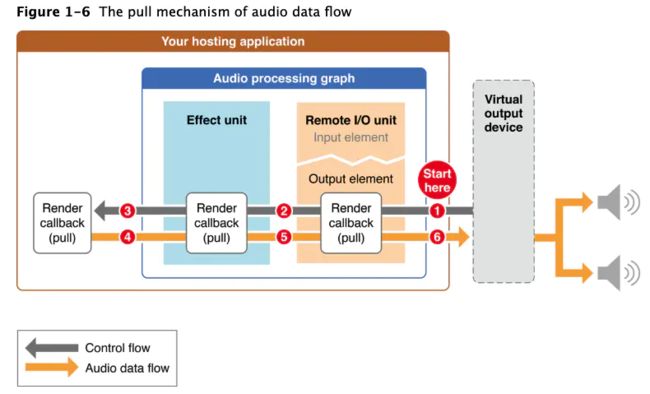
WebRTC与声音设备有关的代码在modules/audio_device目录下面,包括各个平台的录音采集和播放声音的代码。
目前IOS版的源码被移动到sdk/objc/目录下。
其中windows上的使用了Core Audio API。
Core Audio API 应该是Vista之后才支持的API,以前在winxp时代,我用的都是wave API和directsound。不过现在Core Audio API 看上去好像更强大,貌似支持回音消除等功能。
ios上的录音和播放也用到了比较底层的技术:Audio Unit。
参考文章:
AudioUnit
Audio Unit 概念知识
Audio Unit 主要涉及到三个常用的概念知识:
(1)AUGraph:包含和管理Audio Unit 的组织者;
(2)AUNode /AudioComponent:是AUGraph音频处理环节中的一个节点。
(3)AudioUnit: 音频处理组件,是对音频处理节点的实例描述者和操控者。
我们不妨想像演唱会的舞台上,有录制歌声与乐器的麦克风,而从麦克风到输出到音响之间,还串接了大大小小的效果器,在这个过程中,无论是麦克风、音响或是效果器,都是不同的AUNode。AUNode 是这些器材的实体,而我们要操控这些器材、改变这些器材的效果属性,就会需要透过每个器材各自的操控界面,这些介面便是AudioUnit,最后构成整个舞台,便是AUGraph。AUNode 与AudioComponent 的差别在于,其实像上面讲到的各种器材,除了可以放在AUGraph 使用之外,也可以单独使用,比方说我们有台音响,我们除了把音响放在舞台上使用外,也可以单独拿这台音响输出音乐。当我们要在AUGraph 中使用某个器材,我们就要使用AUNode 这种形态,单独使用时,就使用AudioComponent。但无论是操作AUNode 或AudioComponent,都还是得透过AudioUnit 这一层操作界面。(上述文字摘自KKBOX iOS/Mac OS X 基础开发教材)
这儿感觉AUGraph有点像dshow中的多个Filter在 Filter Graph自己组合配合工作。而AudioUnit就是包装好的单个Filter的 FilteGraph。
WebRTC直接使用了AudioComponent来录音和播放,没有使用AUGraph和AUNode。
Audio Units
下面直接来看WebRTC中的代码:
bool VoiceProcessingAudioUnit::Init() {
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(state_, kInitRequired);
// Create an audio component description to identify the Voice Processing
// I/O audio unit.
AudioComponentDescription vpio_unit_description;
vpio_unit_description.componentType = kAudioUnitType_Output;
vpio_unit_description.componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_VoiceProcessingIO;
vpio_unit_description.componentManufacturer = kAudioUnitManufacturer_Apple;
vpio_unit_description.componentFlags = 0;
vpio_unit_description.componentFlagsMask = 0;
// Obtain an audio unit instance given the description.
AudioComponent found_vpio_unit_ref =
AudioComponentFindNext(nullptr, &vpio_unit_description);
// Create a Voice Processing IO audio unit.
OSStatus result = noErr;
result = AudioComponentInstanceNew(found_vpio_unit_ref, &vpio_unit_);
if (result != noErr) {
vpio_unit_ = nullptr;
RTCLogError(@"AudioComponentInstanceNew failed. Error=%ld.", (long)result);
return false;
}
...
}
AudioComponentDescription的componentManufacturer永远为kAudioUnitManufacturer_Apple。componentFlags和componentFlagsMask也为0,不用问为什么,因为文档就这样写着。
componentType和componentSubType结合代表了Audo Unit中的七种类型:
Effect: iPod Equalizer
Mixing: 3D Mixer、Mutichannel Mixer
I/O:Remote I/O、Voice-Processing I/O、Generic Output
Format Conversion:Format Converter
Effect Unit
一个效果单元,iPod Equalizer,与 iPod 内置应用使用相同的均衡器。此 audio unit 提供了一组预设的均衡曲线,例如低音增强,Pop 和 Spoken Word。
Effect Unit:
componentType = kAudioUnitType_Effect
componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_AUiPodEQ
Mixer Units
一共两个 mixer units:3D Mixer unit 和Multichannel Mixer unit。
3D Mixer unit 是 OpenAL 的基础,如果需要实现 3D Mixer unit 的特征,可以优先使用 OpenAL,它提供了高级 API,并且非常适合游戏应用程序。
Multichannel Mixer unit 为任意数量的单声道或立体声提供混音、立体声输出。可以打开和关闭每一个输入,设置输入增益。
Mixer Unit:
1.
componentType = kAudioUnitType_Mixer
componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_AU3DMixerEmbedded
2.
componentType = kAudioUnitType_Mixer
componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_MultiChannelMixer
I/O Units
iOS 提供了三个 I/O units,其中 Remote I/O unit 是最常用的。连接输入输出音频硬件,对传入和传出的样本值低延迟访问,提供硬件音频格式和应用音频格式之间的格式转化。
Voice-Processing I/O unit 是对 Remote I/O unit 的拓展,添加了语音聊天中的回声消除,还提供了自动增益矫正,语音质量调整,静音等特性。
Generic Output unit 不连接音频硬件,而是提供了一种将处理链的输出发送到应用程序的机制。通常会使用做离线音频处理。
I/O Unit:
1.
componentType = kAudioUnitType_Output
componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_RemoteIO
2.
componentType = kAudioUnitType_Output
componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_VoiceProcessingIO
3.
componentType = kAudioUnitType_Output
componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_GenericOutput
Format Converter Unit
Format Converter Unit看上去像用来格式转换。
Format Converter Unit:
componentType = kAudioUnitType_FormatConverter
componentSubType = kAudioUnitSubType_AUConverter
WebRTC使用了Voice-Processing I/O unit。
AudioUnitSetProperty
创建AudioUnit以后可以使用AudioUnitSetProperty设置属性。
在这儿涉及到AudioUnit最令人混乱的概念。
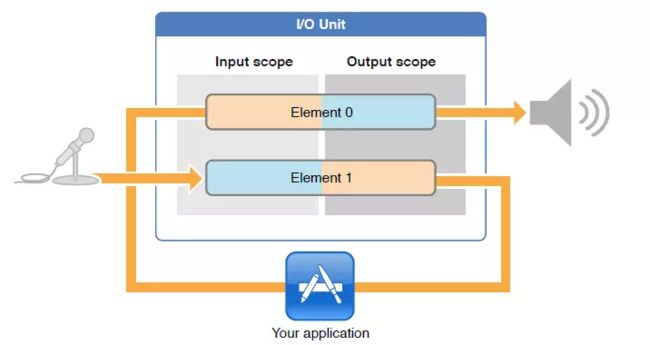
一个I/O Unit包含两个实体对象Element 0、Element 1,两个实体对象相互独立,根据需求可通过kAudioOutputUnitProperty_EnableIO属性去开关它们。Element 1与硬件输入连接,并且Element 1的输入域(input scope)对你不可见,你只能读取它的输出域的数据及设置其输出域的音频格式;Element 0与硬件输出连接,并且Element 0的输出域(ouput scope)对你不可见,你只能写入它的输入域的数据及设置其输入域的音频格式。
Element 1就是上面代码AudioUnitSetProperty的第4个参数:kInputBus,而Element 0就是kOutputBus。
上面创建的AudioUnit是kAudioUnitSubType_VoiceProcessingIO,所以kInputBus相当于录音,kOutputBus相当于播放。
每个Element也就是Bus都有两个Scope:Input Scope 和 Output Scope。
录音的Input Scope数据来自麦克风硬件,得到数据输出到Output Scope。
播放时的数据来自Input Scope,Output Scope就是硬件喇叭或者耳机输出口。
Scope类似dshow里面的Pin:Input Pin、OutputPin,更喜欢dshow里的这种叫法。
Element类似dshow里的filter。
VoiceProcessingIO AuioUnit就像同时封装了录音和声音播放两个filter,Element1是录音filter,Element0是播放filter,可以控制单独打开也可以同时打开两个Element。
所以下面代码:
UInt32 enable_input = 1;
//打开录音输入的input Scope
result = AudioUnitSetProperty(vpio_unit_, kAudioOutputUnitProperty_EnableIO,
kAudioUnitScope_Input, kInputBus, &enable_input,
sizeof(enable_input));
if (result != noErr) {
DisposeAudioUnit();
RTCLogError(@"Failed to enable input on input scope of input element. "
"Error=%ld.",
(long)result);
return false;
}
// Enable output on the output scope of the output element.
UInt32 enable_output = 1;
//打开播放输出的output scope
result = AudioUnitSetProperty(vpio_unit_, kAudioOutputUnitProperty_EnableIO,
kAudioUnitScope_Output, kOutputBus,
&enable_output, sizeof(enable_output));
if (result != noErr) {
DisposeAudioUnit();
RTCLogError(@"Failed to enable output on output scope of output element. "
"Error=%ld.",
(long)result);
return false;
}
enable_input = 1就是打开录音, enable_output = 1就是打开播放。
bool VoiceProcessingAudioUnit::Init() {
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(state_, kInitRequired);
...
// Specify the callback function that provides audio samples to the audio
// unit.
//设置播放的输入的inputscope回调, 也就是播放时的输入数据来自这个回调
AURenderCallbackStruct render_callback;
render_callback.inputProc = OnGetPlayoutData;
render_callback.inputProcRefCon = this;
result = AudioUnitSetProperty(
vpio_unit_, kAudioUnitProperty_SetRenderCallback, kAudioUnitScope_Input,
kOutputBus, &render_callback, sizeof(render_callback));
if (result != noErr) {
DisposeAudioUnit();
RTCLogError(@"Failed to specify the render callback on the output bus. "
"Error=%ld.",
(long)result);
return false;
}
// Disable AU buffer allocation for the recorder, we allocate our own.
// TODO(henrika): not sure that it actually saves resource to make this call.
// 关闭录音的输出output scope的buffer分配器,使用自己的buffer分配器
UInt32 flag = 0;
result = AudioUnitSetProperty(
vpio_unit_, kAudioUnitProperty_ShouldAllocateBuffer,
kAudioUnitScope_Output, kInputBus, &flag, sizeof(flag));
if (result != noErr) {
DisposeAudioUnit();
RTCLogError(@"Failed to disable buffer allocation on the input bus. "
"Error=%ld.",
(long)result);
return false;
}
//设置录音的globalscope的回调方法,应该就是录音的回调
// Specify the callback to be called by the I/O thread to us when input audio
// is available. The recorded samples can then be obtained by calling the
// AudioUnitRender() method.
AURenderCallbackStruct input_callback;
input_callback.inputProc = OnDeliverRecordedData;
input_callback.inputProcRefCon = this;
result = AudioUnitSetProperty(vpio_unit_,
kAudioOutputUnitProperty_SetInputCallback,
kAudioUnitScope_Global, kInputBus,
&input_callback, sizeof(input_callback));
if (result != noErr) {
DisposeAudioUnit();
RTCLogError(@"Failed to specify the input callback on the input bus. "
"Error=%ld.",
(long)result);
return false;
}
state_ = kUninitialized;
return true;
}
OnDeliverRecordedData就是录音时数据的回调方法,得到后传给WebRTC进行进一步音频信号处理,编码、网络传输。
播放时回调OnGetPlayoutData方法获取音频数据进行播放,所以需要在OnGetPlayoutData里填充来自WebRTC的远程的解码后音频数据。
设置录音和播放的音频格式
bool VoiceProcessingAudioUnit::Initialize(Float64 sample_rate) {
RTC_DCHECK_GE(state_, kUninitialized);
RTCLog(@"Initializing audio unit with sample rate: %f", sample_rate);
OSStatus result = noErr;
AudioStreamBasicDescription format = GetFormat(sample_rate);
UInt32 size = sizeof(format);
#if !defined(NDEBUG)
LogStreamDescription(format);
#endif
//设置录音的输出格式
// Set the format on the output scope of the input element/bus.
result =
AudioUnitSetProperty(vpio_unit_, kAudioUnitProperty_StreamFormat,
kAudioUnitScope_Output, kInputBus, &format, size);
if (result != noErr) {
RTCLogError(@"Failed to set format on output scope of input bus. "
"Error=%ld.",
(long)result);
return false;
}
//设置播放的输入格式
// Set the format on the input scope of the output element/bus.
result =
AudioUnitSetProperty(vpio_unit_, kAudioUnitProperty_StreamFormat,
kAudioUnitScope_Input, kOutputBus, &format, size);
if (result != noErr) {
RTCLogError(@"Failed to set format on input scope of output bus. "
"Error=%ld.",
(long)result);
return false;
}
// Initialize the Voice Processing I/O unit instance.
// Calls to AudioUnitInitialize() can fail if called back-to-back on
// different ADM instances. The error message in this case is -66635 which is
// undocumented. Tests have shown that calling AudioUnitInitialize a second
// time, after a short sleep, avoids this issue.
// See webrtc:5166 for details.
int failed_initalize_attempts = 0;
result = AudioUnitInitialize(vpio_unit_);
while (result != noErr) {
RTCLogError(@"Failed to initialize the Voice Processing I/O unit. "
"Error=%ld.",
(long)result);
++failed_initalize_attempts;
if (failed_initalize_attempts == kMaxNumberOfAudioUnitInitializeAttempts) {//重试5次
// Max number of initialization attempts exceeded, hence abort.
RTCLogError(@"Too many initialization attempts.");
return false;
}
RTCLog(@"Pause 100ms and try audio unit initialization again...");
[NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:0.1f];
result = AudioUnitInitialize(vpio_unit_);
}
if (result == noErr) {
RTCLog(@"Voice Processing I/O unit is now initialized.");
}
// AGC should be enabled by default for Voice Processing I/O units but it is
// checked below and enabled explicitly if needed. This scheme is used
// to be absolutely sure that the AGC is enabled since we have seen cases
// where only zeros are recorded and a disabled AGC could be one of the
// reasons why it happens.
int agc_was_enabled_by_default = 0;
UInt32 agc_is_enabled = 0;
//获得AGC增益状态
result = GetAGCState(vpio_unit_, &agc_is_enabled);
if (result != noErr) {
RTCLogError(@"Failed to get AGC state (1st attempt). "
"Error=%ld.",
(long)result);
// Example of error code: kAudioUnitErr_NoConnection (-10876).
// All error codes related to audio units are negative and are therefore
// converted into a postive value to match the UMA APIs.
RTC_HISTOGRAM_COUNTS_SPARSE_100000(
"WebRTC.Audio.GetAGCStateErrorCode1", (-1) * result);
} else if (agc_is_enabled) {
// Remember that the AGC was enabled by default. Will be used in UMA.
agc_was_enabled_by_default = 1;
} else {
// AGC was initially disabled => try to enable it explicitly.
//尝试开启AGC,设置录音的agc增益,这个用的是ios自带agc
UInt32 enable_agc = 1;
result =
AudioUnitSetProperty(vpio_unit_,
kAUVoiceIOProperty_VoiceProcessingEnableAGC,
kAudioUnitScope_Global, kInputBus, &enable_agc,
sizeof(enable_agc));
if (result != noErr) {
RTCLogError(@"Failed to enable the built-in AGC. "
"Error=%ld.",
(long)result);
RTC_HISTOGRAM_COUNTS_SPARSE_100000(
"WebRTC.Audio.SetAGCStateErrorCode", (-1) * result);
}
result = GetAGCState(vpio_unit_, &agc_is_enabled);
if (result != noErr) {
RTCLogError(@"Failed to get AGC state (2nd attempt). "
"Error=%ld.",
(long)result);
RTC_HISTOGRAM_COUNTS_SPARSE_100000(
"WebRTC.Audio.GetAGCStateErrorCode2", (-1) * result);
}
}
// Track if the built-in AGC was enabled by default (as it should) or not.
RTC_HISTOGRAM_BOOLEAN("WebRTC.Audio.BuiltInAGCWasEnabledByDefault",
agc_was_enabled_by_default);
RTCLog(@"WebRTC.Audio.BuiltInAGCWasEnabledByDefault: %d",
agc_was_enabled_by_default);
// As a final step, add an UMA histogram for tracking the AGC state.
// At this stage, the AGC should be enabled, and if it is not, more work is
// needed to find out the root cause.
RTC_HISTOGRAM_BOOLEAN("WebRTC.Audio.BuiltInAGCIsEnabled", agc_is_enabled);
RTCLog(@"WebRTC.Audio.BuiltInAGCIsEnabled: %u",
static_cast(agc_is_enabled));
state_ = kInitialized;
return true;
}
也还是使用AudioUnitSetProperty来设置,我在代码中写了注释就不多说了,AudioUnit自带了AGC增益功能可以直接使用,所以可以不使用WebRTC的AGC。
以上最关键的是要明白Element(Bus)和Scope。Element(Bus)就是输入(录音)或者输出(播放),Scope是Element(Bus)的输入口Input和输出口Output。
附
官方英文文档:
Audio Unit Hosting Guide for iOS