UNIX环境高级编程笔记(1)UNIX基础知识
目录操作
/usr/include/dirent.h:
/* Open a directory stream on NAME.
Return a DIR stream on the directory, or NULL if it could not be opened.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern DIR *opendir (const char *__name);
/* Read a directory entry from DIRP. Return a pointer to a `struct
dirent' describing the entry, or NULL for EOF or error. The
storage returned may be overwritten by a later readdir call on the
same DIR stream.
If the Large File Support API is selected we have to use the
appropriate interface.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern struct dirent *readdir (DIR *__dirp);
/* Close the directory stream DIRP.
Return 0 if successful, -1 if not.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int closedir (DIR *__dirp);
opendir打开一个目录,参数是目录的名字,打不开返回NULL。
readdir读取目录中的entry,可以循环读直到读完之后返回NULL。
DIR的说明:
/* This is the data type of directory stream objects.
The actual structure is opaque to users. */
typedef struct __dirstream DIR;
注意这里的注释,DIR对用户是透明的,所以这里也不能直接看到它的详细结构,我们直接拿来用就行。
dirent的说明:
struct dirent
{
#ifndef __USE_FILE_OFFSET64
__ino_t d_ino;
__off_t d_off;
#else
__ino64_t d_ino;
__off64_t d_off;
#endif
unsigned short int d_reclen; // 文件名长度
unsigned char d_type; // 文件类型
char d_name[256]; /* We must not include limits.h! */
};
代码示例intro/ls1.c:
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
DIR *dp;
struct dirent *dirp;
if (argc != 2)
err_quit("usage: ls directory_name");
if ((dp = opendir(argv[1])) == NULL)
err_sys("can't open %s", argv[1]);
while ((dirp = readdir(dp)) != NULL)
printf("%s: %d %d\n", dirp->d_name, dirp->d_reclen, dirp->d_type);
closedir(dp);
exit(0);
}
输入输出
/usr/include/unistd.h:
/* Read NBYTES into BUF from FD. Return the
number read, -1 for errors or 0 for EOF.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern ssize_t read (int __fd, void *__buf, size_t __nbytes);
/* Write N bytes of BUF to FD. Return the number written, or -1.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern ssize_t write (int __fd, const void *__buf, size_t __n);
这里的__fd是文件描述符,下面是几个最通用的文件描述符:
/* Standard file descriptors. */
#define STDIN_FILENO 0 /* Standard input. */
#define STDOUT_FILENO 1 /* Standard output. */
#define STDERR_FILENO 2 /* Standard error output. */
文件描述符是一个整型,可以通过open来打开/usr/include/fcntl.h:
/* Open FILE and return a new file descriptor for it, or -1 on error.
OFLAG determines the type of access used. If O_CREAT or O_TMPFILE is set
in OFLAG, the third argument is taken as a `mode_t', the mode of the
created file.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern int open (const char *__file, int __oflag, ...);
代码示例fileio/mycat.c:
int
main(void)
{
int n;
char buf[BUFFSIZE];
while ((n = read(STDIN_FILENO, buf, BUFFSIZE)) > 0)
if (write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n) != n)
err_sys("write error");
if (n < 0)
err_sys("read error");
exit(0);
}
这里的open、read、write等是不带缓冲的IO操作。另外还有的输入输出函数/usr/include/stdio.h:
/* Read a character from STREAM.
These functions are possible cancellation points and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int fgetc (FILE *__stream);
extern int getc (FILE *__stream);
/* Write a character to STREAM.
These functions are possible cancellation points and therefore not
marked with __THROW.
These functions is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern int fputc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
FILE是一个文件流结构体,下面是最常见的几个例子/usr/include/stdio.h:
/* Standard streams. */
extern struct _IO_FILE *stdin; /* Standard input stream. */
extern struct _IO_FILE *stdout; /* Standard output stream. */
extern struct _IO_FILE *stderr; /* Standard error output stream. */
下面是一个代码例子stdio/getcputc.c:
int
main(void)
{
int c;
while ((c = getc(stdin)) != EOF)
if (putc(c, stdout) == EOF)
err_sys("output error");
if (ferror(stdin))
err_sys("input error");
exit(0);
}
进程
/usr/include/unistd.h:
/* Get the process ID of the calling process. */
extern __pid_t getpid (void);
这是比较简单的一个函数,就是直接返回一个值,__pid_t就是一个整型。下面是一个代码的例子intro/hello.c:
int
main(void)
{
printf("hello world from process ID %ld\n", (long)getpid());
exit(0);
}
进程控制的主要函数/usr/include/unistd.h:
/* Clone the calling process, creating an exact copy.
Return -1 for errors, 0 to the new process,
and the process ID of the new process to the old process. */
extern __pid_t fork (void);
/* Execute PATH with arguments ARGV and environment from `environ'. */
extern int execv (const char *__path, char *const __argv[]);
/* Replace the current process, executing PATH with arguments ARGV and
environment ENVP. ARGV and ENVP are terminated by NULL pointers. */
extern int execve (const char *__path, char *const __argv[],
char *const __envp[]);
/* Execute FILE, searching in the `PATH' environment variable if it contains
no slashes, with arguments ARGV and environment from `environ'. */
extern int execvp (const char *__file, char *const __argv[]);
/* Execute PATH with all arguments after PATH until
a NULL pointer and environment from `environ'. */
extern int execl (const char *__path, const char *__arg, ...)
__THROW __nonnull ((1, 2));
/* Execute PATH with all arguments after PATH until a NULL pointer,
and the argument after that for environment. */
extern int execle (const char *__path, const char *__arg, ...)
__THROW __nonnull ((1, 2));
/* Execute FILE, searching in the `PATH' environment variable if
it contains no slashes, with all arguments after FILE until a
NULL pointer and environment from `environ'. */
extern int execlp (const char *__file, const char *__arg, ...);
/* Wait for a child matching PID to die.
If PID is greater than 0, match any process whose process ID is PID.
If PID is (pid_t) -1, match any process.
If PID is (pid_t) 0, match any process with the
same process group as the current process.
If PID is less than -1, match any process whose
process group is the absolute value of PID.
If the WNOHANG bit is set in OPTIONS, and that child
is not already dead, return (pid_t) 0. If successful,
return PID and store the dead child's status in STAT_LOC.
Return (pid_t) -1 for errors. If the WUNTRACED bit is
set in OPTIONS, return status for stopped children; otherwise don't.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern __pid_t waitpid (__pid_t __pid, int *__stat_loc, int __options);
fork返回0的是子进程,大于0的是返回给父进程的子进程ID。exec有一系列的函数,具体的差异略。waitpid等待子进程结束。下面是一个代码的例子intro/shell1.c:
int
main(void)
{
char buf[MAXLINE]; /* from apue.h */
pid_t pid;
int status;
printf("%% "); /* print prompt (printf requires %% to print %) */
while (fgets(buf, MAXLINE, stdin) != NULL) {
if (buf[strlen(buf) - 1] == '\n')
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = 0; /* replace newline with null */
if ((pid = fork()) < 0) {
err_sys("fork error");
} else if (pid == 0) { /* child */
execlp(buf, buf, (char *)0);
err_ret("couldn't execute: %s", buf);
exit(127);
}
/* parent */
if ((pid = waitpid(pid, &status, 0)) < 0)
err_sys("waitpid error");
printf("%% ");
}
exit(0);
}
出错处理
UNIX系统函数出错时,通常返回一个负值。系统调用的返回值会赋值给整型变量errno,表示系统调用的结果,每个线程都有属于自己的局部errno,定义如下/usr/include/errno.h:
/* The error code set by various library functions. */
extern int *__errno_location (void) __THROW __attribute_const__;
# define errno (*__errno_location ())
错误的类型有如下一些/usr/include/asm-generic/errno-base.h:
/* SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0 WITH Linux-syscall-note */
#ifndef _ASM_GENERIC_ERRNO_BASE_H
#define _ASM_GENERIC_ERRNO_BASE_H
#define EPERM 1 /* Operation not permitted */
#define ENOENT 2 /* No such file or directory */
#define ESRCH 3 /* No such process */
#define EINTR 4 /* Interrupted system call */
#define EIO 5 /* I/O error */
#define ENXIO 6 /* No such device or address */
#define E2BIG 7 /* Argument list too long */
#define ENOEXEC 8 /* Exec format error */
#define EBADF 9 /* Bad file number */
#define ECHILD 10 /* No child processes */
#define EAGAIN 11 /* Try again */
#define ENOMEM 12 /* Out of memory */
#define EACCES 13 /* Permission denied */
#define EFAULT 14 /* Bad address */
#define ENOTBLK 15 /* Block device required */
#define EBUSY 16 /* Device or resource busy */
#define EEXIST 17 /* File exists */
#define EXDEV 18 /* Cross-device link */
#define ENODEV 19 /* No such device */
#define ENOTDIR 20 /* Not a directory */
#define EISDIR 21 /* Is a directory */
#define EINVAL 22 /* Invalid argument */
#define ENFILE 23 /* File table overflow */
#define EMFILE 24 /* Too many open files */
#define ENOTTY 25 /* Not a typewriter */
#define ETXTBSY 26 /* Text file busy */
#define EFBIG 27 /* File too large */
#define ENOSPC 28 /* No space left on device */
#define ESPIPE 29 /* Illegal seek */
#define EROFS 30 /* Read-only file system */
#define EMLINK 31 /* Too many links */
#define EPIPE 32 /* Broken pipe */
#define EDOM 33 /* Math argument out of domain of func */
#define ERANGE 34 /* Math result not representable */
#endif
0表示成功,其它是错误。
有两个函数用于打印出错信息/usr/include/stdio.h,/usr/include/string.h:
/* Print a message describing the meaning of the value of errno.
This function is a possible cancellation point and therefore not
marked with __THROW. */
extern void perror (const char *__s);
/* Return a string describing the meaning of the `errno' code in ERRNUM. */
extern char *strerror (int __errnum) __THROW;
perror直接打印错误,打印的格式是“__s对应的值: errno对应的出错信息”;strerror是返回对应errno错误的字符串。下面是一个代码例子intro/testerror.c:
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
fprintf(stderr, "EACCES: %s\n", strerror(EACCES));
errno = ENOENT;
perror(argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
从这里可以看到errno可以直接被设置。下面是打印的代码:
EACCES: Permission denied
./testerror: No such file or directory
用户标识
/usr/include/unistd.h:
/* Get the real user ID of the calling process. */
extern __uid_t getuid (void) __THROW;
/* Get the real group ID of the calling process. */
extern __gid_t getgid (void) __THROW;
UID是实际用户ID,GID是用户所在实际组ID。下面是一个代码例子intro/uidgid.c:
int
main(void)
{
printf("uid = %d, gid = %d\n", getuid(), getgid());
exit(0);
}
执行的结果:
jw@X1C:~/code/apue/intro$ ./uidgid
uid = 1000, gid = 1000
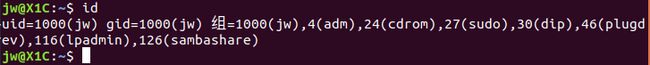
通过id命令查看,也得到相同的结果:
UID、GID对应到了具体的用户,这里就是jw。
信号
信号用于通知进程发生了某种情况。例如:某一进程执行了除0操作,则将名为SIGFPE(浮点异常)的信号发送给该进程;终端键盘有两种产生信号的方法,中断键(Ctrl+c)和退出键(Crl+\);调用kill函数可以向另一个进程发送一个信号(当向一个进程发送信号时,我们必须是那个进程的所有者或者超级用户)。进程对过来的信号有3种处理方式:
-
忽略;
-
按系统默认方式处理;
-
提供一个函数,信号发生时调用该函数,这被称为捕捉该信号。
对应的几个函数说明/usr/include/signal.h:
/* Set the handler for the signal SIG to HANDLER, returning the old
handler, or SIG_ERR on error.
By default `signal' has the BSD semantic. */
extern __sighandler_t signal (int __sig, __sighandler_t __handler);
/* Send signal SIG to process number PID. If PID is zero,
send SIG to all processes in the current process's process group.
If PID is < -1, send SIG to all processes in process group - PID. */
extern int kill (__pid_t __pid, int __sig) __THROW;
signal接受两个函数,第一个是信号;第二个是信号处理函数,它对应的原型如下:
/* Type of a signal handler. */
typedef void (*__sighandler_t) (int);
对应的信号/usr/include/asm-generic/signal.h:
#define SIGHUP 1
#define SIGINT 2
#define SIGQUIT 3
#define SIGILL 4
#define SIGTRAP 5
#define SIGABRT 6
#define SIGIOT 6
#define SIGBUS 7
#define SIGFPE 8
#define SIGKILL 9
#define SIGUSR1 10
#define SIGSEGV 11
#define SIGUSR2 12
#define SIGPIPE 13
#define SIGALRM 14
#define SIGTERM 15
#define SIGSTKFLT 16
#define SIGCHLD 17
#define SIGCONT 18
#define SIGSTOP 19
#define SIGTSTP 20
#define SIGTTIN 21
#define SIGTTOU 22
#define SIGURG 23
#define SIGXCPU 24
#define SIGXFSZ 25
#define SIGVTALRM 26
#define SIGPROF 27
#define SIGWINCH 28
#define SIGIO 29
#define SIGPOLL SIGIO
/*
#define SIGLOST 29
*/
#define SIGPWR 30
#define SIGSYS 31
#define SIGUNUSED 31
/* These should not be considered constants from userland. */
#define SIGRTMIN 32
#ifndef SIGRTMAX
#define SIGRTMAX _NSIG
#endif
下面是一个例子intro/shell2.c:
int
main(void)
{
char buf[MAXLINE]; /* from apue.h */
pid_t pid;
int status;
if (signal(SIGINT, sig_int) == SIG_ERR)
err_sys("signal error");
printf("%% "); /* print prompt (printf requires %% to print %) */
while (fgets(buf, MAXLINE, stdin) != NULL) {
if (buf[strlen(buf) - 1] == '\n')
buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = 0; /* replace newline with null */
if ((pid = fork()) < 0) {
err_sys("fork error");
} else if (pid == 0) { /* child */
execlp(buf, buf, (char *)0);
err_ret("couldn't execute: %s", buf);
exit(127);
}
/* parent */
if ((pid = waitpid(pid, &status, 0)) < 0)
err_sys("waitpid error");
printf("%% ");
}
exit(0);
}
void
sig_int(int signo)
{
printf("interrupt\n%% ");
}
这里注册的中断信号是SIGINT,表示中断信号,按下中断键的时候会触发。这个代码跟之前的intro/shell1.c差别不大,只是增加了SIGINT的处理函数,它覆盖了原来的默认的SIGINT处理函数。