一、springSecurity配置信息详解
参考:http://www.spring4all.com/article/446
二、springSecurity过滤器详解
- 我们已经知道Spring Security使用了springSecurityFillterChian作为了安全过滤的入口,接下来主要分析一下这个过滤器链都包含了哪些关键的过滤器,并且各自的使命是什么。
- springSecurity中过滤链及每一个过滤器的作用(按顺序),同时加粗的部分代表一些核心过滤器,需要重点了解。
1、SecurityContextPersistenceFilter :两个主要职责:请求来临时,创建SecurityContext安全上下文信息,请求结束时清空SecurityContextHolder。
2、HeaderWriterFilter (文档中并未介绍,非核心过滤器) 用来给http响应添加一些Header,比如X-Frame-Options, X-XSS-Protection*,X-Content-Type-Options.
3、CsrfFilter 在spring4这个版本中被默认开启的一个过滤器,用于防止csrf攻击,前后端使用json交互需要注意的一个问题。
4、LogoutFilter 顾名思义,处理注销的过滤器
5、UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 这个会重点分析,表单提交了username和password,被封装成token进行一系列的认证,便是主要通过这个过滤器完成的,在表单认证的方法中,这是最最关键的过滤器。
6、RequestCacheAwareFilter (文档中并未介绍,非核心过滤器) 内部维护了一个RequestCache,用于缓存request请求
7、SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter 此过滤器对ServletRequest进行了一次包装,使得request具有更加丰富的API
8、AnonymousAuthenticationFilter 匿名身份过滤器,这个过滤器个人认为很重要,需要将它与UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 放在一起比较理解,spring security为了兼容未登录的访问,也走了一套认证流程,只不过是一个匿名的身份。
9、SessionManagementFilter 和session相关的过滤器,内部维护了一个SessionAuthenticationStrategy,两者组合使用,常用来防止session-fixation protection attack,以及限制同一用户开启多个会话的数量
10、ExceptionTranslationFilter 直译成异常翻译过滤器,还是比较形象的,这个过滤器本身不处理异常,而是将认证过程中出现的异常交给内部维护的一些类去处理,具体是那些类下面详细介绍
11、FilterSecurityInterceptor 这个过滤器决定了访问特定路径应该具备的权限,访问的用户的角色,权限是什么?访问的路径需要什么样的角色和权限?这些判断和处理都是由该类进行的。
1、SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
- 用户在登录过一次之后,后续的访问便是通过sessionId来识别,从而认为用户已经被认证。具体在何处存放用户信息,便是在SecurityContextHolder中,认证相关的信息是如何被存放到其中的,便是通过SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
- 在Spring Security中,虽然安全上下文信息被存储于Session中,但我们在实际使用中不应该直接操作Session,而应当使用SecurityContextHolder。
- 源码分析:
public class SecurityContextPersistenceFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
static final String FILTER_APPLIED = "__spring_security_scpf_applied";
//安全上下文存储的仓库
private SecurityContextRepository repo;
public SecurityContextPersistenceFilter() {
//HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository是SecurityContextRepository接口的一个实现类
//使用HttpSession来存储SecurityContext
this(new HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository());
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest)req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse)res;
if (request.getAttribute("__spring_security_scpf_applied") != null) {
// ensure that filter is only applied once per request
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
boolean debug = this.logger.isDebugEnabled();
request.setAttribute("__spring_security_scpf_applied", Boolean.TRUE);
if (this.forceEagerSessionCreation) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
if (debug && session.isNew()) {
this.logger.debug("Eagerly created session: " + session.getId());
}
}
//包装request,response
HttpRequestResponseHolder holder = new HttpRequestResponseHolder(request, response);
//从Session中获取安全上下文信息
SecurityContext contextBeforeChainExecution = this.repo.loadContext(holder);
boolean var13 = false;
try {
var13 = true;
//请求开始,设置安全上下文信息,这样就避免了用户直接从Session中获取安全上下文信息 SecurityContextHolder.setContext(contextBeforeChainExecution);
chain.doFilter(holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse());
var13 = false;
} finally {
//过程操作失败,清空session
if (var13) {
SecurityContext contextAfterChainExecution = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
this.repo.saveContext(contextAfterChainExecution, holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse());
request.removeAttribute("__spring_security_scpf_applied");
if (debug) {
this.logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder now cleared, as request processing completed");
}
}
}
//请求结束后,清空安全上下文信息
SecurityContext contextAfterChainExecution = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
this.repo.saveContext(contextAfterChainExecution, holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse());
request.removeAttribute("__spring_security_scpf_applied");
if (debug) {
this.logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder now cleared, as request processing completed");
}
}
}
- 上面可以知道,过滤器一般负责核心的处理流程,而具体的业务实现,通常交给其中聚合的其他实体类。存储安全上下文和读取安全上下文的工作完全委托给了HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository处理,SecurityContextPersistenceFilter和HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository配合使用,构成了Spring Security整个调用链路的入口,为什么将它放在最开始的地方也是显而易见的,后续的过滤器中大概率会依赖Session信息和安全上下文信息。
2、UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
-
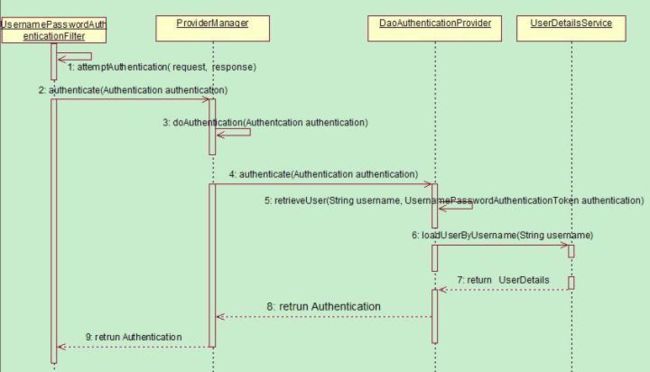
表单认证是最常用的一个认证方式,一个最直观的业务场景便是允许用户在表单中输入用户名和密码进行登录,而这背后的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,在整个Spring Security的认证体系中则扮演着至关重要的角色。UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter主要肩负起了调用身份认证器,校验身份的作用,具体可参照下面的时序图:
- 源码分析:
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
} else {
// //获取表单中的用户名和密码
String username = this.obtainUsername(request);
String password = this.obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
// //组装成username+password形式的token
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
//Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
this.setDetails(request, authRequest);
//交给内部的AuthenticationManager去认证,并返回认证信息
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter本身的代码只包含了上述这么一个方法,非常简略,而在其父类AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter中包含了大量的细节,值得我们分析,整个流程理解起来也并不难,主要就是内部调用了authenticationManager完成认证,根据认证结果执行successfulAuthentication或者unsuccessfulAuthentication,无论成功失败,一般的实现都是转发或者重定向等处理.
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter extends GenericFilterBean
implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware {
//包含了一个身份认证器
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
//用于实现remeberMe
private RememberMeServices rememberMeServices = new NullRememberMeServices();
private RequestMatcher requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher;
//这两个Handler很关键,分别代表了认证成功和失败相应的处理器
private AuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler = new SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler();
private AuthenticationFailureHandler failureHandler = new SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler();
...
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
...
Authentication authResult;
try {
//此处实际上就是调用UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter的attemptAuthentication方法
authResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authResult == null) {
//子类未完成认证,立刻返回
return;
}
//认证成功后,处理一些与session相关的方法
sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response);
}
//在认证过程中可以直接抛出异常,在过滤器中,就像此处一样,进行捕获
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
//内部服务异常
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
catch (AuthenticationException failed) {
//认证失败
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
return;
}
//认证成功
if (continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
//注意,认证成功后过滤器把authResult结果也传递给了成功处理器
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
}
}
- 总结整个过程的四个步骤
1.判断filter是否可以处理当前的请求,如果不可以则放行交给下一个filter
2.调用抽象方法attemptAuthentication进行验证,该方法由子类UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter实现
3.认证成功以后,回调一些与 session 相关的方法;
4.认证成功以后,认证成功后的相关回调方法;认证成功以后,认证成功后的相关回调方法;
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication success. Updating SecurityContextHolder to contain: "
+ authResult);
}
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
}
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
3、AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
- 匿名认证过滤器,可能有人会想:匿名了还有身份?我自己对于Anonymous匿名身份的理解是Spirng Security为了整体逻辑的统一性,即使是未通过认证的用户,也给予了一个匿名身份。而AnonymousAuthenticationFilter该过滤器的位置也是非常的科学的,它位于常用的身份认证过滤器(如UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter、BasicAuthenticationFilter、RememberMeAuthenticationFilter)之后,意味着只有在上述身份过滤器执行完毕后,SecurityContext依旧没有用户信息,AnonymousAuthenticationFilter该过滤器才会有意义——基于用户一个匿名身份。
public class AnonymousAuthenticationFilter extends GenericFilterBean implements
InitializingBean {
private AuthenticationDetailsSource authenticationDetailsSource = new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource();
private String key;
private Object principal;
private List authorities;
//自动创建一个"anonymousUser"的匿名用户,其具有ANONYMOUS角色
public AnonymousAuthenticationFilter(String key) {
this(key, "anonymousUser", AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList("ROLE_ANONYMOUS"));
}
/**
*
* @param key key用来识别该过滤器创建的身份
* @param principal principal代表匿名用户的身份
* @param authorities authorities代表匿名用户的权限集合
*/
public AnonymousAuthenticationFilter(String key, Object principal,
List authorities) {
Assert.hasLength(key, "key cannot be null or empty");
Assert.notNull(principal, "Anonymous authentication principal must be set");
Assert.notNull(authorities, "Anonymous authorities must be set");
this.key = key;
this.principal = principal;
this.authorities = authorities;
}
...
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
//过滤器链都执行到匿名认证过滤器这儿了还没有身份信息,塞一个匿名身份进去
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(
createAuthentication((HttpServletRequest) req));
}
chain.doFilter(req, res);
}
protected Authentication createAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request) {
//创建一个AnonymousAuthenticationToken
AnonymousAuthenticationToken auth = new AnonymousAuthenticationToken(key,
principal, authorities);
auth.setDetails(authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
return auth;
}
...
}
其实对比AnonymousAuthenticationFilter和UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter就可以发现一些门道了,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken对应AnonymousAuthenticationToken,他们都是Authentication的实现类,而Authentication则是被SecurityContextHolder(SecurityContext)持有的,一切都被串联在了一起。
4、ExceptionTranslationFilter
- ExceptionTranslationFilter异常转换过滤器位于整个springSecurityFilterChain的后方,用来转换整个链路中出现的异常,将其转化,顾名思义,转化以意味本身并不处理。一般其只处理两大类异常:AccessDeniedException访问异常和AuthenticationException认证异常
- 这个过滤器非常重要,因为它将Java中的异常和HTTP的响应连接在了一起,这样在处理异常时,我们不用考虑密码错误该跳到什么页面,账号锁定该如何,只需要关注自己的业务逻辑,抛出相应的异常便可。如果该过滤器检测到AuthenticationException,则将会交给内部的AuthenticationEntryPoint去处理,如果检测到AccessDeniedException,需要先判断当前用户是不是匿名用户,如果是匿名访问,则和前面一样运行AuthenticationEntryPoint,否则会委托给AccessDeniedHandler去处理,而AccessDeniedHandler的默认实现,是AccessDeniedHandlerImpl。所以ExceptionTranslationFilter内部的AuthenticationEntryPoint是至关重要的,顾名思义:认证的入口点。
5、FilterSecurityInterceptor
- 由什么控制哪些资源是受限的,这些受限的资源需要什么权限,需要什么角色…这一切和访问控制相关的操作,都是由FilterSecurityInterceptor完成的。也就是说FilterSecurityInterceptor和鉴权有关。
- FilterSecurityInterceptor的工作流程
FilterSecurityInterceptor从SecurityContextHolder中获取Authentication对象,然后比对用户拥有的权限和资源所需的权限。前者可以通过Authentication对象直接获得,而后者则需要引入我们之前一直未提到过的两个类:SecurityMetadataSource,AccessDecisionManager。
- 源码:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
invoke(fi);
}
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
if ((fi.getRequest() != null)
&& (fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
&& observeOncePerRequest) {
// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe
// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
else {
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (fi.getRequest() != null) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
}
#1. before invocation重要
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
#2. 可以理解开始请求真正的 /persons 服务
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
}
finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
#3. after Invocation
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
- 总结整个过程为三个步骤
1、before invocation重要
2、请求真正的 /persons 服务
3、after Invocation
(1)before invocation: AccessDecisionManager
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
...
Collection attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource()
.getAttributes(object);
...
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
// Attempt authorization
try {
#1.重点
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
}
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) {
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,accessDeniedException));
throw accessDeniedException;
}
...
}
attributes和object 是什么?发现object为当前请求的 url:/persons, 那么getAttributes方法就是使用当前的访问资源路径去匹配我们自己定义的匹配规则
三、授权
Spring Security默认使用AffirmativeBased实现 AccessDecisionManager 的 decide 方法来实现授权。
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object,
Collection configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException {
int deny = 0;
#1.调用AccessDecisionVoter 进行vote(投票)
for (AccessDecisionVoter voter : getDecisionVoters()) {
int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configAttributes);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result);
}
switch (result) {
#1.1只要有voter投票为ACCESS_GRANTED,则通过 直接返回
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_GRANTED://1
return;
@#1.2只要有voter投票为ACCESS_DENIED,则记录一下
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_DENIED://-1
deny++;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
if (deny > 0) {
#2.如果有两个及以上AccessDecisionVoter(姑且称之为投票者吧)都投ACCESS_DENIED,则直接就不通过了
throw new AccessDeniedException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied", "Access is denied"));
}
// To get this far, every AccessDecisionVoter abstained
checkAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions();
}
- 总结整个过程
1、调用AccessDecisionVoter 进行vote(投票)
2、只要有投通过(ACCESS_GRANTED)票,则直接判为通过。
3、如果没有投通过则 deny++ ,最后判断if(deny>0 抛出AccessDeniedException(未授权)
参考:
http://www.spring4all.com/article/447
https://github.com/qiuzhangwei/logback