系统学习大前端(4)---ES6+新特性、TS、JS性能优化
1、ES6+新特性
1.1 let、const
块级作用域
变量提升
最佳实践:不使用var ,默认使用const ,明确会改变的使用let。
1.2 解构
- 数组
const arr = [1,2,3]
const [a,b] = arr;
const [,,c] = arr;
使用…方式解构
const [a,...rest] = arr;
//默认值
const [a,b,c,d = 12] = arr
- 对象
const obj = {
name:'zs',
age:18
}
const {
name} = obj;
// 重命名
const {
name:rename} = obj;
1.3 模板字符串
let str = `
i am
${
name}
`
// 带标签的模板字符串
const str = console.log`hello world`
1.4 字符串的扩展方法
- includes()
- startsWith()
- endsWith()
1.5 参数默认值、 剩余参数
… 操作符
function fn(...args){}
1.6 展开数组
const arr = [1,2,3];
console.log(...arr)
1.7 箭头函数
不会改变this的指向。
箭头函数不适用:
- 构造函数
- 没有arguments
- 没有this
1.8 对象字面量
const obj = {
foo:123,
method1(){
console.log('1')
},
//计算属性名
[Math.random](){
}
}
9、Object
- Object.assign 多个对象复制到一个目标对象。
const source1 = {
a:123,
b:23
}
const target = {
a:123,
c:23
}
const res = Object.assign(target,source1)
- Object.is 判断两个值是否一样
1.10 proxy
-
Object.defineProperty – ES5监听数据变更的API vue2的底层实现
-
proxy – ES6 vue3的底层实现
const person = {
name:'ss',
age:19
}
const personProxy = new Proxy(person,{
get(target,key){
console.log(target,key)
return 100;
},
set(target,key,value){
console.log(target,key,value)
}
})
console.log(personProxy.name)
personProxy.sex = '女'
proxy的优势:
- defineProperty只能监视属性的读写,proxy可以监视delete、方法调用等
const person = {
name:'ss',
age:19
}
const personProxy = new Proxy(person,{
deleteProperty(target,property){
console.log('delete')
}
})
delete personProxy.age
- proxy更好的监视数组
const list = []
const listProxy = new Proxy(list,{
set(target,property,value){
console.log(target,property,value)
target[property] = value;
return true//表示设置成功
}
})
listProxy.push(10)
1.11 reflect
统一的对象操作API
静态类
内部封装了一系列对对象的底层操作 。
const person = {
name:'ss',
age:19
}
const personProxy = new Proxy(person,{
get(target,key){
// ... 自定义逻辑
return Reflect.get(target,key)
},
set(target,key,value){
console.log(target,key,value)
}
})
console.log(personProxy.name)
personProxy.sex = '女'
Reflect.has
Reflect.deleteProperty
Reflect.ownkeys
1.12 promise
异步编程解决方案
1.13 class
// es5
function Person(name) {
this.name = name
}
Person.prototype.say = function(){
}
// es6
class Person{
constructor(name){
this.name = name
}
say(){
}
}
const person = new Person('zhangsan');
- 静态方法
class Person{
constructor(name){
this.name = name
}
// 实例方法
say(){
}
// 静态方法
static create(name){
return new Person(name)
}
}
- 实例方法
- 类的继承 – extends
class Person{
constructor(name){
this.name = name
}
say(){
console.log('父say')
}
}
class Student extends Person{
constructor(name,number){
super(name)
this.number = number
}
hello(){
super.say();
console.log('hello')
}
}
let stu = new Student('zhaosi',12342);
stu.hello();
1.14 set、map
Set 不允许重复
const set = new Set();
set.add(1).add(2).add(3)
// 遍历
set.forEach(()=>{
})
for(let i of set){
}
set.size
set.has()
set.delete()
set.clear()
const arr = [1,2,3,1,4,2]
const set1 = new Set(arr)
Array.from(set1)
const arr1 = [...set1]
Map
类似对象,
const obj = {
}
obj[true] = 'value'
obj[123] = 'value'
obj[{
a:1}] = 'value'
Object.keys(obj)
const m = new Map()
const tom = {
name:'tom'}
m.set(tom,99)
m.has()
m.delete()
m.clear()
m.forEach(()=>{
})
1.15 Symbol
const a = Symbol()
console.log(a)
const obj = {
}
obj[Symbol('a')] = 123;
obj[Symbol('b')] = 445;
console.log(obj[Symbol('a')])
const a = Symbol.for('foo')
const b = Symbol.for('foo')
console.log(a===b)
const obj1 = {
[Symbol.toStringTag]:'XObject'
}
console.log(obj1.toString()) // [object XObject]
私有属性
- 唯一性
- for…in \ Object.key() 获取不到
- Object.getOwnPropertySymbol(obj)
1.16 for…of — 迭代器
const arr = [2,324,12,324,2,234]
for(let i of arr){
console.log(i)
if(i>188){
break
}
}
// arr.forEach() //无法中断循环
// arr.some()
// arr.every()
// 遍历set、map
可迭代接口 Iterable
实现Iterable接口,是使用for…of的前提
const arr = [1,23,321,421]
const iterator = arr[Symbol.iterator]()
iterator.next()
实现可迭代接口
const obj= {
store:['foo','bar','baz'],
[Symbol.iterator]:function(){
let index = 0;
const self = this;
return {
next:function(){
const res = {
value:self.store[index],
done:index>=self.store.length
}
index ++
return res;
}
}
}
}
for(let item of obj){
console.log(item)
}
迭代器模式
const todo = {
life:['s','d'],
learn:['e','w2'],
work:['dfa'],
each:function(cb){
const all = [].concat(this.life,this.learn,this.work)
for(const item of all){
cb(item)
}
},
[Symbol.iterator]:function(){
const all = [...this.life,...this.learn,...this.work]
let index = 0;
return {
next:function(){
return {
value:all[index],
done:index++>=all.length
}
}
}
}
}
//for(let item of to.life){}
//for(let item of to.learn){}
//for(let item of to.work){}
todo.each(function(item){
console.log(item)
})
for(let item of todo){
console.log(item)
}
1.17 生成器 generator
避免回调嵌套
function * foo(){
console.log('zcc')
return 100
}
const res = foo();
console.log(res)
res.next()
// 配合 yield
function * boo(){
console.log('111')
yield 100
console.log('222')
yield 200
console.log('333')
yield 300
}
const gen = boo();
gen.next()
生成器应用
// 案例 : 发号器
function * createID(){
let id = 1;
while(true){
yield id++
}
}
const id = createID();
id.next()
// 实现iterator方法
const todo = {
life:['s','d'],
learn:['e','w2'],
work:['dfa'],
[Symbol.iterator]:function * (){
const all = [...this.life,...this.learn,...this.work]
for(let item of all){
console.log(item)
}
}
}
for(let item of todo){
console.log(item)
}
1.18 ES Modules
模块化
1.19 ES2016 ES2017
ES2016
- Array.prototype.includes
- 指数运算符
- Math.pow()
- ** 2**10
ES2017
- Object.values()
- Object.entries()
- Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()
- String.prototype.padStart
- String.prototype.padEnd
- 函数参数中添加尾逗号
function foo(arg1,arg2,){
}
- async/await
2、TypeScript
解决JS类型系统问题
-
强类型 VS 弱类型 (类型安全)
强类型有更强的类型约束。
强类型不允许隐式类型转换。 -
弱类型的问题
- 运行阶段才能发现错误
- 类型不明确,造成函数功能发生改变
- 对对象索引发生错误
const obj = {
}
obj[123] = 456
obj[123] // undefined
- 强类型的优势
- 错误更早的暴露
- 代码更智能,编码更准确
- 重构更牢靠
- 减少不必要的类型判断
TypeScript(语言)
1、JS的超集
- 可以对ES新特性编译(类似babel)
- 功能强大、生态健全、完善
- 任意JS环境都支持
- TS属于渐进式的
- 【缺点】语言本省多了很多概念,如接口、泛型
- 【缺点】项目初期,增加开发成本
2、基本使用
安装typescript
yarn add typescript --dev
tsc .\01-getting-start.ts
3、配置文件 tsconfig.json
tsc --init
4、 原始类型
const a:string = 'foo'
const b: number = 12;
const c:boolean = false;
// 注意:严格模式 不能为空的
const d:void = undefined
const e:null = null
const f:undefined = undefined
// 报错 const g:symbol = Symbol()
// 解决:1、(tsconfig.json)target-->es2015
// 2、 (tsconfig.json) "lib": ['ES2015','DOM'],
// const g:symbol = Symbol()
// Promise
标准库-- 就是内置对象所对应的说明
5、 TS中文错误消息
tsc --locale zh-Ch
或者 vscode中设置

6、类型
- Object类型
// Object 泛指所有非原始类型
const foo :object = function(){
}
const obj :{
foo:number,bar:string} = {
foo:123,bar:'string'}
- 数组类型
const arr1 : Array<number> = [1,2,3]
const arr2:number[] = [1,2,3]
function sum(...args:number[]) {
return args.reduce((pre,cur)=>pre+cur,0)
}
sum(1,2,3)
- 元组类型
// 元组类型
const tuple :[number,string] = [12,'str']
// const age = tuple[0]
const [age,name01] = tuple
- 枚举类型
const post = {
title:'hello ts',
content:'ts is a typed',
status:3
}
// const PostStatus = {
// Draft:0,
// Unpublished:1
// }
enum PostStatus{
Draft = 0,
Unpublished = 1,
Published = 2
}
//常量枚举
const enum PostStatus1{
}
- 函数类型
// 函数
// 可选参数 ? 或 参数默认值
function func1(a:number,b?:number):string {
return 'str'
}
func1(1,2)
// 任意参数 rest
const func2 = (a:number):string=>{
return 'abc'
}
- 任意类型
any
隐式类型推断
类型断言
// as 关键字
const num1 = res as number; //(推荐)
//或
const num2 = <number>res; // 会和JSX标签冲突
7、 接口
// function printPost(post){
// console.log(post.title);
// console.log(post.content);
// }
// 接口
interface Post{
title:string
content:string
subtitle?:string // 可选成员
readonly summary:string // 只读成员
}
function printPost(post:Post){
console.log(post.title);
console.log(post.content);
}
printPost({
title:'标题',
content:'这是一段文字',
summary:'摘要'
})
// 任意成员
interface Cache{
[prop:string]:string
}
8、类
// TS增强了class的特性
class Person {
name:string
age:number
protected gendar:boolean
constructor(name:string,age:number){
this.name = name
this.age =age
this.gendar = true
}
sayHi(msg:string):void{
}
}
// 类的访问修饰符 private(不能外部访问)
// public(默认)
// protected(不能外部访问,子类可访问)
class Student extends Person{
constructor(name:string,age:number){
super(name,age)
console.log(this.gendar);
}
static create(name:string,age:number){
return new Student(name,age)
}
}
const tom = new Person('tom',10)
console.log(tom.name);
const jack = new Student('jack',13)
// 只读属性 - readonly
类和接口
//用接口抽象类的共同属性
interface Eat {
eat(food:string):void
}
interface Run{
run(distance:number) :void
}
class Person1 implements Eat,Run{
eat(food:string):void{
}
run(distance:number):void{
}
}
class Animals implements Eat,Run{
eat(food:string):void{
}
run(distance:number):void{
}
}
抽象类:约束子类必须有某些成员,只能被继承;
子类必须实现父类的抽象方法。
abstract class Animals {
eat(food:string):void{
}
abstract run(distance:number):void
}
9、泛型
// 泛型
function createNumberArray(length:number,value:number):number[] {
const arr = new Array<number>(length).fill(value);
return arr
}
// function createNumberString(length:number,a:string):string[] {
// const arr = new Array(length).fill(a);
// return arr
// }
// function createArray(length:number,value:T):T[] {
// const arr = new Array(length).fill(value);
// return arr
// }
10、类型声明
3、 flow(工具)
1、 JS的类型检查器
通过类型注解的方式,检查类型。
function sum(a:number,b:number){
return a + b
}
通过babel去除注解代码。
2、 使用
yarn add flow-bin --dev // 安装
yarn flow init //初始化配置文件
yarn flow
yarn flow stop //停止命令
3、 编译移除注解
yarn add flow-remove-types --dev // 移除
yarn flow-remove-types . -d dist
// 或者 通过babel方式移除
yarn add @babel/core @babel/cli @babel/preset-flow --dev
yarn babel part01/module02/flow -d dist // 命令
通过babel的 方式 要配置.babelrc文件,配置如下:
{
"presets":["@babel/preset-flow"]
}
4、开发工具插件
Flow Language Support ------------ VScode插件
5、 flow类型
- 原始类型
/**
* @flow
*/
const a : string= '12'
const b :number = NaN // Infinity
const c:boolean = true
const d : null = null
const e:void = undefined
const f:symbol = Symbol()
- 数组类型
/**
* @flow
*/
const arr:Array<number> = [12,3,4]
const arr1 :number[] = [1,2,3]
// 固定长度的数组 --- 元组
const foo:[string,number] = ['s',12]
- 对象类型
/**
* @flow
*/
const obj:{
foo:string,
bar:number
} = {
foo:'s',
bar:125
}
// 可选属性
const obj1:{
foo:string,
bar?:number
} = {
foo:'s'
}
const obj3 :{
[string]:string}= {
}
obj3.key ='value'
obj3.key2 = 'value2'
- 函数类型
/**
* @flow
*/
function fn(a:number,b:number) :number{
return a+b
}
function foo(cb:(string,number)=>void) {
cb('str',100)
}
- 特殊类型
/**
* @flow
*/
// 字面量类型
const a :'foo' = 'foo';
// 联合类型
const type:'success'|'warning'|'danger' = 'success'
const b :string | number = 100;
type StrORNum = string|number;
const c : StrORNum = 123;
// maybe类型 可以为空 ?
const gender : ?number = null
- 任意类型任意类型
// @flow
// mixed 任意类型 --- 强类型
function passMixed(value:mixed){
if(typeof value === 'string'){
value.substr(1)
}
}
passMixed('2ss')
passMixed(20)
// any --- 弱类型
function passMixe2(value:any){
}
/**
* any 和 mixed区别
*
* any是弱类型的,mixed是强类型的。
* 尽量不要使用any
*
*/
6、 flow运行环境API
// @flow
const ele:HTMLElement | null = document.getElementById('app')
4、JS性能优化
1、内存管理
申请、使用、释放空间。
2、垃圾回收 、常见GC算法
- JS中的垃圾
- JS中内存管理是自动的
- 对象不再被引用时是垃圾
- 对象不能从根上访问到时是垃圾
- 可达对象
- 引用、作用域链
- 全局执行上下文(根)
let obj = {
name:'xx'}
let ali = obj;
obj = null;
// 可达对象
function objGroup(obj1,obj2) {
obj1.next = obj2;
obj2.pre = obj1;
return {
o1:obj1,
o2:obj2
}
}
let obj00 = objGroup({
name:'222'},{
name:'333'})
- GC算法
- GC-垃圾回收
- GC可以在内存中找到垃圾
- 程序中不再使用的对象
- 程序中不能访问到的对象
- GC是一种机制(垃圾回收器完成的具体工作)
- 工作内容就是查找垃圾释放空间、回收空间
- 算法就是工作时查找和回收所遵循的规则
- 常见GC算法
- 引用计数
-
[思想] 设置引用数,判断当前引用数是否为0
-
引用计数器
-
引用关系改变时修改引用数字
-
引用数字为0 回收
-
[优点] 发现垃圾时立即回收
-
[优点] 最大限度减少程序暂停
-
[缺点] 无法回收循环引用的对象循环引用
-
[缺点] 时间开销大
// 引用计数 const user1 = { age:11} const user2 = { age:22} const user3 = { age:33} const nameList = [user1.age,user2.age,user3.age] function fn(){ const num = 1 const num1 = 2 } fn();//调用后 num num2 引用为0 回收 // 循环引用 function fn() { const obj1 = { } const obj2 = { } obj1.name = obj2 obj2.name = obj1; return 'x' } fn()
-
- 标记清除
- [原理] 分标记和清除两个阶段
- 遍历所有对象找到标记活动对象
- 遍历所有对象清除没有标记的对象
- 回收相应的空间
- [优点] 解决循环引用的问题
- [缺点] 空间碎片化
- 标记整理
- [原理] 标记清除的增强操作
- 标记阶段和标记清除一样
- 清除阶段会先执行整理,移动对象位置
- 分代回收 (V8)
- 引用计数
3、V8的垃圾回收
- V8
- JS 执行引擎
- 即时编译
- 内存设限
- V8垃圾回收策略
- 分代回收思想
- 内存分新生代和老生代
- 针对不同的生代采用不用的算法
- V8中常用算法
- 分代回收
- 空间复制
- 标记清除
- 标记整理
- 标记增量
- 新生代垃圾回收
- 老生代垃圾回收
- 老生代对象存放在右侧老生代区
- 64位操作系统1.4G 32位 700M
- 老生代对象就是存活时间较长的对象
- 垃圾回收实现
- 主要采用标记清除、标记整理、增量标记算法
- 首先使用标记清除完成垃圾空间的回收
- 采用标记整理进行空间优化(对象晋升时)
- 采用增量标记进行效率优化
- VS 新生代
- 新生代—空间换时间
- 老生代不适合复制算法(空间浪费、复制量大)
4、performance工具
- 为啥使用performance
- GC的目的是为了实现内存空间的良性循环
- 良性循环的基石是合理利用
- 时刻关注才能确定是否合理
- performance提供多种监控方式
- performance使用
- 打开浏览器输入目标网址
- F12面板 — 性能
- 开启录制功能,访问具体页面
- 执行用户行为,一段时间后停止录制
- 分析界面中记录的内存信息
- 内存问题的体现
- 页面出现延迟加载或经常性暂停
- 页面持续性出现槽糕的性能
- 页面性能随时间延长越来越差
- 界定内存问题的标准
- 内存泄漏 内存使用持续升高
- 内存膨胀 在多数设备上都存在性能问题
- 频繁垃圾回收 通过内存变化图分析
- 监控内存的几种方式
5、代码优化
-
如何精准测试JS性能?
- 本质上就是采集大量的执行样本进行数学统计和分析
- 使用基于Benchmark.js的https://jsperf.com完成
-
jsperf使用流程
- 使用GitHub账号登录
- 填写个人信息(非必填)
- 填写详细的测试用例信息(title、slug)
- 填写准备代码(DOM操作时经常使用)
- 填写必要有setup与teardown代码
- 填写测试代码片段
-
慎用全局变量
- 全局变量定义在全局执行上下文,是所有作用域链的顶端
- 全局执行上下文一直存在于上下文执行栈,直到程序退出
- 如果某个局部作用域出现了同名变量则会出现遮蔽或污染全局
-
缓存全局变量
- 将使用中无法避免的全局变量缓存到局部
-
通过原型对象添加附加方法
-
避开闭包陷阱
- 闭包的特点
- 外部具有指向内部的引用
- 在‘外’部作用域访问‘内’部作用域的数据
- 关于闭包
- 闭包是一种强大的语法
- 闭包使用不当很容易出现内存泄漏
- 不要为了闭包而闭包
- 闭包的特点
-
避免属性访问方法使用
- JS不需属性的访问方法,所有属性都是外部可见的
- 使用属性访问方法只会增加一层重定义,没有访问的控制力
-
选择最优的循环方法
- for(中)
- for … in (低)
- foreach (高)
-
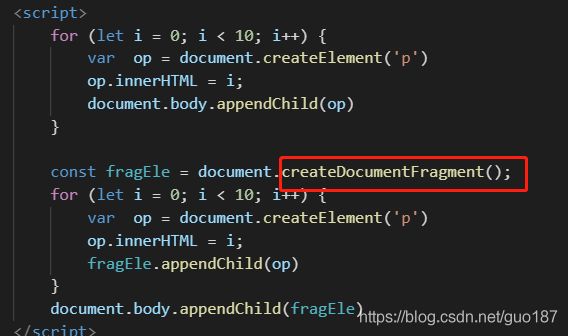
直接量替换new Object
var a = [1,2,3]// 推荐
var a1 = new Array(3)
a1[0] = 1;
a1[1] = 2;
a1[2] = 3;