HTML学习笔记
-
- HTML学习笔记
- 1基础学习
- 1标题
- 2格式简介
- 3HTML 链接
- 4HTML 图像
- 5空的 HTML 元素
- 6HTML 属性
- 7 HTML全局属性
- 8HTML 水平线
- 9HTML 注释
- 10HTML 标签参考手册
- 11HTML 段落
- 12HTML 折行
- 13HTML 样式
- 4HTML 样式实例 - 背景颜色
- 15HTML 样式实例 - 字体颜色和尺寸
- 16HTML 样式实例 - 文本对齐
- 17HTML 用于短的引用
- 18用于长引用的 HTML
- 19用于缩略词的 HTML
- 20用于联系信息的 HTML
- 21用于著作标题的 HTML
- 22用于双向重写的 HTML
- 23HTML 计算机代码元素
- 24HTML 样本格式
- 25HTML 代码格式
- 26HTML 变量格式化
- 27总结HTML 计算机代码元素
- 28如何使用样式
- 29HTML 链接语法
- 30HTML 链接 - target 属性
- 31图像标签和源属性Src
- 32替换文本属性Alt
- 33创建表格
- 34表格标签
- 35无序列表
- 36有序列表
- 37定义列表
- 38HTML 元素
- 39HTML 元素
- 40HTML 分组标签
- 41HTML 类
- 42分类块级元素
- 43分类行内元素
- 44使用 div元素的 HTML 布局
- 45使用 HTML5 的网站布局
- 2HTML 响应式 Web 设计
- 1什么是响应式 Web 设计
- 2创建您自己的响应式设计
- 3使用 Bootstrap
- 3HTML框架
- 1框架
- 2框架标签Frame
- 4HTML Iframe
- 1iframe 用于在网页内显示网页
- 2添加 iframe 的语法
- 3Iframe - 设置高度和宽度
- 4Iframe - 删除边框
- 5使用 iframe 作为链接的目标
- 5HTML背景
- 1背景Backgrounds
- 2背景Background
- 6HTML 脚本
- 1HTML script 元素
- 7HTML 头部元素
- 1HTML 元素
- 2HTML 元素
- 3HTML 元素
- 4HTML 元素
- 5HTML
- 6HTML 元素
- 8HTML 字符实体
- 1HTML 实体
- 9HTML 统一资源定位器
- 10HTML Web Server
- 11HTML 颜色
- 1HTML 颜色
- 2HTML 颜色名
- 1HTML 颜色
- 12HTML 401 快速参考
- 1基础学习
- HTML学习笔记
HTML学习笔记
1:基础学习
1:标题
<h1>我的第一个标题h1>
<p>我的第一个段落。p>
2:格式简介
• <html> 与 html> 之间的文本描述网页
• <body> 与 body> 之间的文本是可见的页面内容
• <h1> 与 h1> 之间的文本被显示为标题
• <p> 与 p> 之间的文本被显示为段落
3:HTML 链接
HTML 链接是通过 <a> 标签进行定义的。
实例
<a href="http://www.w3school.com.cn">This is a linka>
4:HTML 图像
HTML 图像是通过 <img> 标签进行定义的。
实例
<img src="w3school.jpg" width="104" height="142" />
注释:图像的名称和尺寸是以属性的形式提供的。
5:空的 HTML 元素
在开始标签中添加斜杠,比如 <br />,是关闭空元素的正确方法,HTML、XHTML 和 XML 都接受这种方式。
6:HTML 属性
HTML 标签可以拥有属性。属性提供了有关 HTML 元素的更多的信息。
属性总是以名称/值对的形式出现,比如:name="value"。
属性总是在 HTML 元素的开始标签中规定
属性例子 1:
<h1> 定义标题的开始。
<h1 align="center"> 拥有关于对齐方式的附加信息。
属性例子 2:
<body> 定义 HTML 文档的主体。
<body bgcolor="yellow"> 拥有关于背景颜色的附加信息。
属性例子 3:
<table> 定义 HTML 表格。(您将在稍后的章节学习到更多有关 HTML 表格的内容)
<table border="1"> 拥有关于表格边框的附加信息
7: HTML全局属性
HTML全局属性
8:HTML 水平线
<hr /> 标签在 HTML 页面中创建水平线。
hr 元素可用于分隔内容。
9:HTML 注释
10:HTML 标签参考手册
W3School 的标签参考手册提供了有关这些标题及其属性的更多信息。
您将在本教程下面的章节中学到更多有关 HTML 标签和属性的知识。
标签 描述
定义 HTML 文档。
定义文档的主体。
to 定义 HTML 标题
定义水平线。
11:HTML 段落
段落是通过 <p> 标签定义的。
实例
<p>This is a paragraphp>
<p>This is another paragraphp>
12:HTML 折行
如果您希望在不产生一个新段落的情况下进行换行(新行),请使用 <br /> 标签:
<p>This is<br />a para<br />graph with line breaksp>
13:HTML 样式
<html>
<body style="background-color:PowderBlue;">
<h1>Look! Styles and colorsh1>
<p style="font-family:verdana;color:red">
This text is in Verdana and redp>
<p style="font-family:times;color:green">
This text is in Times and greenp>
<p style="font-size:30px">This text is 30 pixels highp>
body>
html>
4:HTML 样式实例 - 背景颜色
background-color 属性为元素定义了背景颜色:
<html>
<body style="background-color:yellow">
<h2 style="background-color:red">This is a headingh2>
<p style="background-color:green">This is a paragraph.p>
body>
html>
15:HTML 样式实例 - 字体、颜色和尺寸
font-family、color 以及 font-size 属性分别定义元素中文本的字体系列、颜色和字体尺寸:
<html>
<body>
<h1 style="font-family:verdana">A headingh1>
<p style="font-family:arial;color:red;font-size:20px;">A paragraph.p>
body>
html>
16:HTML 样式实例 - 文本对齐
text-align 属性规定了元素中文本的水平对齐方式:
<html>
<body>
<h1 style="text-align:center">This is a headingh1>
<p>The heading above is aligned to the center of this page.p>
body>
html>
17:HTML 用于短的引用
HTML <q> 元素定义短的引用。
浏览器通常会为 <q> 元素包围引号。
实例
<p>WWF 的目标是:<q>构建人与自然和谐共存的世界。q>p>
18:用于长引用的 HTML
HTML <blockquote> 元素定义被引用的节。
浏览器通常会对 <blockquote> 元素进行缩进处理。
实例
<p>以下内容引用自 WWF 的网站:p>
<blockquote cite="http://www.worldwildlife.org/who/index.html">
五十年来,WWF 一直致力于保护自然界的未来。
世界领先的环保组织,WWF 工作于 100 个国家,
并得到美国一百二十万会员及全球近五百万会员的支持。
blockquote>
19:用于缩略词的 HTML
HTML <abbr> 元素定义缩写或首字母缩略语。
对缩写进行标记能够为浏览器、翻译系统以及搜索引擎提供有用的信息。
实例
<p><abbr title="World Health Organization">WHOabbr> 成立于 1948 年。p>
20:用于联系信息的 HTML
HTML <address> 元素定义文档或文章的联系信息(作者/拥有者)。
此元素通常以斜体显示。大多数浏览器会在此元素前后添加折行。
实例
<address>
Written by Donald Duck.<br>
Visit us at:<br>
Example.com<br>
Box 564, Disneyland<br>
USA
address>
21:用于著作标题的 HTML
HTML <cite> 元素定义著作的标题。
浏览器通常会以斜体显示 <cite> 元素。
实例
<p><cite>The Screamcite> by Edward Munch. Painted in 1893.p>
22:用于双向重写的 HTML
HTML <bdo> 元素定义双流向覆盖(bi-directional override)。
<bdo> 元素用于覆盖当前文本方向:
实例
<bdo dir="rtl">This text will be written from right to leftbdo>
23:HTML 计算机代码元素
HTML 键盘格式
HTML <kbd> 元素定义键盘输入:
实例
<p><kbd>File | Open...kbd>p>
24:HTML 样本格式
HTML <samp> 元素定义计算机输出示例:
实例
<samp>
demo.example.com login: Apr 12 09:10:17
Linux 2.6.10-grsec+gg3+e+fhs6b+nfs+gr0501+++p3+c4a+gr2b-reslog-v6.189
samp>
25:HTML 代码格式
HTML <code> 元素定义编程代码示例:
实例
<code>
var person = { firstName:"Bill", lastName:"Gates", age:50, eyeColor:"blue" }
code>
<p>code 元素不保留多余的空格和折行:p>
<p>如需解决该问题,您必须在 pre 元素中包围代码:p>
<code>
<pre>
var person = {
firstName:"Bill",
lastName:"Gates",
age:50,
eyeColor:"blue"
}
pre>
code>
26:HTML 变量格式化
HTML <var> 元素定义数学变量:
实例
<p>Einstein wrote:p>
<p><var>E = m c<sup>2sup>var>p>
27:(总结)HTML 计算机代码元素
标签 描述
<code> 定义计算机代码文本
<kbd> 定义键盘文本
<samp> 定义计算机代码示例
<var> 定义变量
<pre> 定义预格式化文本
28:如何使用样式
当浏览器读到一个样式表,它就会按照这个样式表来对文档进行格式化。有以下三种方式来插入样式表:
外部样式表
当样式需要被应用到很多页面的时候,外部样式表将是理想的选择。使用外部样式表,你就可以通过更改一个文件来改变整个站点的外观。
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="mystyle.css">
head>
内部样式表
当单个文件需要特别样式时,就可以使用内部样式表。你可以在 head 部分通过 <style> 标签定义内部样式表。
<head>
<style type="text/css">
body {
background-color: red}
p {
margin-left: 20px}
style>
head>
内联样式
当特殊的样式需要应用到个别元素时,就可以使用内联样式。 使用内联样式的方法是在相关的标签中使用样式属性。样式属性可以包含任何 CSS 属性。以下实例显示出如何改变段落的颜色和左外边距。
<p style="color: red; margin-left: 20px">
This is a paragraph
p>
标签 描述
<style> 定义样式定义。
<link> 定义资源引用。
<div> 定义文档中的节或区域(块级)。
<span> 定义文档中的行内的小块或区域。
<font> 规定文本的字体、字体尺寸、字体颜色。不赞成使用。请使用样式。
<basefont> 定义基准字体。不赞成使用。请使用样式。
<center> 对文本进行水平居中。不赞成使用。请使用样式
29:HTML 链接语法
链接的 HTML 代码很简单。它类似这样:
<a href="url">Link texta>
href 属性规定链接的目标。
开始标签和结束标签之间的文字被作为超级链接来显示。
实例
<a href="http://www.w3school.com.cn/">Visit W3Schoola>
30:HTML 链接 - target 属性
使用 Target 属性,你可以定义被链接的文档在何处显示。
下面的这行会在新窗口打开文档:
<a href="http://www.w3school.com.cn/" target="_blank">Visit W3School!a>
31:图像标签()和源属性(Src)
在 HTML 中,图像由 ![]() 标签定义。
标签定义。
![]() 是空标签,意思是说,它只包含属性,并且没有闭合标签。
要在页面上显示图像,你需要使用源属性(src)。src 指 "source"。源属性的值是图像的 URL 地址。
定义图像的语法是:
是空标签,意思是说,它只包含属性,并且没有闭合标签。
要在页面上显示图像,你需要使用源属性(src)。src 指 "source"。源属性的值是图像的 URL 地址。
定义图像的语法是:
 "url" />
URL 指存储图像的位置。如果名为 "boat.gif" 的图像位于 www.w3school.com.cn 的 images 目录中,那么其 URL 为 http://www.w3school.com.cn/images/boat.gif。
浏览器将图像显示在文档中图像标签出现的地方。如果你将图像标签置于两个段落之间,那么浏览器会首先显示第一个段落,然后显示图片,最后显示第二段。
"url" />
URL 指存储图像的位置。如果名为 "boat.gif" 的图像位于 www.w3school.com.cn 的 images 目录中,那么其 URL 为 http://www.w3school.com.cn/images/boat.gif。
浏览器将图像显示在文档中图像标签出现的地方。如果你将图像标签置于两个段落之间,那么浏览器会首先显示第一个段落,然后显示图片,最后显示第二段。
32:替换文本属性(Alt)
alt 属性用来为图像定义一串预备的可替换的文本。替换文本属性的值是用户定义的。
<img src="boat.gif" alt="Big Boat">
在浏览器无法载入图像时,替换文本属性告诉读者她们失去的信息。此时,浏览器将显示这个替代性的文本而不是图像。为页面上的图像都加上替换文本属性是个好习惯,这样有助于更好的显示信息,并且对于那些使用纯文本浏览器的人来说是非常有用的
<body background="/i/eg_background.jpg">
<h3>图像背景h3>
<p>gif 和 jpg 文件均可用作 HTML 背景。p>
<p>如果图像小于页面,图像会进行重复。p>
body>
33:创建表格
<html>
<body>
<p>每个表格由 table 标签开始。p>
<p>每个表格行由 tr 标签开始。p>
<p>每个表格数据由 td 标签开始。p>
<h4>一列:h4>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td>100td>
tr>
table>
<h4>一行三列:h4>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td>100td>
<td>200td>
<td>300td>
tr>
table>
<h4>两行三列:h4>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td>100td>
<td>200td>
<td>300td>
tr>
<tr>
<td>400td>
<td>500td>
<td>600td>
tr>
table>
body>
html>
34:表格标签
表格 描述
<table> 定义表格
<caption> 定义表格标题。
<th> 定义表格的表头。
<tr> 定义表格的行。
<td> 定义表格单元。
<thead> 定义表格的页眉。
<tbody> 定义表格的主体。
<tfoot> 定义表格的页脚。
<col> 定义用于表格列的属性。
<colgroup> 定义表格列的组。35:无序列表
无序列表是一个项目的列表,此列项目使用粗体圆点(典型的小黑圆圈)进行标记。
无序列表始于 <ul> 标签。每个列表项始于 <li>。
<ul>
<li>Coffeeli>
<li>Milkli>
ul>
浏览器显示如下:
• Coffee
• Milk
列表项内部可以使用段落、换行符、图片、链接以及其他列表等等。
36:有序列表
同样,有序列表也是一列项目,列表项目使用数字进行标记。
有序列表始于 <ol> 标签。每个列表项始于 <li> 标签。
<ol>
<li>Coffeeli>
<li>Milkli>
ol>
浏览器显示如下:
1. Coffee
2. Milk
列表项内部可以使用段落、换行符、图片、链接以及其他列表等等。
37:定义列表
自定义列表不仅仅是一列项目,而是项目及其注释的组合。
自定义列表以 <dl> 标签开始。每个自定义列表项以 <dt> 开始。每个自定义列表项的定义以 <dd> 开始。
<dl>
<dt>Coffeedt>
<dd>Black hot drinkdd>
<dt>Milkdt>
<dd>White cold drinkdd>
dl>
浏览器显示如下:
Coffee
Black hot drink
Milk
White cold drink
38:HTML
元素
HTML <div> 元素是块级元素,它是可用于组合其他 HTML 元素的容器。
<div> 元素没有特定的含义。除此之外,由于它属于块级元素,浏览器会在其前后显示折行。
如果与 CSS 一同使用,<div> 元素可用于对大的内容块设置样式属性。
<div> 元素的另一个常见的用途是文档布局。它取代了使用表格定义布局的老式方法。
使用 <table> 元素进行文档布局不是表格的正确用法。<table> 元素的作用是显示表格化的数据。
39:HTML 元素
HTML <span> 元素是内联元素,可用作文本的容器。
<span> 元素也没有特定的含义。
当与 CSS 一同使用时,<span> 元素可用于为部分文本设置样式属性
40:HTML 分组标签
标签 描述
<div>
定义文档中的分区或节(division/section)。
<span>
定义 span,用来组合文档中的行内元素。
41:HTML 类
对 HTML 进行分类(设置类),使我们能够为元素的类定义 CSS 样式。
为相同的类设置相同的样式,或者为不同的类设置不同的样式。
实例
<html>
<head>
<style>
.cities {
background-color:black;
color:white;
margin:20px;
padding:20px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="cities">
<h2>Londonh2>
<p>
London is the capital city of England.
It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom,
with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.
p>
div>
body>
html>
42:分类块级元素
HTML <div> 元素是块级元素。它能够用作其他 HTML 元素的容器。
设置 <div> 元素的类,使我们能够为相同的 <div> 元素设置相同的类:
实例
<html>
<head>
<style>
.cities {
background-color:black;
color:white;
margin:20px;
padding:20px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div class="cities">
<h2>Londonh2>
<p>London is the capital city of England.
It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom,
with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.p>
div>
<div class="cities">
<h2>Parish2>
<p>Paris is the capital and most populous city of France.p>
div>
<div class="cities">
<h2>Tokyoh2>
<p>Tokyo is the capital of Japan, the center of the Greater Tokyo Area,
and the most populous metropolitan area in the world.p>
div>
body>
html>
43:分类行内元素
HTML <span> 元素是行内元素,能够用作文本的容器。
设置 <span> 元素的类,能够为相同的 <span> 元素设置相同的样式。
实例
<html>
<head>
<style>
span.red {
color:red;}
style>
head>
<body>
<h1>My <span class="red">Importantspan> Headingh1>
body>
html>
44:使用 div元素的 HTML 布局
注释:<div> 元素常用作布局工具,因为能够轻松地通过 CSS 对其进行定位。
这个例子使用了四个 <div> 元素来创建多列布局:
实例
<div id="header">
City Gallery
div>
<div id="nav">
London
Paris
Tokyo
div>
<div id="section">
London
London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom,
with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.
Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia,
its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium.
div>
<div id="footer">
Copyright W3School.com.cn
div>
45:使用 HTML5 的网站布局
HTML5 提供的新语义元素定义了网页的不同部分:
HTML5 语义元素
header 定义文档或节的页眉
nav 定义导航链接的容器
section 定义文档中的节
article 定义独立的自包含文章
aside 定义内容之外的内容(比如侧栏)
footer 定义文档或节的页脚
details 定义额外的细节
summary 定义 details 元素的标题
这个例子使用 <header>, <nav>, <section>, 以及 <footer> 来创建多列布局:
实例
<body>
<header>
<h1>City Galleryh1>
header>
<nav>
London<br>
Paris<br>
Tokyo<br>
nav>
<section>
<h1>Londonh1>
<p>
London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom,
with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.
p>
<p>
Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia,
its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium.
p>
section>
<footer>
Copyright W3School.com.cn
footer>
body>
2:HTML 响应式 Web 设计
1:什么是响应式 Web 设计?
• RWD 指的是响应式 Web 设计(Responsive Web Design)
• RWD 能够以可变尺寸传递网页
• RWD 对于平板和移动设备是必需的
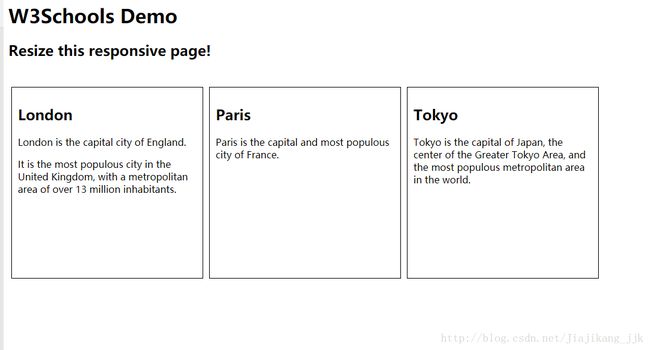
2:创建您自己的响应式设计
创建响应式设计的一个方法,是自己来创建它:
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<style>
.city {
float: left;
margin: 5px;
padding: 15px;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<h1>W3School Demoh1>
<h2>Resize this responsive page!h2>
<br>
<div class="city">
<h2>Londonh2>
<p>London is the capital city of England.p>
<p>It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom,
with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.p>
div>
<div class="city">
<h2>Parish2>
<p>Paris is the capital and most populous city of France.p>
div>
<div class="city">
<h2>Tokyoh2>
<p>Tokyo is the capital of Japan, the center of the Greater Tokyo Area,
and the most populous metropolitan area in the world.p>
div>
body>
html>
3:使用 Bootstrap
另一个创建响应式设计的方法,是使用现成的 CSS 框架。
Bootstrap 是最流行的开发响应式 web 的 HTML, CSS, 和 JS 框架。
Bootstrap 帮助您开发在任何尺寸都外观出众的站点:显示器、笔记本电脑、平板电脑或手机:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="http://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.2.0/css/bootstrap.min.css">
head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="jumbotron">
<h1>W3School Demoh1>
<p>Resize this responsive page!p>
div>
div>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
<h2>Londonh2>
<p>London is the capital city of England.p>
<p>It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom,
with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.p>
div>
<div class="col-md-4">
<h2>Parish2>
<p>Paris is the capital and most populous city of France.p>
div>
<div class="col-md-4">
<h2>Tokyoh2>
<p>Tokyo is the capital of Japan, the center of the Greater Tokyo Area,
and the most populous metropolitan area in the world.p>
div>
div>
div>
body>
html>
3:HTML框架
1:框架
通过使用框架,你可以在同一个浏览器窗口中显示不止一个页面。每份HTML文档称为一个框架,并且每个框架都独立于其他的框架。
使用框架的坏处:
• 开发人员必须同时跟踪更多的HTML文档
• 很难打印整张页面
2:框架标签(Frame)
Frame 标签定义了放置在每个框架中的 HTML 文档。
在下面的这个例子中,我们设置了一个两列的框架集。第一列被设置为占据浏览器窗口的 25%。第二列被设置为占据浏览器窗口的 75%。HTML 文档 "frame_a.htm" 被置于第一个列中,而 HTML 文档 "frame_b.htm" 被置于第二个列中:
<frameset cols="25%,75%">
<frame src="frame_a.htm">
<frame src="frame_b.htm">
frameset>
基本的注意事项 - 有用的提示:
假如一个框架有可见边框,用户可以拖动边框来改变它的大小。为了避免这种情况发生,可以在 <frame> 标签中加入:noresize="noresize"。
为不支持框架的浏览器添加 <noframes> 标签。
重要提示:不能将 <body>body> 标签与 <frameset>frameset> 标签同时使用!不过,假如你添加包含一段文本的 <noframes> 标签,就必须将这段文字嵌套于 <body>body> 标签内。(在下面的第一个实例中,可以查看它是如何实现的。)
4:HTML Iframe
1:iframe 用于在网页内显示网页
2:添加 iframe 的语法
<iframe src="URL">iframe>
URL 指向隔离页面的位置。
3:Iframe - 设置高度和宽度
height 和 width 属性用于规定 iframe 的高度和宽度。
属性值的默认单位是像素,但也可以用百分比来设定(比如 "80%")。
实例
<iframe src="demo_iframe.htm" width="200" height="200">iframe>
<html>
<body>
<iframe src="http://www.w3school.com.cn/html/html_iframe.asp" width="2000" height="200">iframe>
<p>某些老式的浏览器不支持内联框架。p>
<p>如果不支持,则 iframe 是不可见的。p>
body>
html>
4:Iframe - 删除边框
frameborder 属性规定是否显示 iframe 周围的边框。
设置属性值为 "0" 就可以移除边框:
实例
<iframe src="demo_iframe.htm" frameborder="0">iframe>
<html>
<body>
<iframe src="http://www.w3school.com.cn/html/html_iframe.asp" width="1000" height="200" frameborder="0">iframe>
<p>某些老式的浏览器不支持内联框架。p>
<p>如果不支持,则 iframe 是不可见的。p>
body>
html>
5:使用 iframe 作为链接的目标
iframe 可用作链接的目标(target)。
链接的 target 属性必须引用 iframe 的 name 属性:
实例
<iframe src="demo_iframe.htm" name="iframe_a">iframe>
<p><a href="http://www.w3school.com.cn" target="iframe_a">W3School.com.cna>p>
<html>
<body>
<iframe src="/example/html/demo_iframe.html" name="iframe_a">iframe>
<p><a href="http://www.w3school.com.cn" target="iframe_a">W3School.com.cna>p>
<p><b>注释:b>由于链接的目标匹配 iframe 的名称,所以链接会在 iframe 中打开。p>
body>
html>
5:HTML背景
1:背景(Backgrounds)
<body> 拥有两个配置背景的标签。背景可以是颜色或者图像。背景颜色(Bgcolor)
背景颜色属性将背景设置为某种颜色。属性值可以是十六进制数、RGB 值或颜色名。
<body bgcolor="#000000">
<body bgcolor="rgb(0,0,0)">
<body bgcolor="black">
以上的代码均将背景颜色设置为黑色。
2:背景(Background)
背景属性将背景设置为图像。属性值为图像的URL。如果图像尺寸小于浏览器窗口,那么图像将在整个浏览器窗口进行复制。
<body background="clouds.gif">
<body background="http://www.w3school.com.cn/clouds.gif">
URL可以是相对地址,如第一行代码。也可以使绝对地址,如第二行代码。
6:HTML 脚本
1:HTML script 元素
<script> 标签用于定义客户端脚本,比如 JavaScript。
script 元素既可包含脚本语句,也可通过 src 属性指向外部脚本文件。
必需的 type 属性规定脚本的 MIME 类型。
JavaScript 最常用于图片操作、表单验证以及内容动态更新。
下面的脚本会向浏览器输出“Hello World!”:
<script type="text/javascript">
document.write("Hello World!")
script>
7:HTML 头部元素
1:HTML 元素
<head> 元素是所有头部元素的容器。<head> 内的元素可包含脚本,指示浏览器在何处可以找到样式表,提供元信息,等等。
以下标签都可以添加到 head 部分:<title>、<base>、<link>、<meta>、<script> 以及