BUS.post(new DegradeCheckEvent(succeed));
}
}
}
接下来到seata事务的核心,事务模板TransactionalTemplate,里面封装了spring的事务传播模式:
NOT_SUPPORTED(如果有事务则挂起,不在事务中执行原方法)
REQUIRES_NEW(如果有事务则挂起,新建事务中执行原方法)
SUPPORTS(如果不存在事务则直接执行原方法,若存在事务则在原事务执行原方法)
REQUIRED(不进行任何处理,若存在事务则在事务中执行,否则相反)
NEVER(若存在事务直接报错,没有事务则执行)
MANDATORY(不存在事务则报错,必须在原事务中执行)
,还有类似spring的事务执行顺序,beginTransaction->business.execute->completeTransactionAfterThrowing->commitTransaction->cleanUp。似曾相识,在seata还能复习下spring事务,哈哈。这里的英文注释非常详细,很容易看明白seata的封装方式。
public Object execute(TransactionalExecutor business) throws Throwable {
// 1. Get transactionInfo
TransactionInfo txInfo = business.getTransactionInfo();
if (txInfo == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("transactionInfo does not exist");
}
// 1.1 Get current transaction, if not null, the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Participant'.
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrent();
// 1.2 Handle the transaction propagation.
Propagation propagation = txInfo.getPropagation();
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResourcesHolder = null;
try {
switch (propagation) {
case NOT_SUPPORTED:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
}
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
case REQUIRES_NEW:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it, and then begin new transaction.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case SUPPORTS:
// If transaction is not existing, execute without transaction.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
return business.execute();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case REQUIRED:
// If current transaction is existing, execute with current transaction,
// else continue and execute with new transaction.
break;
case NEVER:
// If transaction is existing, throw exception.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException(
String.format("Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never', xid = %s"
, tx.getXid()));
} else {
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
}
case MANDATORY:
// If transaction is not existing, throw exception.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException("No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// Continue and execute with current transaction.
break;
default:
throw new TransactionException("Not Supported Propagation:" + propagation);
}
// 1.3 If null, create new transaction with role 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher'.
if (tx == null) {
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// set current tx config to holder
GlobalLockConfig previousConfig = replaceGlobalLockConfig(txInfo);
try {
// 2. If the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher', send the request of beginTransaction to TC,
// else do nothing. Of course, the hooks will still be triggered.
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs;
try {
// Do Your Business
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 3. The needed business exception to rollback.
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 4. everything is fine, commit.
commitTransaction(tx);
return rs;
} finally {
//5. clear
resumeGlobalLockConfig(previousConfig);
triggerAfterCompletion();
cleanUp();
}
} finally {
// If the transaction is suspended, resume it.
if (suspendedResourcesHolder != null) {
tx.resume(suspendedResourcesHolder);
}
}
}
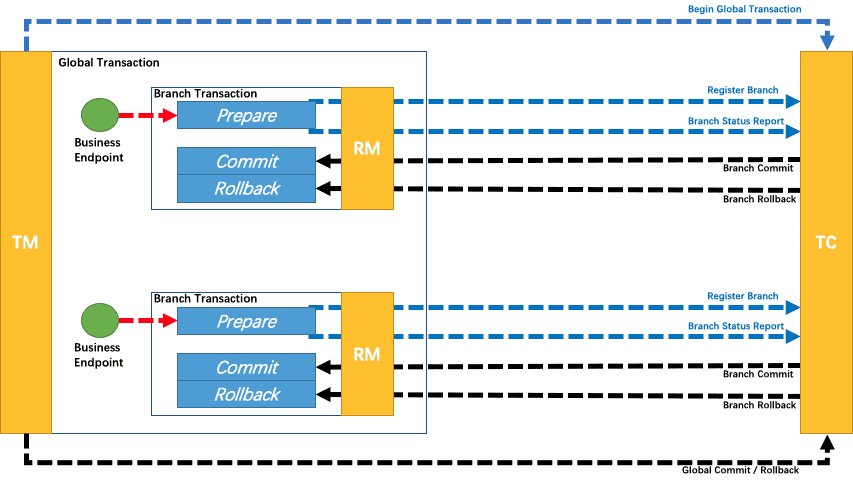
1.来到beginTransaction,如果看过镇楼图,就是TM向TC注册事务的过程,调用链路是TransactionalTemplate->DefaultGlobalTransaction->DefaultTransactionManager的begin方法,值得一提的是,TM端(DefaultTransactionManager)和TC端(DefaultCore)处理事务的类,都是实现了TransactionManager接口,的确TM和TC端的处理方法是一一对应的。在DefaultTransactionManager使用TmNettyRemotingClient发送事务注册请求,还记得刚开始初始化的TMclient吗?养兵千日,用在一时。
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
GlobalBeginRequest request = new GlobalBeginRequest();
request.setTransactionName(name);
request.setTimeout(timeout);
GlobalBeginResponse response = (GlobalBeginResponse) syncCall(request);
if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BeginFailed, response.getMsg());
}
return response.getXid();
}
2.business.execute会在AT-RM端进行分析,此处省略。
3.completeTransactionAfterThrowing是在原方法调用后报错进行rollback,跟begin注册事务的方式几乎一模一样,都是使用TMclient向TC发出rollback请求,此处省略。
4.commitTransaction是在原方法调用成功后进行commit,跟begin注册事务的方式几乎一模一样,都是使用TMclient向TC发出commit请求,此处省略。
5.cleanUp是在事务模板执行后进行清扫现场的方法,目的是对保存在ThreadLocal中的事务钩子进行清除。
AT-TM端总结:
AT-TM端使用了动态代理,将原方法封装成事务模板进行执行,是事务的注册到事务的提交或回滚的发起方。AT-TM端生于spring,也对spring的事务处理进行增强。
AT-RM端分析
AT-RM端的思想比较巧妙,是通过自上而下的动态代理数据库相关类(Database、Connection、Statement),对sql的执行拦截处理,在AT模式中,主要流程是向TC注册、向TC提交全局锁、本地sql与undolog的执行与提交、向TC提交四部分。
首先AT-RM端会将原DataSource进行代理形成DataSourceProxy,这样可以通过DataSourceProxy从原DataSource获取Connection进行代理形成ConnectionProxy,最后可以通过ConnectionProxy获取Statement进行代理形成StatementProxy。
@Bean
public DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy(DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceProxy(dataSource);
}
@Override
public ConnectionProxy getConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection targetConnection = targetDataSource.getConnection();
return new ConnectionProxy(this, targetConnection);
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
Statement statement = targetConnection.createStatement(resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency);
return new StatementProxy(this, statement);
}
直接进入StatementProxy,可以看到里面的方法都是使用了ExecuteTemplate执行模板进行处理,比如executeUpdate方法,ExecuteTemplate.execute的入参是statementProxy,原sql的执行回调、sql。
@Override
public int executeUpdate(String sql) throws SQLException {
this.targetSQL = sql;
return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.executeUpdate((String) args[0]), sql);
}
可以看到ExecuteTemplate.execute会区别对待不同的sql类型,生成不同的Executor,最后调用Executor.execute执行sql。
public static T execute(List sqlRecognizers,
StatementProxy statementProxy,
StatementCallback statementCallback,
Object... args) throws SQLException {
if (!RootContext.requireGlobalLock() && BranchType.AT != RootContext.getBranchType()) {
// Just work as original statement
return statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
}
String dbType = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().getDbType();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(
statementProxy.getTargetSQL(),
dbType);
}
Executor executor;
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
} else {
if (sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {
SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);
switch (sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
case INSERT:
executor = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(InsertExecutor.class, dbType,
new Class[]{StatementProxy.class, StatementCallback.class, SQLRecognizer.class},
new Object[]{statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer});
break;
case UPDATE:
executor = new UpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case DELETE:
executor = new DeleteExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
case SELECT_FOR_UPDATE:
executor = new SelectForUpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
break;
default:
executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
break;
}
} else {
executor = new MultiExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizers);
}
}
T rs;
try {
rs = executor.execute(args);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
if (!(ex instanceof SQLException)) {
// Turn other exception into SQLException
ex = new SQLException(ex);
}
throw (SQLException) ex;
}
return rs;
}
选取一个比较简单又能体现完整AT-RM端流程的UpdateExecutor进行分析,如果设置了自动提交,会进入executeAutoCommitTrue流程,否则会进入executeAutoCommitFalse流程。
继续选取executeAutoCommitTrue流程进行分析,首先设置自动提交为false,然后执行executeAutoCommitFalse后会调用ConnectionProxy的commit方法。
protected T executeAutoCommitTrue(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
try {
connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(false);
return new LockRetryPolicy(connectionProxy).execute(() -> {
T result = executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
connectionProxy.commit();
return result;
});
} catch (Exception e) {
// when exception occur in finally,this exception will lost, so just print it here
LOGGER.error("execute executeAutoCommitTrue error:{}", e.getMessage(), e);
if (!LockRetryPolicy.isLockRetryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict()) {
connectionProxy.getTargetConnection().rollback();
}
throw e;
} finally {
connectionProxy.getContext().reset();
connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(true);
}
}
executeAutoCommitFalse流程会执行beforeImage保存前置镜像,调用原sql执行回调,afterImage保存后置镜像,合并镜像形成待提交的undolog与待提交的全局lockkey。
形成镜像的原理是根据原sql生成等价的查询sql,执行查询sql形成镜像。
形成lockkey的原理是根据镜像获取主键列表(primary key 简称pk)进行拼接形成lockkey。
protected T executeAutoCommitFalse(Object[] args) throws Exception {
if (!JdbcConstants.MYSQL.equalsIgnoreCase(getDbType()) && isMultiPk()) {
throw new NotSupportYetException("multi pk only support mysql!");
}
TableRecords beforeImage = beforeImage();
T result = statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
TableRecords afterImage = afterImage(beforeImage);
prepareUndoLog(beforeImage, afterImage);
return result;
}
protected void prepareUndoLog(TableRecords beforeImage, TableRecords afterImage) throws SQLException {
if (beforeImage.getRows().isEmpty() && afterImage.getRows().isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (SQLType.UPDATE == sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
if (beforeImage.getRows().size() != afterImage.getRows().size()) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("Before image size is not equaled to after image size, probably because you updated the primary keys.");
}
}
ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
TableRecords lockKeyRecords = sqlRecognizer.getSQLType() == SQLType.DELETE ? beforeImage : afterImage;
String lockKeys = buildLockKey(lockKeyRecords);
connectionProxy.appendLockKey(lockKeys);
SQLUndoLog sqlUndoLog = buildUndoItem(beforeImage, afterImage);
connectionProxy.appendUndoLog(sqlUndoLog);
}
connectionProxy.commit就是最终的收尾流程,经过上面的一系列流程,sql执行了,undolog与lockkey有了,接下来就是向TC进行注册并且加全局锁,本地sql与undolog一起提交,向TC报告本身状态,当然,RM与TC的交互还是用最开始初始化的RmClient,就不再细说了。
private void processGlobalTransactionCommit() throws SQLException {
try {
register();
} catch (TransactionException e) {
recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, context.buildLockKeys());
}
try {
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);
targetConnection.commit();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
LOGGER.error("process connectionProxy commit error: {}", ex.getMessage(), ex);
report(false);
throw new SQLException(ex);
}
if (IS_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE) {
report(true);
}
context.reset();
}
AT-RM端总结:
AT-RM端同样使用了动态代理,将原方法封装成执行模板进行执行,保证了全局事务的锁执行、向TC的注册、报告本身状态、本地提交sql时同时提交undolog为全局回滚做好准备。
AT-TC端分析
AT-TC端是负责整个全局事务的注册、提交或回滚的总控制节点。
由上文可知,AT-TC端接收并处理了TM端的全局事务的注册、提交或回滚请求,RM端的分支事务的注册、报告本身状态请求。
当TM发起全局提交或回滚时,会调用全局事务底下所有RM的最终提交或回滚接口,删除undolog或者根据undolog进行重放恢复数据。做到全局事务的提交或者回滚。seata-AT模式的本质可以说就是类2pc的一致性算法实现。
AT-TC端同样是以NettyRemotingServer启动并且接收处理来自TM于RM的请求,请求会流经DefaultCoordinator->DefaultCore到达默认的核心处理类。
首先看TM发起的全局事务的注册,会调用DefaultCore的begin方法,创建GlobalSession通过生命周期监听服务保存到数据库,向事务总线发送消息,调用完成后返回GlobalSession的xid给到TM,xid将由TM保存在执行链路的上下文中,保证RM分支事务提交时关联到TM全局事务。
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
GlobalSession session = GlobalSession.createGlobalSession(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, name,
timeout);
session.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
session.begin();
// transaction start event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(session.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
session.getTransactionName(), session.getBeginTime(), null, session.getStatus()));
return session.getXid();
}
RM的分支注册,会调用DefaultCore的branchRegister方法,创建BatchSession,检查全局锁,同样会通过生命周期监听服务保存到数据库,调用完成后返回BatchSession的btachId给到RM,btachId对RM的主要作用是与xid一起定位唯一一条undolog。
@Override
public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid,
String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {
GlobalSession globalSession = assertGlobalSessionNotNull(xid, false);
return SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
globalSessionStatusCheck(globalSession);
globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
BranchSession branchSession = SessionHelper.newBranchByGlobal(globalSession, branchType, resourceId,
applicationData, lockKeys, clientId);
branchSessionLock(globalSession, branchSession);
try {
globalSession.addBranch(branchSession);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
branchSessionUnlock(branchSession);
throw new BranchTransactionException(FailedToAddBranch, String
.format("Failed to store branch xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(),
branchSession.getBranchId()), ex);
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Register branch successfully, xid = {}, branchId = {}, resourceId = {} ,lockKeys = {}",
globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId(), resourceId, lockKeys);
}
return branchSession.getBranchId();
});
}
RM的分支报告本身状态,会调用DefaultCore的branchReport方法,会根据xid获取到关联的GlobalSession,再根据batchId获取到BranchSession,调用GlobalSession的changeBranchStatus改变分支状态,同样会通过生命周期监听服务保存到数据库。
@Override
public void branchReport(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, BranchStatus status,
String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
GlobalSession globalSession = assertGlobalSessionNotNull(xid, true);
BranchSession branchSession = globalSession.getBranch(branchId);
if (branchSession == null) {
throw new BranchTransactionException(BranchTransactionNotExist,
String.format("Could not found branch session xid = %s branchId = %s", xid, branchId));
}
globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
globalSession.changeBranchStatus(branchSession, status);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Report branch status successfully, xid = {}, branchId = {}", globalSession.getXid(),
branchSession.getBranchId());
}
}
TM的全局提交,会调用DefaultCore的commit方法,会通过加锁与判断全局事务模式与分支节点是否进行异步提交,如果是异步提交则将globalSession的status置为AsyncCommitting,等待定时线程池捞取此状态的GlobalSession进行提交,否则直接调用doGlobalCommit进行全局提交,若全局事务提交成功,但是还拥有分支节点,则继续走异步提交流程,清除分支节点。
@Override
public GlobalStatus commit(String xid) throws TransactionException {
GlobalSession globalSession = SessionHolder.findGlobalSession(xid);
if (globalSession == null) {
return GlobalStatus.Finished;
}
globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
// just lock changeStatus
boolean shouldCommit = SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
// Highlight: Firstly, close the session, then no more branch can be registered.
globalSession.closeAndClean();
if (globalSession.getStatus() == GlobalStatus.Begin) {
if (globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
globalSession.asyncCommit();
return false;
} else {
globalSession.changeStatus(GlobalStatus.Committing);
return true;
}
}
return false;
});
if (shouldCommit) {
boolean success = doGlobalCommit(globalSession, false);
//If successful and all remaining branches can be committed asynchronously, do async commit.
if (success && globalSession.hasBranch() && globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
globalSession.asyncCommit();
return GlobalStatus.Committed;
} else {
return globalSession.getStatus();
}
} else {
return globalSession.getStatus() == GlobalStatus.AsyncCommitting ? GlobalStatus.Committed : globalSession.getStatus();
}
}
doGlobalCommit执行全局事务下的所有分支提交方法,若分支提交状态不是PhaseTwo_Committed会进行重试,将globalSession的状态置为CommitRetrying,等待定时线程池捞取此状态的GlobalSession进行提交。
@Override
public boolean doGlobalCommit(GlobalSession globalSession, boolean retrying) throws TransactionException {
boolean success = true;
// start committing event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(globalSession.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
globalSession.getTransactionName(), globalSession.getBeginTime(), null, globalSession.getStatus()));
if (globalSession.isSaga()) {
success = getCore(BranchType.SAGA).doGlobalCommit(globalSession, retrying);
} else {
for (BranchSession branchSession : globalSession.getSortedBranches()) {
// if not retrying, skip the canBeCommittedAsync branches
if (!retrying && branchSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
continue;
}
BranchStatus currentStatus = branchSession.getStatus();
if (currentStatus == BranchStatus.PhaseOne_Failed) {
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
continue;
}
try {
BranchStatus branchStatus = getCore(branchSession.getBranchType()).branchCommit(globalSession, branchSession);
switch (branchStatus) {
case PhaseTwo_Committed:
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
continue;
case PhaseTwo_CommitFailed_Unretryable:
if (globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
LOGGER.error(
"Committing branch transaction[{}], status: PhaseTwo_CommitFailed_Unretryable, please check the business log.", branchSession.getBranchId());
continue;
} else {
SessionHelper.endCommitFailed(globalSession);
LOGGER.error("Committing global transaction[{}] finally failed, caused by branch transaction[{}] commit failed.", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
return false;
}
default:
if (!retrying) {
globalSession.queueToRetryCommit();
return false;
}
if (globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
LOGGER.error("Committing branch transaction[{}], status:{} and will retry later",
branchSession.getBranchId(), branchStatus);
continue;
} else {
LOGGER.error(
"Committing global transaction[{}] failed, caused by branch transaction[{}] commit failed, will retry later.", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
return false;
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
StackTraceLogger.error(LOGGER, ex, "Committing branch transaction exception: {}",
new String[] {branchSession.toString()});
if (!retrying) {
globalSession.queueToRetryCommit();
throw new TransactionException(ex);
}
}
}
//If has branch and not all remaining branches can be committed asynchronously,
//do print log and return false
if (globalSession.hasBranch() && !globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
LOGGER.info("Committing global transaction is NOT done, xid = {}.", globalSession.getXid());
return false;
}
}
//If success and there is no branch, end the global transaction.
if (success && globalSession.getBranchSessions().isEmpty()) {
SessionHelper.endCommitted(globalSession);
// committed event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(globalSession.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
globalSession.getTransactionName(), globalSession.getBeginTime(), System.currentTimeMillis(),
globalSession.getStatus()));
LOGGER.info("Committing global transaction is successfully done, xid = {}.", globalSession.getXid());
}
return success;
}
全局提交对每个branchSession都进行分支提交的回调,在RM端由DataSourceManager.branchCommit方法提交到待提交队列ASYNC_COMMIT_BUFFER,异步等待timerExecutor进行删除undolog。
@Override
public BranchStatus branchCommit(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, String resourceId,
String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
if (!ASYNC_COMMIT_BUFFER.offer(new Phase2Context(branchType, xid, branchId, resourceId, applicationData))) {
LOGGER.warn("Async commit buffer is FULL. Rejected branch [{}/{}] will be handled by housekeeping later.", branchId, xid);
}
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_Committed;
}
private void doBranchCommits() {
if (ASYNC_COMMIT_BUFFER.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
Map> mappedContexts = new HashMap<>(DEFAULT_RESOURCE_SIZE);
List contextsGroupedByResourceId;
while (!ASYNC_COMMIT_BUFFER.isEmpty()) {
Phase2Context commitContext = ASYNC_COMMIT_BUFFER.poll();
contextsGroupedByResourceId = CollectionUtils.computeIfAbsent(mappedContexts, commitContext.resourceId, key -> new ArrayList<>());
contextsGroupedByResourceId.add(commitContext);
}
for (Map.Entry> entry : mappedContexts.entrySet()) {
Connection conn = null;
DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy;
try {
try {
DataSourceManager resourceManager = (DataSourceManager) DefaultResourceManager.get()
.getResourceManager(BranchType.AT);
dataSourceProxy = resourceManager.get(entry.getKey());
if (dataSourceProxy == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("Failed to find resource on " + entry.getKey());
}
conn = dataSourceProxy.getPlainConnection();
} catch (SQLException sqle) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to get connection for async committing on " + entry.getKey(), sqle);
continue;
}
contextsGroupedByResourceId = entry.getValue();
Set xids = new LinkedHashSet<>(UNDOLOG_DELETE_LIMIT_SIZE);
Set branchIds = new LinkedHashSet<>(UNDOLOG_DELETE_LIMIT_SIZE);
for (Phase2Context commitContext : contextsGroupedByResourceId) {
xids.add(commitContext.xid);
branchIds.add(commitContext.branchId);
int maxSize = Math.max(xids.size(), branchIds.size());
if (maxSize == UNDOLOG_DELETE_LIMIT_SIZE) {
try {
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(dataSourceProxy.getDbType()).batchDeleteUndoLog(
xids, branchIds, conn);
} catch (Exception ex) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to batch delete undo log [" + branchIds + "/" + xids + "]", ex);
}
xids.clear();
branchIds.clear();
}
}
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(xids) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(branchIds)) {
return;
}
try {
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(dataSourceProxy.getDbType()).batchDeleteUndoLog(xids,
branchIds, conn);
} catch (Exception ex) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to batch delete undo log [" + branchIds + "/" + xids + "]", ex);
}
if (!conn.getAutoCommit()) {
conn.commit();
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOGGER.error(e.getMessage(), e);
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.rollback();
}
} catch (SQLException rollbackEx) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to rollback JDBC resource while deleting undo_log ", rollbackEx);
}
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException closeEx) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to close JDBC resource while deleting undo_log ", closeEx);
}
}
}
}
}
TM的全局回滚,会调用DefaultCore的rollback方法,会通过加锁与判断全局事务模式是否进行回滚,如果是进行回滚则将globalSession的status置为Rollbacking,直接调用doGlobalRollback进行全局回滚。
@Override
public GlobalStatus rollback(String xid) throws TransactionException {
GlobalSession globalSession = SessionHolder.findGlobalSession(xid);
if (globalSession == null) {
return GlobalStatus.Finished;
}
globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
// just lock changeStatus
boolean shouldRollBack = SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
globalSession.close(); // Highlight: Firstly, close the session, then no more branch can be registered.
if (globalSession.getStatus() == GlobalStatus.Begin) {
globalSession.changeStatus(GlobalStatus.Rollbacking);
return true;
}
return false;
});
if (!shouldRollBack) {
return globalSession.getStatus();
}
doGlobalRollback(globalSession, false);
return globalSession.getStatus();
}
在doGlobalRollback中,会执行全局事务下的所有分支回滚方法,若分支提交状态不是PhaseTwo_Rollbacked会进行重试,将globalSession的状态置为TimeoutRollbackRetrying或者RollbackRetrying,等待定时线程池捞取此状态的GlobalSession进行回滚。
@Override
public boolean doGlobalRollback(GlobalSession globalSession, boolean retrying) throws TransactionException {
boolean success = true;
// start rollback event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(globalSession.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
globalSession.getTransactionName(), globalSession.getBeginTime(), null, globalSession.getStatus()));
if (globalSession.isSaga()) {
success = getCore(BranchType.SAGA).doGlobalRollback(globalSession, retrying);
} else {
for (BranchSession branchSession : globalSession.getReverseSortedBranches()) {
BranchStatus currentBranchStatus = branchSession.getStatus();
if (currentBranchStatus == BranchStatus.PhaseOne_Failed) {
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
continue;
}
try {
BranchStatus branchStatus = branchRollback(globalSession, branchSession);
switch (branchStatus) {
case PhaseTwo_Rollbacked:
globalSession.removeBranch(branchSession);
LOGGER.info("Rollback branch transaction successfully, xid = {} branchId = {}", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
continue;
case PhaseTwo_RollbackFailed_Unretryable:
SessionHelper.endRollbackFailed(globalSession);
LOGGER.info("Rollback branch transaction fail and stop retry, xid = {} branchId = {}", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
return false;
default:
LOGGER.info("Rollback branch transaction fail and will retry, xid = {} branchId = {}", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
if (!retrying) {
globalSession.queueToRetryRollback();
}
return false;
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
StackTraceLogger.error(LOGGER, ex,
"Rollback branch transaction exception, xid = {} branchId = {} exception = {}",
new String[] {globalSession.getXid(), String.valueOf(branchSession.getBranchId()), ex.getMessage()});
if (!retrying) {
globalSession.queueToRetryRollback();
}
throw new TransactionException(ex);
}
}
// In db mode, there is a problem of inconsistent data in multiple copies, resulting in new branch
// transaction registration when rolling back.
// 1. New branch transaction and rollback branch transaction have no data association
// 2. New branch transaction has data association with rollback branch transaction
// The second query can solve the first problem, and if it is the second problem, it may cause a rollback
// failure due to data changes.
GlobalSession globalSessionTwice = SessionHolder.findGlobalSession(globalSession.getXid());
if (globalSessionTwice != null && globalSessionTwice.hasBranch()) {
LOGGER.info("Rollbacking global transaction is NOT done, xid = {}.", globalSession.getXid());
return false;
}
}
if (success) {
SessionHelper.endRollbacked(globalSession);
// rollbacked event
eventBus.post(new GlobalTransactionEvent(globalSession.getTransactionId(), GlobalTransactionEvent.ROLE_TC,
globalSession.getTransactionName(), globalSession.getBeginTime(), System.currentTimeMillis(),
globalSession.getStatus()));
LOGGER.info("Rollback global transaction successfully, xid = {}.", globalSession.getXid());
}
return success;
}
全局回滚对每个branchSession都进行分支回滚的回调,在RM端由DataSourceManager.branchRollback方法调用UndoLogManager.undo逻辑,将undolog进行重放恢复数据。
@Override
public BranchStatus branchRollback(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, String resourceId,
String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = get(resourceId);
if (dataSourceProxy == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException();
}
try {
UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(dataSourceProxy.getDbType()).undo(dataSourceProxy, xid, branchId);
} catch (TransactionException te) {
StackTraceLogger.info(LOGGER, te,
"branchRollback failed. branchType:[{}], xid:[{}], branchId:[{}], resourceId:[{}], applicationData:[{}]. reason:[{}]",
new Object[]{branchType, xid, branchId, resourceId, applicationData, te.getMessage()});
if (te.getCode() == TransactionExceptionCode.BranchRollbackFailed_Unretriable) {
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_RollbackFailed_Unretryable;
} else {
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_RollbackFailed_Retryable;
}
}
return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_Rollbacked;
}
@Override
public void undo(DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy, String xid, long branchId) throws TransactionException {
Connection conn = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
PreparedStatement selectPST = null;
boolean originalAutoCommit = true;
for (; ; ) {
try {
conn = dataSourceProxy.getPlainConnection();
// The entire undo process should run in a local transaction.
if (originalAutoCommit = conn.getAutoCommit()) {
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
}
// Find UNDO LOG
selectPST = conn.prepareStatement(SELECT_UNDO_LOG_SQL);
selectPST.setLong(1, branchId);
selectPST.setString(2, xid);
rs = selectPST.executeQuery();
boolean exists = false;
while (rs.next()) {
exists = true;
// It is possible that the server repeatedly sends a rollback request to roll back
// the same branch transaction to multiple processes,
// ensuring that only the undo_log in the normal state is processed.
int state = rs.getInt(ClientTableColumnsName.UNDO_LOG_LOG_STATUS);
if (!canUndo(state)) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, ignore {} undo_log", xid, branchId, state);
}
return;
}
String contextString = rs.getString(ClientTableColumnsName.UNDO_LOG_CONTEXT);
Map context = parseContext(contextString);
byte[] rollbackInfo = getRollbackInfo(rs);
String serializer = context == null ? null : context.get(UndoLogConstants.SERIALIZER_KEY);
UndoLogParser parser = serializer == null ? UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance()
: UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance(serializer);
BranchUndoLog branchUndoLog = parser.decode(rollbackInfo);
try {
// put serializer name to local
setCurrentSerializer(parser.getName());
List sqlUndoLogs = branchUndoLog.getSqlUndoLogs();
if (sqlUndoLogs.size() > 1) {
Collections.reverse(sqlUndoLogs);
}
for (SQLUndoLog sqlUndoLog : sqlUndoLogs) {
TableMeta tableMeta = TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(dataSourceProxy.getDbType()).getTableMeta(
conn, sqlUndoLog.getTableName(), dataSourceProxy.getResourceId());
sqlUndoLog.setTableMeta(tableMeta);
AbstractUndoExecutor undoExecutor = UndoExecutorFactory.getUndoExecutor(
dataSourceProxy.getDbType(), sqlUndoLog);
undoExecutor.executeOn(conn);
}
} finally {
// remove serializer name
removeCurrentSerializer();
}
}
// If undo_log exists, it means that the branch transaction has completed the first phase,
// we can directly roll back and clean the undo_log
// Otherwise, it indicates that there is an exception in the branch transaction,
// causing undo_log not to be written to the database.
// For example, the business processing timeout, the global transaction is the initiator rolls back.
// To ensure data consistency, we can insert an undo_log with GlobalFinished state
// to prevent the local transaction of the first phase of other programs from being correctly submitted.
// See https://github.com/seata/seata/issues/489
if (exists) {
deleteUndoLog(xid, branchId, conn);
conn.commit();
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log deleted with {}", xid, branchId,
State.GlobalFinished.name());
}
} else {
insertUndoLogWithGlobalFinished(xid, branchId, UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance(), conn);
conn.commit();
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log added with {}", xid, branchId,
State.GlobalFinished.name());
}
}
return;
} catch (SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException e) {
// Possible undo_log has been inserted into the database by other processes, retrying rollback undo_log
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("xid {} branch {}, undo_log inserted, retry rollback", xid, branchId);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException rollbackEx) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to close JDBC resource while undo ... ", rollbackEx);
}
}
throw new BranchTransactionException(BranchRollbackFailed_Retriable, String
.format("Branch session rollback failed and try again later xid = %s branchId = %s %s", xid,
branchId, e.getMessage()), e);
} finally {
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (selectPST != null) {
selectPST.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
if (originalAutoCommit) {
conn.setAutoCommit(true);
}
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException closeEx) {
LOGGER.warn("Failed to close JDBC resource while undo ... ", closeEx);
}
}
}
}
AT-TC端总结:
AT-TM将数据存放在数据库,就可以通过zk、etcd等分布式协调服务进行高可用的部署使用,它的主要功能是将全局事务的数据进行保存,掌控全局的提交与回滚回调,并且可以对全局事务进行补偿重试。
最后总结
AT模式通过本地事务先提交,全局事务提交时异步删除undolog,优化了AT模式全局事务的性能,但是相对于朴素的正向补偿,AT模式带来了形成镜像的查询耗时、与TC通信的网络耗时等负面效果,只能说“软件的艺术之美源于trade-off”,是否使用seata-AT还是要看业务形态的适用情况与布道者在关键时机的推广落地。