简介
每个系统都会有一些配置信息需要处理,比如通用的数据源的配置,连接池的配置,log信息的配置。原来系统的处理方式都是通过将配置文件打包部署到线上,对于需要动态修改的配置也就需要单独开发功能,比如通过提供修改接口将值修改。这样的方式有下面几个问题:
1:打包进文件的配置需要通过运维走上线流程,响应自然就那么快。
2:对于需要提供动态修改的配置,需要开发相应的功能。
3:增加了运维的复杂性
4:没法对配置的修改进行跟踪,出现问题没发找到对应的负责人。
Spring Cloud Config采用一种集中式的配置方式,将分布式系统的配置集中管理,底层依赖版本控制系统,能对配置的历史信息进行追踪。
Spring Cloud Config Server的搭建
-
首先你需要有一个git服务器,可以用网上提供的开源git服务器,比始码云。在上在新建一个代码库,如下图我新建的代码库:
- 新建项目,引入依赖包。pom.xml文件的代码如下:
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-dependencies
Edgware.SR4
pom
import
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-config-server
org.apache.httpcomponents
httpclient
4.3.4
这里面要引入httpclient包,否则会报错。
- application.properties文件配置如下:
server.port=8853
spring.application.name=spring-cloud-config-server
spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri=https://gitee.com/ivanchen2017/spring-cloud-config-test.git #这里需要改成你测试时的仓库地址
spring.cloud.config.server.git.search-paths=provider # # git仓库地址下的相对地址,可以配置多个,用,分割。
spring.cloud.config.server.git.username=#改成访问你仓库的username
spring.cloud.config.server.git.password=#改成访问你仓库的password
- 启动类的代码需要加上EnableConfigServer注解,代码如下:
package com.ivan.sever.config;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
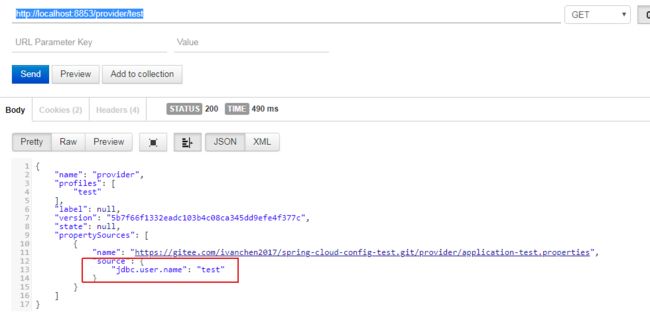
- 访问http://localhost:8853/provider/test ,效果如下图:
仓库中的配置文件会被转换成web接口,访问可以参照以下的规则:
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
其中application表示应用的名称,label用于表示Git的分支,比如master/develop分支,而profile用于表示不同环境的配置。在实际的项目中,不同的项目配置可以新建不同的文件夹,但是里面的文件需要把项目名称写上。因为在逻辑上application并不对应于文件夹的名称
Spring Cloud Server Client
这里所谓的Server Client其实就是我们提供的微服务系统,他会从Config Server里读取数据,比如我们可以把端口号,Eureka Server信息配置的Config Server里配置。比如我在provider文件下的jdbc-dev.properties文件内容如下:
url=www.sina.com
server.port=8003
spring.application.name=provider
eureka.instance.hostname=localhost
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
- 在Client 端的pom.xml文件里加入如下依赖
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-config
- 修改或新建一个bootstrap.properties。里面需要配置config server相关的信息。我们的微服务首先会读取这个文件里的配置。然后根据这个配置文件里config server的配置读取配置中心里的数据进行加载。配置的属性如下:
spring.cloud.config.name=jdbc #application
spring.cloud.config.profile=dev #proflle
spring.cloud.config.uri=http://localhost:8853/ #配置中心的url
spring.cloud.config.label=master #label
#spring.cloud.config.discovery.service-id:#指定配置中心的service-id,便于扩展为高可用配置集群。
#spring.cloud.config.discovery.enabled :开启Config服务发现支持用于根据service-id来发现config server时需要开启
启动App后,发现系统加载了配置中心的相关配置,启动端口变成了我们配置的8003。
解决配置文件修改后,客户端获取修改后的配置
上面的例子只展示了客户端能够得到相应的配置信息,但如果配置修改了,客户端要如何获取修改后的值呢。下面几步用于获取配置修改后,客户端相应的实例里的配置信息也会作相应的改变,这样我们采用集中式的配置才有意义。
- 首先需要在pom.xml文件里加入如下依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
1.5.14.RELEASE
spring-boot-starter-actuator是一套监控的功能,可以监控程序在运行时状态,其中就包括/refresh的功能。
- 在需要加载变量的类上加上RefreshScope注解,这个注解的功能会在SpringCloud配置中心配置更新的时候,自动将新的配置更新到该类对应的字段中。代码如下:
package com.ivan.provider.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.ivan.provider.entity.User;
@RestController
@RefreshScope
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id) {
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("调用了客户端啦");
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setName("ivan chen");
user.setAge(18);
return user;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/create", method = RequestMethod.POST, consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public User createUserPerson(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println(user.getName());
user.setId(15);
return user;
}
@Value("${url}")
private String url;
@RequestMapping(value = "/url", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
}
- 在 application.properties文件里加上如下配置,用于关闭安全认证
management.security.enabled=false
- 在更新完了配置后,需要手动访问url : http://localhost:8000/refresh 这里是需要提交的是post请求噢
整体用下来会发现Spring Cloud Config有如下优势:
1:依赖svn或git,能够有很好的版本控制并能很好的追踪到修改的历史。
2:使用起来简单。
缺点便是自动更新了数据后,需要手动通过访问url来更新具体的微服务。当然也可以通过git的WebHook配合Spring Cloud Bus来解决手动更新的问题。