黑马程序员3天玩转Python深度学习tensorflow(第一天)
文章目录
- 一、深度学习的介绍
-
- 1.1 深度学习与机器学习的区别
-
- 1.1.1 特征提取方面
- 1.1.2 数据量和计算性能要求
- 1.1.3 算法代表
- 1.2 深度学习的应用场景
- 1.3 深度学习框架介绍
-
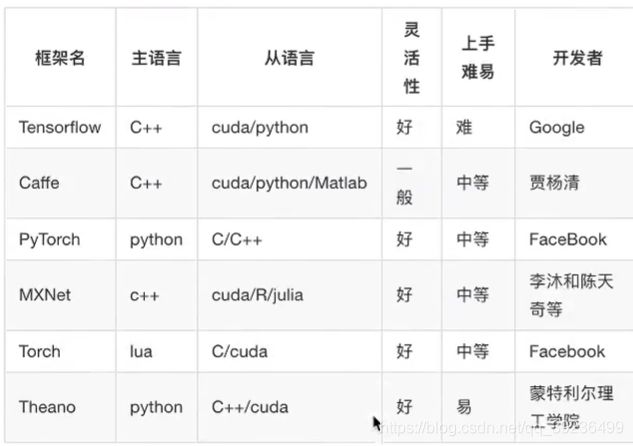
- 1.3.1 常见深度学习框架对比
- 1.3.2 tensorflow的特点
- 1.3.3 tensorflow的安装
- 二、tensorflow框架介绍
-
- 2.1 TF数据流图
-
- 2.1.1 案例:tensorflow实现一个加法运算
- 2.2 图与TensorBoard
-
- 2.2.1 什么是图结构
- 2.2.2 图相关操作
- 2.2.3 TensorBoard可视化学习
- 2.2.4 OP
- 2.3 会话
-
- 2.3.1 会话创建
- 2.4 张量
-
- 2.4.1 张量(Tensor)
- 2.4.2 创建张量的指令
- 2.4.3 张量的变换
- 2.4.4 张量的数学运算
- 2.5 变量OP
-
- 2.5.1 创建变量
- 2.5.2 使用tf.variable_scope()修改变量的命名空间
- 2.6 高级API
-
- 2.6.1 其他基础API
- 2.6.2 高级API
- 2.7 案例:实现线性回归
-
- 2.7.2 案例:实现线性回归的训练
- 2.7.3 增加其他功能
学习目标:
- 第一天:tensorflow框架实用
- 第二天:数据读取、神经网络基础
- 第三天:卷积神经网络、验证码识别
第一天:
- 学习学习介绍
- tensorflow框架的使用
-
- 1)tensorflow的结构
-
- 2)tensorflow的各个组件:图、会话、张量、变量
-
- 3)简单的线性回归案例----将TensorFlow用起来
一、深度学习的介绍
1.1 深度学习与机器学习的区别
学习目标:知道深度学习与机器学习的区别
区别:深度学习没有特征提取

1.1.1 特征提取方面
- 机器学习的特征工程步骤是要靠手动完成的,而且需要大量领域专业知识
- 深度学习通常由多个层组成,它们通常将更简单的模型组合在一起,将数据从一层传递到另一层来构建更复杂的模型。通过训练大量数据自动得到模型,不需要人工特征提取环节
深度学习算法试图从数据中学习高级功能,这是深度学习的一个非常独特的部分。因此,减少了为每个问题开发新特征提取器的任务。适合用在难提取特征的图像、语音、自然语言处理领域
1.1.2 数据量和计算性能要求
机器学习需要的执行时间远少于深度学习,深度学习参数往往很庞大,需要通过大量
数据的多次优化来训练参数
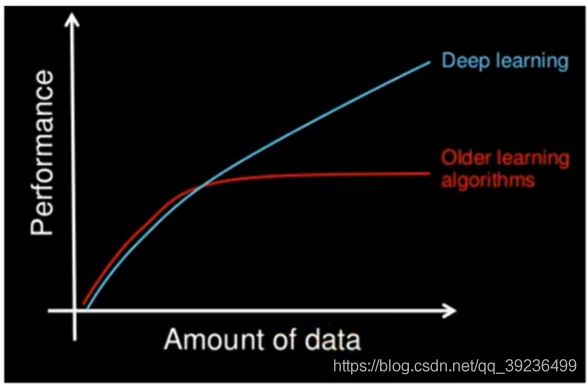
- 第一,深度学习需要大量的训练数据集
- 第二,训练深度神经网络需要大量的算力
可能要花费数天、甚至数周的时间,才能使用数百万张图像的数据集训练出一个深度网络。所以深度学习通常需要强大的GPU服务器来进行计算
1.1.3 算法代表
机器学习:朴素贝叶斯,决策树
深度学习:神经网络
1.2 深度学习的应用场景
图像识别:物体识别、场景识别、车型识别、人脸检测跟踪、人脸关键点定位、人脸身份认证
自然语言处理技术:机器翻译、文本识别、聊天对话
语音技术:语音识别
1.3 深度学习框架介绍
1.3.1 常见深度学习框架对比
1.3.2 tensorflow的特点
官网:https://www.tensorflow.org/
1.3.3 tensorflow的安装
1 CPU版本
2 GPU版本:核芯数量多,更适合处理并行任务
pip install tensorflow==1.8 -i https://pypi.douban.com/simple
二、tensorflow框架介绍
2.1 TF数据流图
学习目标:说明tensorflow的数据流图结构
2.1.1 案例:tensorflow实现一个加法运算
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def tensorflow_demo():
"""
tensorflow的基本结构
:return:
"""
# tensorflow实现加法运算
a_t = tf.constant(2)
b_t = tf.constant(3)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("c_t:", c_t)
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
print("c_t_value:", c_t_value)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
tensorflow_demo()
c_t: Tensor("add:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
c_t_value: 5
2 TensorFlow结构分析
TensorFlow程序通常被组织成一个构件图阶段和一个执行图阶段。
在构建阶段,数据与操作的执行步骤被描述为一个图
在执行阶段,使用会话执行构建好的图中的操作
图:这是TensorFlow将计算表示为指令之间的依赖关系的一种表示法
会话:TensorFlow跨一个或多个本地或远程设备运行数据流图的机制
张量:TensorFlow中的基本数据对象
节点:提供图当中执行的操作
2.2 图与TensorBoard
学习目标:
- 说明图的基本使用
- 应用tf.Graph创建图,tf.get_default_graph获取默认图
- 知道开启TensorBoard过程
- 知道图当中op的名字以及命名空间
2.2.1 什么是图结构
图包含了一组tf.Operation代表的计算单元对象和tf.Tensor代表的计算单元之间流动的数据
2.2.2 图相关操作
1 默认图
通常tensorflow会默认帮我们创建一张图
查看默认图的两种方法:
- 通过调用**tf.get_default_graph()**访问,要将操作添加到默认图形中,直接创建OP即可
- op、sess都含有graph属性,默认都在一张图中
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def graph_demo():
"""
图的演示
:return:
"""
# tensorflow实现加法运算
a_t = tf.constant(2)
b_t = tf.constant(3)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("c_t:", c_t)
# 查看默认图
# 方法1:调用方法
default_g = tf.get_default_graph()
print("default_g:", default_g)
# 方法2:查看属性
print("a_t的图属性:", a_t.graph)
print("c_t的图属性:", c_t.graph)
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
print("c_t_value:", c_t_value)
print("sess的图属性:", sess.graph)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
graph_demo()
c_t: Tensor("add:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
default_g: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x000002A49DEA72B0>
a_t的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x000002A49DEA72B0>
c_t的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x000002A49DEA72B0>
c_t_value: 5
sess的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x000002A49DEA72B0>
2 创建图
- 可以通过**tf.Graph()**自定义创建图
- 如果要在这张图中创建OP,典型用法是使用**tf.Graph.as_default()**上下文管理器
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def graph_demo():
"""
图的演示
:return:
"""
# tensorflow实现加法运算
a_t = tf.constant(2)
b_t = tf.constant(3)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("c_t:", c_t)
# 查看默认图
# 方法1:调用方法
default_g = tf.get_default_graph()
print("default_g:", default_g)
# 方法2:查看属性
print("a_t的图属性:", a_t.graph)
print("c_t的图属性:", c_t.graph)
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
print("c_t_value:", c_t_value)
print("sess的图属性:", sess.graph)
print("--------------------------------")
# 自定义图
new_g = tf.Graph()
# 在自己的图中定义数据和操作
with new_g.as_default():
a_new = tf.constant(20)
b_new = tf.constant(30)
c_new = a_new + b_new
print("c_new:", c_new)
print("a_new的图属性:", a_new.graph)
print("c_new的图属性:", c_new.graph)
# 开启new_g的会话
with tf.Session(graph=new_g) as new_sess:
# 试图运行自定义图中的数据,操作
c_new_value = new_sess.run(c_new)
print("c_new_value:", c_new_value)
print("new_sess的图属性:", new_sess.graph)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
graph_demo()
c_t: Tensor("add:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
default_g: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x00000152C1C87400>
a_t的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x00000152C1C87400>
c_t的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x00000152C1C87400>
c_t_value: 5
sess的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x00000152C1C87400>
--------------------------------
c_new: Tensor("add:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
a_new的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x00000152E6FFD9B0>
c_new的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x00000152E6FFD9B0>
c_new_value: 50
new_sess的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x00000152E6FFD9B0>
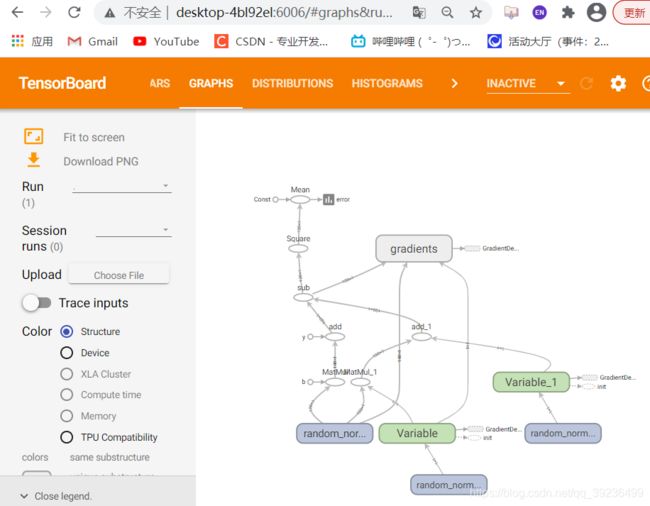
2.2.3 TensorBoard可视化学习
tensorflow可用于训练大规模深度神经网络所需的计算,使用该工具设计的计算往往复杂而深奥。为了更方便tensorflow程序的理解、调试与优化,tensorflow提供了TensorBoard可视化工具
实现程序可视化过程:
1 数据序列化-events文件
TensorBoard通过读取TensorFlow的事件文件来运行,需要将数据生成一个序列化的Summary protobuf对象
tf.summary.FileWriter(path, graph=sess.graph)
2 启动TensorBoard
tensorboard --logdir=path
例:
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def graph_demo():
"""
图的演示
:return:
"""
# tensorflow实现加法运算
a_t = tf.constant(2)
b_t = tf.constant(3)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("c_t:", c_t)
# 查看默认图
# 方法1:调用方法
default_g = tf.get_default_graph()
print("default_g:", default_g)
# 方法2:查看属性
print("a_t的图属性:", a_t.graph)
print("c_t的图属性:", c_t.graph)
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
print("c_t_value:", c_t_value)
print("sess的图属性:", sess.graph)
# 1)将图写入本地生成events文件
tf.summary.FileWriter("summary", graph=sess.graph) # tmp文件夹下
print("--------------------------------")
# 自定义图
new_g = tf.Graph()
# 在自己的图中定义数据和操作
with new_g.as_default():
a_new = tf.constant(20)
b_new = tf.constant(30)
c_new = a_new + b_new
print("c_new:", c_new)
print("a_new的图属性:", a_new.graph)
print("c_new的图属性:", c_new.graph)
# 开启new_g的会话
with tf.Session(graph=new_g) as new_sess:
# 试图运行自定义图中的数据,操作
c_new_value = new_sess.run(c_new)
print("c_new_value:", c_new_value)
print("new_sess的图属性:", new_sess.graph)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
graph_demo()
2.2.4 OP
即操作对象
| 操作函数 | 操作对象 |
|---|---|
| tf.constant(Tensor对象) | 输入Tensor对象-Const输出 Tensor对象 |
| tf.add(Tensor对象1,Tensor对象2) | 输入(Tensor对象1,Tensor对象2) ,add对象,输出 Tensor对象3 |
- 一个图一个命名空间,互不干扰影响
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def graph_demo():
"""
图的演示
:return:
"""
# tensorflow实现加法运算
a_t = tf.constant(2, name="a_t")
b_t = tf.constant(3, name="b_t")
c_t = tf.add(a_t, b_t, name="c_t")
print("c_t:", c_t)
# 查看默认图
# 方法1:调用方法
default_g = tf.get_default_graph()
print("default_g:", default_g)
# 方法2:查看属性
print("a_t的图属性:", a_t.graph)
print("c_t的图属性:", c_t.graph)
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
print("c_t_value:", c_t_value)
print("sess的图属性:", sess.graph)
# 1)将图写入本地生成events文件
tf.summary.FileWriter("logs", graph=sess.graph)
print("--------------------------------")
# 自定义图
new_g = tf.Graph()
# 在自己的图中定义数据和操作
with new_g.as_default():
a_new = tf.constant(20, name="a_new")
b_new = tf.constant(30, name="b_new")
c_new = tf.add(a_new, b_new, name="c_new")
print("c_new:", c_new)
print("a_new的图属性:", a_new.graph)
print("c_new的图属性:", c_new.graph)
tf.summary.FileWriter("log2", graph=sess.graph)
# 开启new_g的会话
with tf.Session(graph=new_g) as new_sess:
# 试图运行自定义图中的数据,操作
c_new_value = new_sess.run(c_new)
print("c_new_value:", c_new_value)
print("new_sess的图属性:", new_sess.graph)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
graph_demo()
2.3 会话
学习目标:
- 应用sess.rn或者eval运行图程序并获取张量值
- 应用feed_dict机制实现运行时填充数据
- 应用placeholder实现创建占位符
2.3.1 会话创建
上下文管理器:
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(sth)
- target:如果将此参数留空(默认设置),会话将仅使用本地计算机中的设备。可以指定grpc://网址,以便指定TensorFlow服务器的地址,这使得会话可以访问该服务器控制的计算机上的所有设备
- graph:默认情况下,新的tf.Session将绑定到当前的默认图
- config:此参数允许您指定一个tf.ConfigProto以便控制会话的行为。例如,ConfigProto协议用于打印设备使用信息
# 运行会话并打印设备信息
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=True))
2 会话的run()
通过使用sess.run(0)来运行operation
run(fetches, feed_dict=None, options=None, run_metadata=None)
- fetches:单一的operation,或者列表、元组(其他不属于tensorflow的类型不行)
- feed_dict:参数运行调用者覆盖图中张量的值,运行时赋值,与tf.placeholder搭配使用,则会检查值的形式是否与占位符兼容
# 创建图
a = tf.constant(5.0)
b = tf.constant(6.0)
c = a + b
# 创建会话
sess = tf.Session()
# 计算C的值
print(sess.run(c))
print(c.eval(session=sess))
3 feed操作
- placeholder提供占位符,run时候通过feed_dict指定参数
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def session_demo():
"""
会话的演示:打印设备信息
:return:
"""
# tensorflow实现加法运算
a_t = tf.constant(2, name="a_t")
b_t = tf.constant(3, name="b_t")
c_t = tf.add(a_t, b_t, name="c_t")
print("a_t", a_t)
print("b_t", b_t)
print("c_t:", c_t)
print("------------------------------")
# 定义占位符
a_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
b_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
c_ph = tf.add(a_ph, b_ph)
print("a_ph:", a_ph)
print("b_ph:", b_ph)
print("c_ph:", c_ph)
print("------------------------------")
# 查看默认图
# 方法1:调用方法
default_g = tf.get_default_graph()
print("default_g:", default_g)
# 方法2:查看属性
print("a_t的图属性:", a_t.graph)
print("c_t的图属性:", c_t.graph)
print("-------------------------------")
# 开启会话
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True,
log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
# 运行placeholder
c_ph_value = sess.run(c_ph, feed_dict={
a_ph:3.9, b_ph:4.8})
print('c_ph_value', c_ph_value)
print("------------------------------")
abc = sess.run([a_t, b_t, c_t]) # 传入列表,返回列表
print("abc:", abc)
print("c_t_value;", c_t.eval())
print("sess的图属性:", sess.graph)
#tf.summary.FileWriter("logs", graph=sess.graph) # 1)将图写入本地生成events文件
if __name__ == "__main__":
session_demo()
a_t Tensor("a_t:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
b_t Tensor("b_t:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
c_t: Tensor("c_t:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
------------------------------
a_ph: Tensor("Placeholder:0", dtype=float32)
b_ph: Tensor("Placeholder_1:0", dtype=float32)
c_ph: Tensor("Add:0", dtype=float32)
------------------------------
default_g: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x000001618EF65748>
a_t的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x000001618EF65748>
c_t的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x000001618EF65748>
-------------------------------
Device mapping: no known devices.
Add: (Add): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
c_t: (Add): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
Placeholder_1: (Placeholder): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
Placeholder: (Placeholder): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
b_t: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
a_t: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
c_ph_value 8.700001
------------------------------
abc: [2, 3, 5]
c_t_value; 5
sess的图属性: <tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x000001618EF65748>
2.4 张量
学习目标:
- 知道常见的TensorFlow创建张量
- 知道常见的张量数学运算操作
- 说明numpy的数组与张量相同性
- 说明张量的两种形状改变特点
- 应用set_shape和tf.reshape山西爱你张量形状的修改
- 应用tf.matmul实现张量的矩阵运算修改
- 应用tf.cast实现张量的类型
2.4.1 张量(Tensor)
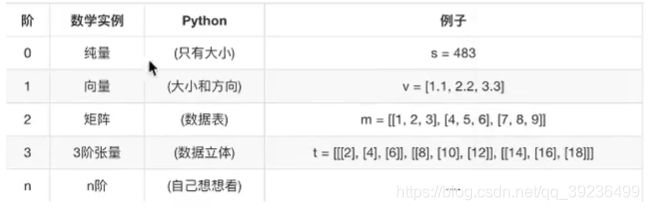
TensorFlow的张量就是一个N维数组,类型为tf.Tensor。
张量:在计算机当中如何存储?N维数组
标量:一个数字----0阶张量
向量:一维数组-----1阶张量
矩阵:二维数组------2阶张量
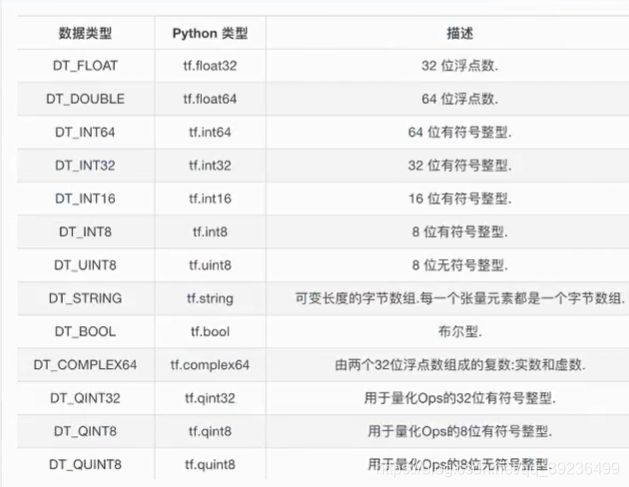
- type:数据类型
- shape:形状(阶)
- 整型:tf.int32
- 浮点型:tf.float32
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def tensor_demo():
"""
张量的演示
:return:
"""
tensor1 = tf.constant(4.0)
tensor2 = tf.constant([1,2,3,4]) # 未指定类型,默认类型
linear_squares = tf.constant([[4],[9],[16],[25]],dtype=tf.int32)
print("tensor1:", tensor1)
print("tensor2:", tensor2)
print("linear_square:", linear_squares)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
tensor_demo()
tensor1: Tensor("Const:0", shape=(), dtype=float32)
tensor2: Tensor("Const_1:0", shape=(4,), dtype=int32)
linear_square: Tensor("Const_2:0", shape=(4, 1), dtype=int32)
2.4.2 创建张量的指令
固定值张量
1 创建多个0
tf.zeros(shape, dtype=tf.float32, name=None)
2 创建多个1
tf.ones(shape, dtype=tf.float32, name=None)
3 创建常数张量
tf.constant(value, dtype=tf.float32, name='Const')
2.4.3 张量的变换
1 类型改变
- tf.string_to_number(string_tensor, out_type=None, name=None)
- tf.to_double(x, name=‘ToDouble’)
- tf.to_float(x, name=‘ToFloat’)
- tf.to_bfloat16(x, name=“ToBFloat16”)
- tf.to_int32(x, name=‘Tolnt32’)
- tf.to_int64(x, name=‘Tolnt64’)
- tf.cast(x, dtype, name=None),通用类型转换
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def tensor_demo():
"""
张量的演示
:return:
"""
tensor1 = tf.constant(4.0)
tensor2 = tf.constant([1,2,3,4]) # 未指定类型,默认类型
linear_squares = tf.constant([[4],[9],[16],[25]],dtype=tf.int32)
print("tensor1:", tensor1)
print("tensor2:", tensor2)
print("linear_square:", linear_squares)
print("----------------")
# 张量类型的修改:不会改变原始的Tensor
l_cast = tf.cast(linear_squares, dtype=tf.float32)
print("linear_square_after:", linear_squares)
print('l_cast:', l_cast)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
tensor_demo()
tensor1: Tensor("Const:0", shape=(), dtype=float32)
tensor2: Tensor("Const_1:0", shape=(4,), dtype=int32)
linear_square: Tensor("Const_2:0", shape=(4, 1), dtype=int32)
----------------
linear_square_after: Tensor("Const_2:0", shape=(4, 1), dtype=int32)
l_cast: Tensor("Cast:0", shape=(4, 1), dtype=float32)
2 形状改变
tensorflow的张量具有两种形状变换,动态形状和静态形状
-
tf.reshape:改变动态形状
-
tf.set_shape:改变静态形状
-
静态形状:初始创建张量时的形状
-
动态形状:
什么情况下可以改变静态形状:只有在形状还没有完全固定下来的情况下;转换形状的时候,只能一维到一维,二维到二维,而不能跨维度改变形状
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def tensor_demo():
"""
张量的演示
:return:
"""
tensor1 = tf.constant(4.0)
tensor2 = tf.constant([1,2,3,4]) # 未指定类型,默认类型
linear_squares = tf.constant([[4],[9],[16],[25]],dtype=tf.int32)
print("tensor1:", tensor1)
print("tensor2:", tensor2)
print("linear_square:", linear_squares)
print("----------------")
# 张量类型的修改:不会改变原始的Tensor
l_cast = tf.cast(linear_squares, dtype=tf.float32)
print("linear_square_after:", linear_squares)
print('l_cast:', l_cast)
print('------------------')
# 更新、改变静态形状
# 定义占位符
a_p = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, None]) # 形状没有完全固定下来的静态形状
b_p = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, 10])
c_p = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[3, 2])
print("a_p:", a_p)
print("b_p:", b_p)
print("c_p:", c_p)
print("-----------------------")
# 更新形状未确定的部分
a_p.set_shape([2,3])
b_p.set_shape([2,10])
print("a_p:", a_p)
print("b_p:", b_p)
print('-------------')
# 动态形状修改
a_p_reshape = tf.reshape(a_p, shape=[2, 3, 1])
print("a_p:", a_p)
print("a_p_reshape:", a_p_reshape)
c_p_reshape = tf.reshape(c_p, shape=[2, 3, 1]) # 必须保持改变前后元素的数量一致
print("c_p:", c_p)
print("c_p_reshape:", c_p_reshape)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
tensor_demo()
tensor1: Tensor("Const:0", shape=(), dtype=float32)
tensor2: Tensor("Const_1:0", shape=(4,), dtype=int32)
linear_square: Tensor("Const_2:0", shape=(4, 1), dtype=int32)
----------------
linear_square_after: Tensor("Const_2:0", shape=(4, 1), dtype=int32)
l_cast: Tensor("Cast:0", shape=(4, 1), dtype=float32)
------------------
a_p: Tensor("Placeholder:0", shape=(?, ?), dtype=float32)
b_p: Tensor("Placeholder_1:0", shape=(?, 10), dtype=float32)
c_p: Tensor("Placeholder_2:0", shape=(3, 2), dtype=float32)
-----------------------
a_p: Tensor("Placeholder:0", shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32)
b_p: Tensor("Placeholder_1:0", shape=(2, 10), dtype=float32)
-------------
a_p: Tensor("Placeholder:0", shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32)
a_p_reshape: Tensor("Reshape:0", shape=(2, 3, 1), dtype=float32)
c_p: Tensor("Placeholder_2:0", shape=(3, 2), dtype=float32)
c_p_reshape: Tensor("Reshape_1:0", shape=(2, 3, 1), dtype=float32)
2.4.4 张量的数学运算
- 算术运算符
- 基本数学函数
- 矩阵运算
- reduce操作
- 序列索引操作
2.5 变量OP
学习目标:
- 说明变量op的特殊作用
- 说明变量op的trainable参数的作用
- 应用global_variables_initializer实现变量op的初始化
变量的特点:
- 存储持久化
- 可修改值
- 可指定被训练
2.5.1 创建变量
tf.Variable(initia_value=None, trainable=True, collections=None, name=None)
- initial_value:初始化的值
- trainable:是否被训练
- collections:新变量将添加到列出的图的集合中collections,默认为[GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES],如果trainable是True变量也被添加到图形集合GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES
变量需要显示初始化,才能运行值
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def variable_demo():
"""
变量的演示
:return:
"""
# 创建变量
a = tf.Variable(initial_value=50)
b = tf.Variable(initial_value=40)
c = tf.add(a, b)
print("a:", a)
print("b", b)
print("c", c)
print('----------------------')
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 运行初始化
sess.run(init)
a_value, b_value, c_value = sess.run([a,b,c])
print("a_value:", a_value)
print("b_value", b_value)
print("c_value", c_value)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
variable_demo()
a: <tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=() dtype=int32_ref>
b <tf.Variable 'Variable_1:0' shape=() dtype=int32_ref>
c Tensor("Add:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
----------------------
a_value: 50
b_value 40
c_value 90
2.5.2 使用tf.variable_scope()修改变量的命名空间
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def variable_demo():
"""
变量的演示
:return:
"""
# 创建变量
with tf.variable_scope("my_scope"):
a = tf.Variable(initial_value=50)
b = tf.Variable(initial_value=40)
with tf.variable_scope("your_scope"):
c = tf.add(a, b)
print("a:", a)
print("b", b)
print("c", c)
print('----------------------')
# 初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 运行初始化
sess.run(init)
a_value, b_value, c_value = sess.run([a,b,c])
print("a_value:", a_value)
print("b_value", b_value)
print("c_value", c_value)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
variable_demo()
a: <tf.Variable 'my_scope/Variable:0' shape=() dtype=int32_ref>
b <tf.Variable 'my_scope/Variable_1:0' shape=() dtype=int32_ref>
c Tensor("your_scope/Add:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
----------------------
a_value: 50
b_value 40
c_value 90
2.6 高级API
2.6.1 其他基础API
1 tf.app
这个模块相当于为TensorFlow进行的脚本提供一个main函数入口,可以定义脚本运行的flags
2 tf.image
TensorFlow的图像处理操作。主要是一些颜色变换、变形和图像的编码和解码
3 tf.gfile
这个模块提供了一组文件操作函数
4 tf.summary
用来生成TensorBoard可用的统计日志,目前Summary主要提供了4种类型:
audio、image、histogram、scalar
5 tf.python_io
用来读写TFRecords文件
6 tf.train
这个模块提供了一些训练器,与tf.nn结合起来,实现一些网络的优化计算
7 tf.nn
这个模块提供了一些构建神经网络的底层函数。TensorFlow构建网络的核心模块,其中包含了添加各种层的函数,比如添加卷积层、池化层等。
2.6.2 高级API
1 tf.keras
Kears本来是一个独立的深度学习库,tensorflow将其学习过来,增加这部分模块在于快速构建模型
2 tf.layers
高级API,以便高级的概念层来定义一个模型。类似tf.kears
3 tf.contrib
tf.contrib.layers提供够将计算图中的网络层、正则化、摘要操作,是构建计算图的高级操作,但是tf.contrib包含不稳定和实验代码,有可能以后API会改变
4 tf.estimator
一个estimator相当于model + training + evaluate 的合体。在模块中,已经实现了几种简单的分类器和回归其,包括:Baseline,learning 和 DNN。这里的DNN的网络,只是全连接网络,没有提供卷积之类的
2.7 案例:实现线性回归
学习目标:
- 应用op的name参数实现op的名字修改
- 应用variable_scope实现图程序作用域的添加
- 应用scalar或histogram实现张良志的跟踪显示
- 应用merge_all实现张量值的合并
- 应用add_summary实现张量值的写入文件
- 应用tf.train.saver实现TensorFlow的模型保存以及加载
- 应用tf.app.flags实现命令行参数添加和使用
- 应用reduce_mean、square实现均方误差计算
- 应用tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer实现有梯度下降优化器创建
- 应用minimize函数优化损失
- 知道梯度爆炸以及常见解决技巧
2.7.2 案例:实现线性回归的训练
1)构建模型
2)构建损失函数:均方误差
3)优化损失:梯度下降
准备真实数据:
x:特征值,形状:(100,1)
y_true:目标值 (100,1)
y_true = 0.8x + 0.7 ,100个样本
假设满足: y =kx + b
流程分析:
(100,1) * (1,1) = (100,1)
y_predict = x * weight(1,1) + bias(1,1)
1)构建模型
y_predict = tf.matmul(x, weights) + bias
2)构造损失函数
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true))
3)优化损失:梯度下降优化器
optimizer = tf.train.GrandientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
运算:
- 矩阵运算:tf.matmu(x,w)
- 平方:tf.square(error)
- 均方:tf.reduce_mean(error)
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def linear_regression():
"""
实现线性回归
:return:
"""
# 1)准备数据
X = tf.random_normal(shape=[100, 1]) # 形状:100行1列
y_true = tf.matmul(X, [[0.8]]) + 0.7 # y_true = 0.8x + 0.7
# 2)构造模型
# 定义模型参数,用变量
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]))
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]))
y_predict = tf.matmul(X, weights) + bias
# 3)构造损失函数
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true))
# 4)优化损失
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 显式地初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 初始化变量
sess.run(init)
# 查看初始化模型参数之后的值
print("训练前模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失为%f" %
(weights.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# 开始训练
for i in range(200):
sess.run(optimizer)
print("第%d训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失为%f" %
(i+1, weights.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
linear_regression()
...
第195训练后模型参数为:权重0.784588,偏置0.704202,损失为0.000298
第196训练后模型参数为:权重0.784881,偏置0.704130,损失为0.000259
第197训练后模型参数为:权重0.785245,偏置0.704024,损失为0.000256
第198训练后模型参数为:权重0.785542,偏置0.703911,损失为0.000219
第199训练后模型参数为:权重0.785778,偏置0.703855,损失为0.000218
第200训练后模型参数为:权重0.786084,偏置0.703762,损失为0.000211
5 学习率的设置、步数的设置与梯度爆炸
- 学习率越大,训练
2.7.3 增加其他功能
- 变量TensorBoard显示
- 增加命名空间
- 模型保存于加载
- 命令行参数设置
1 增加变量显示
目的:在TensorBoard当中观察模型的参数、损失值等变量值的变化

1)创建事件文件
2)收集变量
3)合并变量
4)每次迭代运行合并变量
5)每次迭代将summary事件写入事件文件
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def linear_regression():
"""
实现线性回归
:return:
"""
# 1)准备数据
X = tf.random_normal(shape=[100, 1]) # 形状:100行1列
y_true = tf.matmul(X, [[0.8]]) + 0.7 # y_true = 0.8x + 0.7
# 2)构造模型
# 定义模型参数,用变量
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]))
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]))
y_predict = tf.matmul(X, weights) + bias
# 3)构造损失函数
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true))
# 4)优化损失
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 2)收集变量
tf.summary.scalar("error", error)
tf.summary.histogram("weights", weights)
tf.summary.histogram("bias", bias)
# 3)合并变量
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
# 显式地初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 初始化变量
sess.run(init)
# 1)创建事件文件
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs', graph=sess.graph)
# 查看初始化模型参数之后的值
print("训练前模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失为%f" %
(weights.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# 开始训练
for i in range(100):
sess.run(optimizer)
print("第%d训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失为%f" %
(i+1, weights.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# 运行合并变量操作
summary = sess.run(merged)
# 每次迭代后的变量写入事件
file_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
linear_regression()
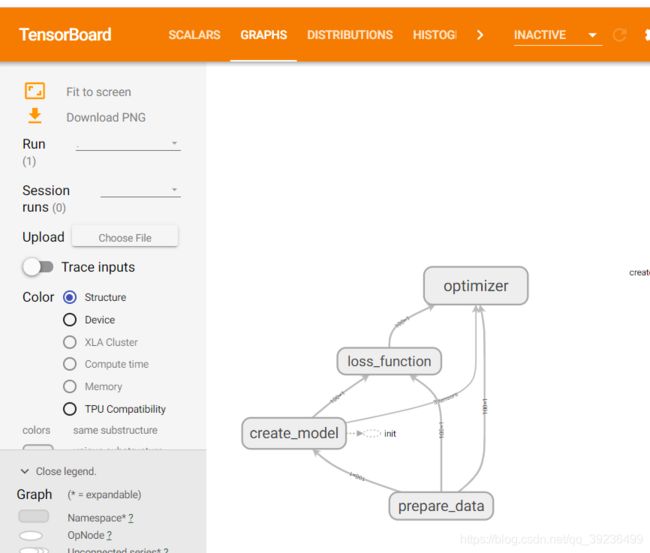
2 增加命名空间
使得代码结构更加信息,TensorBoard图结构更加清楚
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def linear_regression():
"""
实现线性回归
:return:
"""
with tf.variable_scope("prepare_data"):
# 1)准备数据
X = tf.random_normal(shape=[100, 1], name='feature') # 形状:100行1列
y_true = tf.matmul(X, [[0.8]]) + 0.7 # y_true = 0.8x + 0.7
with tf.variable_scope("create_model"):
# 2)构造模型
# 定义模型参数,用变量
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]), name="Weights")
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]), name="Bias")
y_predict = tf.matmul(X, weights) + bias
with tf.variable_scope("loss_function"):
# 3)构造损失函数
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true))
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
# 4)优化损失
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 2)收集变量
tf.summary.scalar("error", error)
tf.summary.histogram("weights", weights)
tf.summary.histogram("bias", bias)
# 3)合并变量
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
# 显式地初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 初始化变量
sess.run(init)
# 1)创建事件文件
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs', graph=sess.graph)
# 查看初始化模型参数之后的值
print("训练前模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失为%f" %
(weights.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# 开始训练
for i in range(100):
sess.run(optimizer)
print("第%d训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失为%f" %
(i+1, weights.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# 运行合并变量操作
summary = sess.run(merged)
# 每次迭代后的变量写入事件
file_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
linear_regression()
3 模型的保存与加载

步骤:
1)实例化Saver
2)保存:saver.save(sess, path)
3)加载:saver.restore(sess, path)
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def linear_regression():
"""
实现线性回归
:return:
"""
with tf.variable_scope("prepare_data"):
# 1)准备数据
X = tf.random_normal(shape=[100, 1], name='feature') # 形状:100行1列
y_true = tf.matmul(X, [[0.8]]) + 0.7 # y_true = 0.8x + 0.7
with tf.variable_scope("create_model"):
# 2)构造模型
# 定义模型参数,用变量
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]), name="Weights")
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]), name="Bias")
y_predict = tf.matmul(X, weights) + bias
with tf.variable_scope("loss_function"):
# 3)构造损失函数
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true))
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
# 4)优化损失
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1).minimize(error)
# 2)收集变量
tf.summary.scalar("error", error)
tf.summary.histogram("weights", weights)
tf.summary.histogram("bias", bias)
# 3)合并变量
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
# 创建Saver对象
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# 显式地初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 初始化变量
sess.run(init)
# 1)创建事件文件
file_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs', graph=sess.graph)
# 查看初始化模型参数之后的值
print("训练前模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失为%f" %
(weights.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# # 开始训练
# for i in range(100):
# sess.run(optimizer)
# print("第%d训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失为%f" %
# (i+1, weights.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
#
# # 运行合并变量操作
# summary = sess.run(merged)
# # 每次迭代后的变量写入事件
# file_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
#
# # 保存模型
# if i % 10 == 0:
# saver.save(sess, "model/my_Linear.ckpt")
# 加载模型
if os.path.exists("model/checkpoint"):
saver.restore(sess, "model/my_Linear.ckpt")
print("训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失为%f" %
(weights.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
linear_regression()
训练前模型参数为:权重-0.726173,偏置-1.391275,损失为6.139051
训练后模型参数为:权重0.800000,偏置0.700000,损失为0.000000
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
# 1)定义命令行参数
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer("max_step", 100, "训练模型的步数")
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string("model_dir", "Unknown", "模型保存的路径+模型的名字")
# 2)简化变量名
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS
def command_demo():
"""
命令行参数演示
:return:
"""
print("max_step:", FLAGS.max_step)
print("model_dir:", FLAGS.model_dir)
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
command_demo()
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' # 去警告
def main(argv):
print(argv)
print("code start")
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
tf.app.run() # 自动运行main函数
#command_demo()
['D:/programming_software/pycharm/PycharmProjects/deep_learning/day01_deeplearning.py']
code start