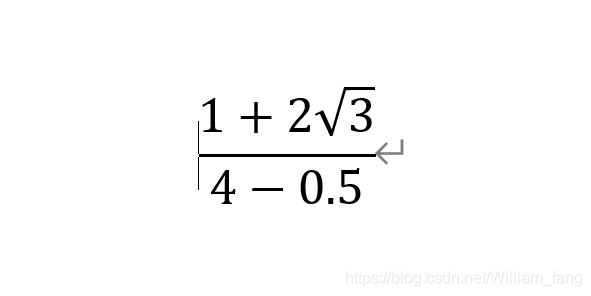C++基础教程10-数学运算
文章目录
- 1.数学函数
- 2.用数学函数进行公式运算
- 3.随机数
- 篇章
1.数学函数
#include 2.用数学函数进行公式运算
#include 3.随机数
随机函数与时间函数搭配使用
#include #include 篇章
上一篇:C++基础教程9-二维数组
下一篇:C++基础教程11-函数