PyTorch 实现 Classification 分类
跟着莫凡大神学习
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# make fake data
n_data =torch.ones(100,2)
# https://ptorch.com/docs/1/torchlists
x0 = torch.normal(2*n_data,1) # class0 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
# torch.normal(means, std, out=None) means (Tensor) – 均值 , std (Tensor) – 标准差, out (Tensor) – 可选的输出张量
y0 = torch.zeros(100)
x1 = torch.normal(-2*n_data,1) # class1 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y1 = torch.ones(100)
x=torch.cat((x0,x1),0).type(torch.FloatTensor) # shape (200, 2) FloatTensor = 32-bit floating
y=torch.cat((y0,y1),0).type(torch.LongTensor) # shape (200,) LongTensor = 64-bit integer
x,y=Variable(x),Variable(y)
# plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(),y.data.numpy())
# plt.show()
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,n_feature,n_hidden,n_output):
super(Net,self).__init__()
self.hidden = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature,n_hidden)
self.predict = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden,n_output)
def forward(self, x):
x=F.relu(self.hidden(x))
x=self.predict(x)
return x
net =Net(2,10,2) # define the network
plt.ion() # something about plotting
plt.show()
optimizer =torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr=0.002) #优化参数
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is NOT an one-hotted
for t in range(100):
out =net(x) #开始训练
loss = loss_func(out,y) # 一定要预测的值在前,真实值在后
# below are
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step()
if t % 2==0: # 每训练2次 ,打印一次
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla()
prediction = torch.max(out,1)[1] # why is 1
predy = prediction.data.numpy().squeeze()
target_y = y.data.numpy()
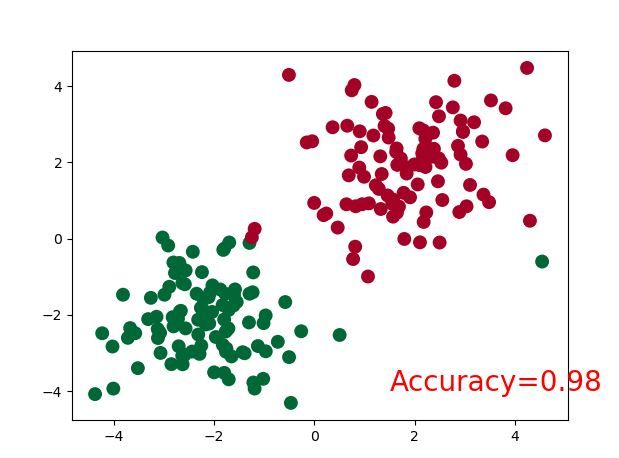
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:,0], x.data.numpy()[:,1],c=predy,s=100,lw=0,cmap='RdYlGn')
accuracy = sum(predy == target_y)/200
plt.text(1.5,-4,'Accuracy=%.2f' % accuracy,fontdict={'size':20,'color':'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()刚开始不太清楚上面使用的数据,所以自己做了一些其他测试
import torch
n_data =torch.ones(4,2)
print(n_data)
x0 = torch.normal(2*n_data,1)
print('x0\n', x0)
y0 = torch.zeros(4)
print('yo\n',y0)
x1 = torch.normal(-2*n_data,1)
print('x1\n', x1)
y1 = torch.ones(4)
print('y1\n',y1)
x=torch.cat((x0,x1),0).type(torch.FloatTensor) # shape (200, 2) FloatTensor = 32-bit floating
print('x\n',x)
y=torch.cat((y0,y1),0).type(torch.LongTensor) # shape (200,) LongTensor = 64-bit integer
print('y\n',y)输出结果如下:
1 1
1 1
1 1
1 1
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4x2]
x0
0.2261 3.0315
2.0241 1.5661
4.7188 2.0684
1.8433 2.0262
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4x2]
yo
0
0
0
0
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4]
x1
-0.4156 -1.0854
-1.5244 -1.1929
-2.2120 -0.3639
-1.4513 -2.1948
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4x2]
y1
1
1
1
1
[torch.FloatTensor of size 4]
x (PS: 二维平面的坐标)
0.2261 3.0315
2.0241 1.5661
4.7188 2.0684
1.8433 2.0262
-0.4156 -1.0854
-1.5244 -1.1929
-2.2120 -0.3639
-1.4513 -2.1948
[torch.FloatTensor of size 8x2]
y (针对二维平面每个坐标的 标签)
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
[torch.LongTensor of size 8]
Process finished with exit code 0