基于springboot2.1.4
在springboot中对于动态代理的实现,主要通过org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer实现,主要的方式有两种:1、通过Enhancer 对目标class进行封装(EnhancerBySpringCGlib的后缀),在需要实例化时,调用newInstance,生成proxyBean(EnhancerBySpringCGlib的后缀)。2、直接通过Enhancer生成目标class的proxybean(EnhancerBySpringCGlib的后缀)
springboot的源码这两种用法表达得比较复杂,本文通过简易版的demo,呈现springboot对enhancer的使用原理。大概理解其使用方式
1、通过Enhancer 对目标class进行封装
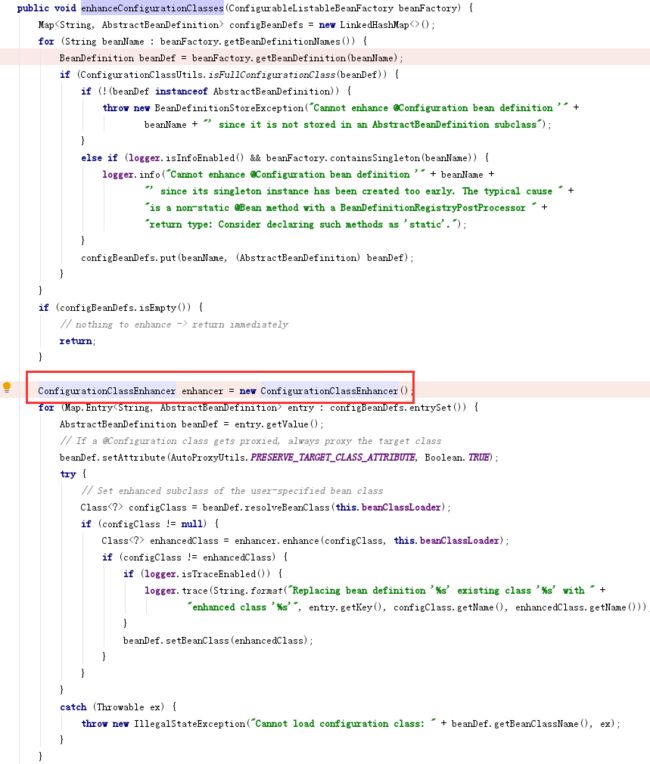
在beandefinition阶段,对所有的bean都定义完成之后,会对@Configuration的配置类都通过Enhancer封装对应的class--->org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#enhanceConfigurationClasses在ConfigurationClassEnhancer中实现了一些org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor,调用proxyBean的方法时会通过filter对拦截的方法适配对应的MethodInterceptor。Enhancer封装对应的class需要等到org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean时在org.springframework.beans.factory.support.SimpleInstantiationStrategy#instantiate处,才生成具体的proxyBean实例
简化版demo如下:
//先定义一个target class
public class TargetService {
public void doService(){
System.out.println("doService() TargetService");
}
public void testService(){
System.out.println("testService() TargetService");
}
}
//创建interceptor和filter
//org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor
class TestMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor{
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("before");
Object res = methodProxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
System.out.println("after");
return res;
}
}
class TestCallbackFilter implements CallbackFilter{
@Override
public int accept(Method method) {
if(method.getName().equals("doService")){
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
}
//单元测试
@Test
public void test1() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(TargetService.class);
// enhancer.setCallbackType(TestMethodInterceptor.class);
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new TestCallbackFilter());//filter要比callbacks先设置
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(new Class[]{TestMethodInterceptor.class,NoOp.class});
Class subclass = enhancer.createClass();
Enhancer.registerCallbacks(subclass, new Callback[] {
new TestMethodInterceptor(),NoOp.INSTANCE
});
System.out.println(subclass);
TargetService obj = (TargetService) subclass.newInstance();
obj.doService();
obj.testService();
}
filter返回中的数字表示的是callback列表中的下标,通过该下标调用对应的interceptor
2、直接通过Enhancer生成目标class的proxybean
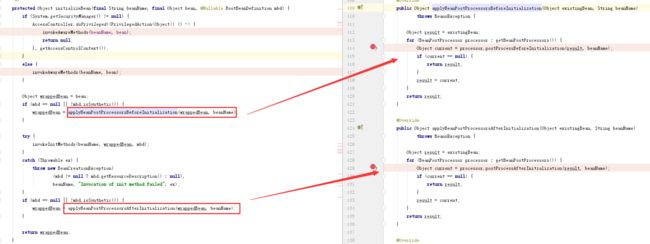
这个主要体现在生成bean过程中对用@Async注解的方法对应的类进行封装的时候-->org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean
其中一个processor是org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor该processor会通过AsyncAnnotationAdvisor创建拦截器(org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor 父类是advice,跟org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor不是同一个东西)和拦截位置(pointcut 定位使用了@Async的方法)
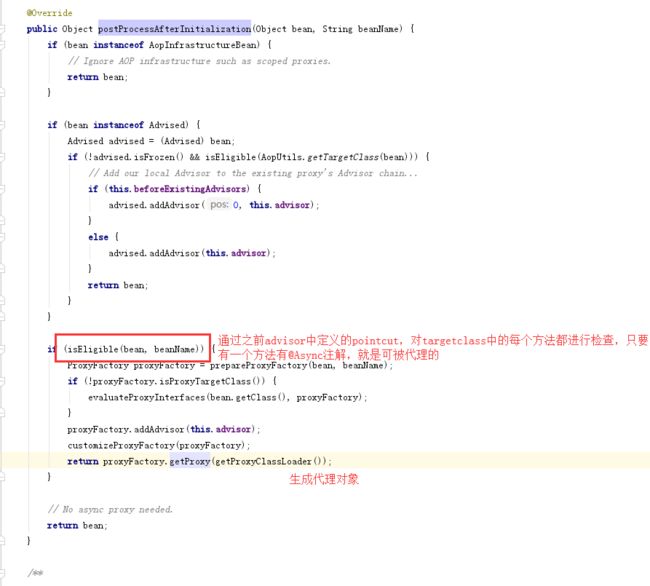
通过org.springframework.aop.framework.AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization生成ProxyBean
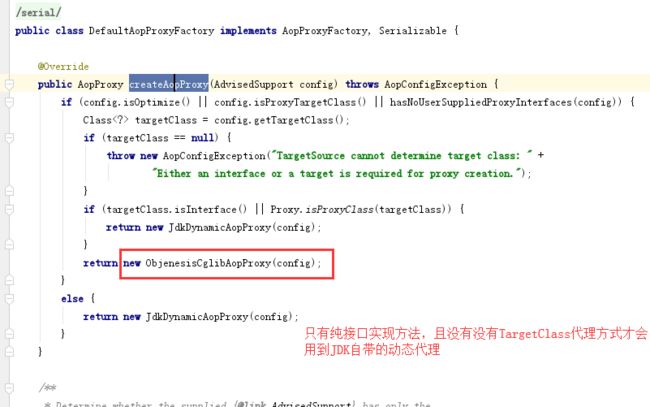
当一个bean时proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());主要通过org.springframework.aop.framework.DefaultAopProxyFactory#createAopProxy
然后通过org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy#getProxy(java.lang.ClassLoader)获取代理实例
其中有个org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptor (implements org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor)会通过链式调用的方式,对advisor中的advice(实际上以org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor方式存在)进行调用,具体代码不分析了, 可参考此处,大致的调用方式以简单demo呈现(原理类似,但是spring的封装要复杂很多)
package com.eshin.autotest;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.*;
import java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author Eshin
* @title: TestInterceptorChain
* @projectName pay
* @date 2019/6/2619:38
*/
public class TestInterceptorChain {
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
}
@Test
public void name() {
}
@Test
public void test() {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(TargetService.class);
Callback callbacks[] = new Callback[] {new TestMethodInterceptor(), NoOp.INSTANCE};
enhancer.setCallbacks(callbacks);
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new CallbackFilter() {
@Override
public int accept(Method method) {
if(method.getName().equals("testService")){
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
});
TargetService proxyBean = (TargetService)enhancer.create();
proxyBean.doService();
proxyBean.testService();
}
class TestMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor{
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("before");
// Object res = methodProxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
AdviceChainMethodInvocation ac = new AdviceChainMethodInvocation(methodProxy, obj, args);
ac.addChain(new TestAdviceInterceptor());
ac.addChain(new TestAdviceInterceptor2());
Object res = ac.proceed();
System.out.println("after");
return res;
}
}
class TestAdviceInterceptor implements org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor{
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("before TestAdviceInterceptor advice");
Object rsp = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("after TestAdviceInterceptor advice");
return rsp;
}
}
class TestAdviceInterceptor2 implements org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor{
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("before TestAdviceInterceptor2 advice");
Object rsp = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("after TestAdviceInterceptor2 advice");
return rsp;
}
}
class AdviceChainMethodInvocation implements MethodInvocation {
List chain = new ArrayList<>();
int index = 0;
Object targetMethod = null;
Object proxy = null;
Object[] args = null;
public AdviceChainMethodInvocation(Object targetMethod, Object proxy, Object[]args){
this.targetMethod = targetMethod;
this.proxy = proxy;
this.args = args;
}
public void addChain(org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor ir){
chain.add(ir);
}
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
if(index < chain.size()){
index +=1;
result = chain.get(index-1).invoke(this);
return result;
}
return ((MethodProxy)this.targetMethod).invokeSuper(this.proxy,this.args);
}
@Override
public Object getThis() {
return null;
}
@Override
public AccessibleObject getStaticPart() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Method getMethod() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Object[] getArguments() {
return new Object[0];
}
}
}
注意:Enhancer有个硬伤,就是无法对已经封装过的targetclass,再继续封装多一次,无法实现多个interceptor的链式调用。
3、再来看看ProxyFactory
ProxyFactory总是和Enhaner的使用同时出现,在ScopeProxyFactoryBean和@Async的解析都有用到
先看一个简单例子
public interface IService {
void doService();
}
public interface IWork {
void doWork();
}
public class TargetService {
public void doService(){
System.out.println("doService() TargetService");
}
public void testService(){
System.out.println("testService() TargetService");
}
}
public class TargetService1 implements IService, IWork {
public void doService(){
System.out.println("doService() TargetService1");
}
public void testService(){
System.out.println("testService() TargetService1");
}
@Override
public void doWork() {
System.out.println("doWork() TargetService1");
}
}
@Test
public void testProxyFactory(){
ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory();
pf.setTarget(new TargetService());
pf.addAdvice(new TestAdviceInterceptor());
pf.addAdvice(new TestAdviceInterceptor2());
TargetService targetService = (TargetService) pf.getProxy();
targetService.testService();
}
@Test
public void testProxyFactory1(){
ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory();
pf.setTarget(new TargetService1());
pf.addAdvice(new TestAdviceInterceptor());
pf.addAdvice(new TestAdviceInterceptor2());
TargetService1 targetService = (TargetService1) pf.getProxy();
targetService.testService();
targetService.doService();
targetService.doWork();
System.out.println("==========================");
pf.addInterface(IWork.class);//指定能代理的接口,指定后代理的对象只能转换成对应接口对象
IWork work = (IWork) pf.getProxy();
work.doWork();
}
f.getProxy()的逻辑可以参考这里第2点