第01章 Pandas基础
第02章 DataFrame基础运算
第03章 创建和持久化DataFrame
第04章 开始数据分析
第05章 探索性数据分析
第06章 选取数据子集
第07章 过滤行
第08章 索引对齐
7.1 计算布尔统计信息
读取电影数据集,检查前几行:
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> movie = pd.read_csv(
... "data/movie.csv", index_col="movie_title"
... )
>>> movie[["duration"]].head()
Duration
movie_title
Avatar 178.0
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End 169.0
Spectre 148.0
The Dark Knight Rises 164.0
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens NaN
判断电影时长是否超过两小时:
>>> movie_2_hours = movie["duration"] > 120
>>> movie_2_hours.head(10)
movie_title
Avatar True
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End True
Spectre True
The Dark Knight Rises True
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens False
John Carter True
Spider-Man 3 True
Tangled False
Avengers: Age of Ultron True
Harry Potter and the Half-Blood Prince True
Name: duration, dtype: bool
使用这个Series判断时长超过两小时的电影总和:
>>> movie_2_hours.sum()
1039
时长超过两小时的电影所占的比例:
>>> movie_2_hours.mean() * 100
21.13506916192026
前面的步骤没有删除缺失值,其实有误导性:
>>> movie["duration"].dropna().gt(120).mean() * 100
21.199755152009794
使用.describe方法输出概括统计性信息:
>>> movie_2_hours.describe()
count 4916
unique 2
top False
freq 3877
Name: duration, dtype: object
原理
使用.value_counts方法统计False和True所占的比例:
>>> movie_2_hours.value_counts(normalize=True)
False 0.788649
True 0.211351
Name: duration, dtype: float64
更多
可以使用DataFrame中的两列,创建布尔Series:
>>> actors = movie[
... ["actor_1_facebook_likes", "actor_2_facebook_likes"]
... ].dropna()
>>> (
... actors["actor_1_facebook_likes"]
... > actors["actor_2_facebook_likes"]
... ).mean()
0.9777687130328371
7.2 构造布尔条件
读取数据:
>>> movie = pd.read_csv(
... "data/movie.csv", index_col="movie_title"
... )
创建变量用于存储布尔数组:
>>> criteria1 = movie.imdb_score > 8
>>> criteria2 = movie.content_rating == "PG-13"
>>> criteria3 = (movie.title_year < 2000) | (
... movie.title_year > 2009
... )
将所有过滤器组成一个布尔数组:
>>> criteria_final = criteria1 & criteria2 & criteria3
>>> criteria_final.head()
movie_title
Avatar False
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End False
Spectre False
The Dark Knight Rises True
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens False
dtype: bool
更多
比较运算符是有顺序的:
>>> 5 < 10 and 3 > 4
False
>>> 5 < 10 and 3 > 4
False
>>> True and 3 > 4
False
>>> True and False
False
>>> False
False
7.3 使用布尔数组进行过滤
读取数据,设置过滤条件:
>>> movie = pd.read_csv(
... "data/movie.csv", index_col="movie_title"
... )
>>> crit_a1 = movie.imdb_score > 8
>>> crit_a2 = movie.content_rating == "PG-13"
>>> crit_a3 = (movie.title_year < 2000) | (
... movie.title_year > 2009
... )
>>> final_crit_a = crit_a1 & crit_a2 & crit_a3
再创建一组条件:
>>> crit_b1 = movie.imdb_score < 5
>>> crit_b2 = movie.content_rating == "R"
>>> crit_b3 = (movie.title_year >= 2000) & (
... movie.title_year <= 2010
... )
>>> final_crit_b = crit_b1 & crit_b2 & crit_b3
将这两个条件组成最后的条件:
>>> final_crit_all = final_crit_a | final_crit_b
>>> final_crit_all.head()
movie_title
Avatar False
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End False
Spectre False
The Dark Knight Rises True
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens False
dtype: bool
用最后的条件过滤数据:
>>> movie[final_crit_all].head()
color ... movie/likes
movie_title ...
The Dark Knight Rises Color ... 164000
The Avengers Color ... 123000
Captain America: Civil War Color ... 72000
Guardians of the Galaxy Color ... 96000
Interstellar Color ... 349000
.loc也可以使用这个过滤条件:
>>> movie.loc[final_crit_all].head()
color ... movie/likes
movie_title ...
The Dark Knight Rises Color ... 164000
The Avengers Color ... 123000
Captain America: Civil War Color ... 72000
Guardians of the Galaxy Color ... 96000
Interstellar Color ... 349000
另外也可以在.loc中指定列:
>>> cols = ["imdb_score", "content_rating", "title_year"]
>>> movie_filtered = movie.loc[final_crit_all, cols]
>>> movie_filtered.head(10)
imdb_score content_rating title_year
movie_title
The Dark ... 8.5 PG-13 2012.0
The Avengers 8.1 PG-13 2012.0
Captain A... 8.2 PG-13 2016.0
Guardians... 8.1 PG-13 2014.0
Interstellar 8.6 PG-13 2014.0
Inception 8.8 PG-13 2010.0
The Martian 8.1 PG-13 2015.0
Town & Co... 4.4 R 2001.0
Sex and t... 4.3 R 2010.0
Rollerball 3.0 R 2002.0
.iloc不支持布尔数组,但支持NumPy数组:
>>> movie.iloc[final_crit_all]
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
ValueError: iLocation based boolean indexing cannot use an indexable as a mask
>>> movie.iloc[final_crit_all.to_numpy()]
color ... movie/likes
movie_title ...
The Dark Knight Rises Color ... 164000
The Avengers Color ... 123000
Captain America: Civil War Color ... 72000
Guardians of the Galaxy Color ... 96000
Interstellar Color ... 349000
... ... ... ...
The Young Unknowns Color ... 4
Bled Color ... 128
Hoop Dreams Color ... 0
Death Calls Color ... 16
The Legend of God's Gun Color ... 13
更多
可以将所有条件放入一行:
>>> final_crit_a2 = (
... (movie.imdb_score > 8)
... & (movie.content_rating == "PG-13")
... & (
... (movie.title_year < 2000)
... | (movie.title_year > 2009)
... )
... )
>>> final_crit_a2.equals(final_crit_a)
True
7.4 对比行过滤和索引过滤
读取数据,并进行筛选:
>>> college = pd.read_csv("data/college.csv")
>>> college[college["STABBR"] == "TX"].head()
INSTNM ... GRAD_/_SUPP
3610 Abilene Christian University ... 25985
3611 Alvin Community College ... 6750
3612 Amarillo College ... 10950
3613 Angelina College ... PrivacySuppressed
3614 Angelo State University ... 21319.5
重复上面的步骤,使用STABBR列作为行索引,然后使用基于标签的进行提取:
>>> college2 = college.set_index("STABBR")
>>> college2.loc["TX"].head()
INSTNM ... GRAD_/_SUPP
3610 Abilene Christian University ... 25985
3611 Alvin Community College ... 6750
3612 Amarillo College ... 10950
3613 Angelina College ... PrivacySuppressed
3614 Angelo State University ... 21319.5
比较两种方法的速度:
>>> %timeit college[college['STABBR'] == 'TX']
1.75 ms ± 187 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
>>> %timeit college2.loc['TX']
882 µs ± 69.3 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
虽然用行索引快,但是创建行索引也需要时间:
>>> %timeit college2 = college.set_index('STABBR')
2.01 ms ± 107 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
更多
使用布尔条件选取多列:
>>> states = ["TX", "CA", "NY"]
>>> college[college["STABBR"].isin(states)]
INSTNM CITY ... MD_EARN_WNE_P10 GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP
192 Academy ... San Fran... ... 36000 35093
193 ITT Tech... Rancho C... ... 38800 25827.5
194 Academy ... Oakland ... NaN PrivacyS...
195 The Acad... Huntingt... ... 28400 9500
196 Avalon S... Alameda ... 21600 9860
... ... ... ... ... ...
7528 WestMed ... Merced ... NaN 15623.5
7529 Vantage ... El Paso ... NaN 9500
7530 SAE Inst... Emeryville ... NaN 9500
7533 Bay Area... San Jose ... NaN PrivacyS...
7534 Excel Le... San Antonio ... NaN 12125
>>> college2.loc[states]
INSTNM CITY ... MD_EARN_WNE_P10 GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP
STABBR ...
TX Abilene ... Abilene ... 40200 25985
TX Alvin Co... Alvin ... 34500 6750
TX Amarillo... Amarillo ... 31700 10950
TX Angelina... Lufkin ... 26900 PrivacyS...
TX Angelo S... San Angelo ... 37700 21319.5
... ... ... ... ... ...
NY Briarcli... Patchogue ... 38200 28720.5
NY Jamestow... Salamanca ... NaN 12050
NY Pratt Ma... New York ... 40900 26691
NY Saint Jo... Patchogue ... 52000 22143.5
NY Franklin... Brooklyn ... 20000 PrivacyS...
7.5 使用唯一和有序索引选取
读取数据集,使用STABBR作为索引,判断索引是否是单调的:
>>> college = pd.read_csv("data/college.csv")
>>> college2 = college.set_index("STABBR")
>>> college2.index.is_monotonic
False
对索引进行排序,并判断是否单调:
>>> college3 = college2.sort_index()
>>> college3.index.is_monotonic
True
查询从这三个DataFrame选取TX的速度:
>>> %timeit college[college['STABBR'] == 'TX']
1.75 ms ± 187 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
>>> %timeit college2.loc['TX']
1.09 ms ± 232 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
>>> %timeit college3.loc['TX']
304 µs ± 17.8 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
有序索引大大提高了速度。现在试试唯一索引:
>>> college_unique = college.set_index("INSTNM")
>>> college_unique.index.is_unique
True
使用布尔索引选取数据,返回的是个DataFrame:
>>> college[college["INSTNM"] == "Stanford University"]
INSTNM CITY ... MD_EARN_WNE_P10 GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP
4217 Stanford... Stanford ... 86000 12782
使用行索引进行选取:
>>> college_unique.loc["Stanford University"]
CITY Stanford
STABBR CA
HBCU 0
MENONLY 0
WOMENONLY 0
...
PCTPELL 0.1556
PCTFLOAN 0.1256
UG25ABV 0.0401
MD_EARN_WNE_P10 86000
GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP 12782
Name: Stanford University, Length: 26, dtype: object
更多
使用城市名和州缩写作为行索引:
>>> college.index = (
... college["CITY"] + ", " + college["STABBR"]
... )
>>> college = college.sort_index()
>>> college.head()
INSTNM CITY ... MD_EARN_WNE_P10 GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP
ARTESIA, CA Angeles ... ARTESIA ... NaN 16850
Aberdeen, SD Presenta... Aberdeen ... 35900 25000
Aberdeen, SD Northern... Aberdeen ... 33600 24847
Aberdeen, WA Grays Ha... Aberdeen ... 27000 11490
Abilene, TX Hardin-S... Abilene ... 38700 25864
选取所有来自Miami, FL的学校:
>>> college.loc["Miami, FL"].head()
INSTNM CITY ... MD_EARN_WNE_P10 GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP
Miami, FL New Prof... Miami ... 18700 8682
Miami, FL Manageme... Miami ... PrivacyS... 12182
Miami, FL Strayer ... Miami ... 49200 36173.5
Miami, FL Keiser U... Miami ... 29700 26063
Miami, FL George T... Miami ... 38600 PrivacyS...
比较二者的速度:
>>> %%timeit
>>> crit1 = college["CITY"] == "Miami"
>>> crit2 = college["STABBR"] == "FL"
>>> college[crit1 & crit2]
3.05 ms ± 66.4 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
>>> %timeit college.loc['Miami, FL']
369 µs ± 130 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
7.6 翻译SQL的WHERE子句
SQL语句如下:
SELECT
UNIQUE_ID,
DEPARTMENT,
GENDER,
BASE_SALARY
FROM
EMPLOYEE
WHERE
DEPARTMENT IN ('Houston Police Department-HPD',
'Houston Fire Department (HFD)') AND
GENDER = 'Female' AND
BASE_SALARY BETWEEN 80000 AND 120000;
使用Pandas实现上面SQL语句同样的目的:
>>> employee = pd.read_csv("data/employee.csv")
查看数据集的信息:
>>> employee.dtypes
UNIQUE_ID int64
POSITION_TITLE object
DEPARTMENT object
BASE_SALARY float64
RACE object
EMPLOYMENT_TYPE object
GENDER object
EMPLOYMENT_STATUS object
HIRE_DATE object
JOB_DATE object
dtype: object
>>> employee.DEPARTMENT.value_counts().head()
Houston Police Department-HPD 638
Houston Fire Department (HFD) 384
Public Works & Engineering-PWE 343
Health & Human Services 110
Houston Airport System (HAS) 106
Name: DEPARTMENT, dtype: int64
>>> employee.GENDER.value_counts()
Male 1397
Female 603
Name: GENDER, dtype: int64
>>> employee.BASE_SALARY.describe()
count 1886.000000
mean 55767.931601
std 21693.706679
min 24960.000000
25% 40170.000000
50% 54461.000000
75% 66614.000000
max 275000.000000
Name: BASE_SALARY, dtype: float64
创建过滤条件:
>>> depts = [
... "Houston Police Department-HPD",
... "Houston Fire Department (HFD)",
... ]
>>> criteria_dept = employee.DEPARTMENT.isin(depts)
>>> criteria_gender = employee.GENDER == "Female"
>>> criteria_sal = (employee.BASE_SALARY >= 80000) & (
... employee.BASE_SALARY <= 120000
... )
>>> criteria_final = (
... criteria_dept & criteria_gender & criteria_sal
... )
使用过滤条件筛选数据:
>>> select_columns = [
... "UNIQUE_ID",
... "DEPARTMENT",
... "GENDER",
... "BASE_SALARY",
... ]
>>> employee.loc[criteria_final, select_columns].head()
UNIQUE_ID DEPARTMENT GENDER BASE_SALARY
61 61 Houston ... Female 96668.0
136 136 Houston ... Female 81239.0
367 367 Houston ... Female 86534.0
474 474 Houston ... Female 91181.0
513 513 Houston ... Female 81239.0
更多
和SQL类似,Pandas也有between方法:
''' {.sourceCode .pycon}
>>> criteria_sal = employee.BASE_SALARY.between(
... 80_000, 120_000
... )
'''
7.7 用查询方法提高布尔索引的可读性
本节使用DataFrame的query方法。
读取数据:
>>> employee = pd.read_csv("data/employee.csv")
>>> depts = [
... "Houston Police Department-HPD",
... "Houston Fire Department (HFD)",
... ]
>>> select_columns = [
... "UNIQUE_ID",
... "DEPARTMENT",
... "GENDER",
... "BASE_SALARY",
... ]
创建查询字符串:
>>> qs = (
... "DEPARTMENT in @depts "
... " and GENDER == 'Female' "
... " and 80000 <= BASE_SALARY <= 120000"
... )
>>> emp_filtered = employee.query(qs)
>>> emp_filtered[select_columns].head()
UNIQUE_ID DEPARTMENT GENDER BASE_SALARY
61 61 Houston ... Female 96668.0
136 136 Houston ... Female 81239.0
367 367 Houston ... Female 86534.0
474 474 Houston ... Female 91181.0
513 513 Houston ... Female 81239.0
>>> top10_depts = (
... employee.DEPARTMENT.value_counts()
... .index[:10]
... .tolist()
... )
>>> qs = "DEPARTMENT not in @top10_depts and GENDER == 'Female'"
>>> employee_filtered2 = employee.query(qs)
>>> employee_filtered2.head()
UNIQUE_ID POSITION_TITLE ... HIRE_DATE JOB_DATE
0 0 ASSISTAN... ... 2006-06-12 2012-10-13
73 73 ADMINIST... ... 2011-12-19 2013-11-23
96 96 ASSISTAN... ... 2013-06-10 2013-06-10
117 117 SENIOR A... ... 1998-03-20 2012-07-21
146 146 SENIOR S... ... 2014-03-17 2014-03-17
7.8 用.where方法保留Series的大小
读取数据,电影名作为索引,actor_1_facebook_likes列不为空:
>>> movie = pd.read_csv(
... "data/movie.csv", index_col="movie_title"
... )
>>> fb_likes = movie["actor_1_facebook_likes"].dropna()
>>> fb_likes.head()
movie_title
Avatar 1000.0
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End 40000.0
Spectre 11000.0
The Dark Knight Rises 27000.0
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens 131.0
Name: actor_1_facebook_likes, dtype: float64
使用describe方法查看:
>>> fb_likes.describe()
count 4909.000000
mean 6494.488491
std 15106.986884
min 0.000000
25% 607.000000
50% 982.000000
75% 11000.000000
max 640000.000000
Name: actor_1_facebook_likes, dtype: float64
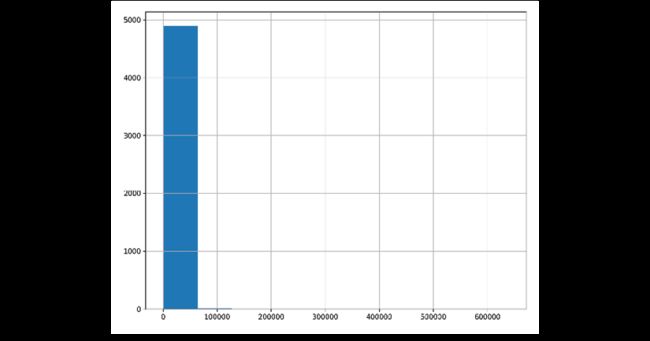
用柱状图查看分布:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 8))
>>> fb_likes.hist(ax=ax)
>>> fig.savefig(
... "c7-hist.png", dpi=300
... )
这张图看不出数据分布,大部分都是小于20000的:
>>> criteria_high = fb_likes < 20_000
>>> criteria_high.mean().round(2)
0.91
数据中有缺失值:
>>> fb_likes.where(criteria_high).head()
movie_title
Avatar 1000.0
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End NaN
Spectre 11000.0
The Dark Knight Rises NaN
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens 131.0
Name: actor_1_facebook_likes, dtype: float64
where中可以设置other参数可以用于控制替换值:
>>> fb_likes.where(criteria_high, other=20000).head()
movie_title
Avatar 1000.0
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End 20000.0
Spectre 11000.0
The Dark Knight Rises 20000.0
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens 131.0
Name: actor_1_facebook_likes, dtype: float64
创建另一个where条件:
>>> criteria_low = fb_likes > 300
>>> fb_likes_cap = fb_likes.where(
... criteria_high, other=20_000
... ).where(criteria_low, 300)
>>> fb_likes_cap.head()
movie_title
Avatar 1000.0
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End 20000.0
Spectre 11000.0
The Dark Knight Rises 20000.0
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens 300.0
Name: actor_1_facebook_likes, dtype: float64
前后两个Series大小相同:
>>> len(fb_likes), len(fb_likes_cap)
(4909, 4909)
重新用柱状图查看分布:
>>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 8))
>>> fb_likes_cap.hist(ax=ax)
>>> fig.savefig(
... "c7-hist2.png", dpi=300
... )
更多
Pandas有.clip、.clip_lower、.clip_upper三个方法用于最低值和最高值:
>>> fb_likes_cap2 = fb_likes.clip(lower=300, upper=20000)
>>> fb_likes_cap2.equals(fb_likes_cap)
True
7.9 遮掩DataFrame的行
读取数据,创建条件:
>>> movie = pd.read_csv(
... "data/movie.csv", index_col="movie_title"
... )
>>> c1 = movie["title_year"] >= 2010
>>> c2 = movie["title_year"].isna()
>>> criteria = c1 | c2
用mask方法遮挡上述条件的数据:
>>> movie.mask(criteria).head()
color ...
movie_title ...
Avatar Color ...
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End Color ...
Spectre NaN ...
The Dark Knight Rises NaN ...
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens NaN ...
注意上面三四五是缺失值:
>>> movie_mask = movie.mask(criteria).dropna(how="all")
>>> movie_mask.head()
color ...
movie_title ...
Avatar Color ...
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End Color ...
Spider-Man 3 Color ...
Harry Potter and the Half-Blood Prince Color ...
Superman Returns Color ...
.equals方法检查这两个条件是不一样的:
>>> movie_boolean = movie[movie["title_year"] < 2010]
>>> movie_mask.equals(movie_boolean)
False
但形状是一样的:
>>> movie_mask.shape == movie_boolean.shape
True
检查两个条件的数据类型:
>>> movie_mask.dtypes == movie_boolean.dtypes
color True
director_name True
num_critic_for_reviews True
duration True
director_facebook_likes True
...
title_year True
actor_2_facebook_likes True
imdb_score True
aspect_ratio True
movie_facebook_likes False
Length: 27, dtype: bool
Pandas有一个assert_frame_equal方法,也可以判断DataFrame是否相同:
>>> from pandas.testing import assert_frame_equal
>>> assert_frame_equal(
... movie_boolean, movie_mask, check_dtype=False
... )
更多
比较这两个条件的速度:
>>> %timeit movie.mask(criteria).dropna(how='all')
11.2 ms ± 144 μs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
>>> %timeit movie[movie['title_year'] < 2010]
1.07 ms ± 34.9 μs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
7.10 使用布尔值、整数位置和标签选取数据
读取数据,创建条件:
>>> movie = pd.read_csv(
... "data/movie.csv", index_col="movie_title"
... )
>>> c1 = movie["content_rating"] == "G"
>>> c2 = movie["imdb_score"] < 4
>>> criteria = c1 & c2
使用.loc过滤行:
>>> movie_loc = movie.loc[criteria]
>>> movie_loc.head()
color ... movie/likes
movie_title ...
The True Story of Puss'N Boots Color ... 90
Doogal Color ... 346
Thomas and the Magic Railroad Color ... 663
Barney's Great Adventure Color ... 436
Justin Bieber: Never Say Never Color ... 62000
这两个方法是等价的:
>>> movie_loc.equals(movie[criteria])
True
iloc需要将条件转换为numpy数组:
>>> movie_iloc = movie.iloc[criteria.to_numpy()]
>>> movie_iloc.equals(movie_loc)
True
选取数据类型是int64的:
>>> criteria_col = movie.dtypes == np.int64
>>> criteria_col.head()
color False
director_name False
num_critic_for_reviews False
duration False
director_facebook_likes False
dtype: bool
>>> movie.loc[:, criteria_col].head()
num_voted_users cast_total_facebook_likes movie_facebook_likes
movie_title
Avatar 886204 4834 33000
Pirates o... 471220 48350 0
Spectre 275868 11700 85000
The Dark ... 1144337 106759 164000
Star Wars... 8 143 0
因为是Series,criteria_col必须要转化为numpy就可以用于iloc:
>>> movie.iloc[:, criteria_col.to_numpy()].head()
num_voted_users cast_total_facebook_likes movie_facebook_likes
movie_title
Avatar 886204 4834 33000
Pirates o... 471220 48350 0
Spectre 275868 11700 85000
The Dark ... 1144337 106759 164000
Star Wars... 8 143 0
loc中将条件和列合用:
>>> cols = [
... "content_rating",
... "imdb_score",
... "title_year",
... "gross",
... ]
>>> movie.loc[criteria, cols].sort_values("imdb_score")
content_rating imdb_score title_year gross
movie_title
Justin Bi... G 1.6 2011.0 73000942.0
Sunday Sc... G 2.5 2008.0 NaN
Doogal G 2.8 2006.0 7382993.0
Barney's ... G 2.8 1998.0 11144518.0
The True ... G 2.9 2009.0 NaN
Thomas an... G 3.6 2000.0 15911333.0
.iloc必须使用列的位置:
>>> col_index = [movie.columns.get_loc(col) for col in cols]
>>> col_index
[20, 24, 22, 8]
>>> movie.iloc[criteria.to_numpy(), col_index].sort_values(
... "imdb_score"
... )
content_rating imdb_score title_year gross
movie_title
Justin Bi... G 1.6 2011.0 73000942.0
Sunday Sc... G 2.5 2008.0 NaN
Doogal G 2.8 2006.0 7382993.0
Barney's ... G 2.8 1998.0 11144518.0
The True ... G 2.9 2009.0 NaN
Thomas an... G 3.6 2000.0 15911333.0
(这小节和之前的内容重复不少)
第01章 Pandas基础
第02章 DataFrame基础运算
第03章 创建和持久化DataFrame
第04章 开始数据分析
第05章 探索性数据分析
第06章 选取数据子集
第07章 过滤行
第08章 索引对齐