leetcode--5 Longest Palindromic Substring
1. 题目:
Given a string S, find the longest palindromic substring in S. You may assume that the maximum length of S is 1000, and there exists one unique longest palindromic substring.
注:
palindromic substring :回文序列,如:aba,abba 等。
2.1 C++ 暴力解决—— 时间复杂度O(N³)
思路:
(1). 构造一个map,存储原字符出现的所有位置;
(2). 从头到位扫描字符串,根据map中的位置,选取子字符串,判断是否为回文序列
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
unsigned long long string_len=s.length();
if(string_len==0)
return "";
if(string_len==1)
return s;
string current_str="",longest_str="";
unsigned long long current_len=0,longest_len=0;
map<char,vector<unsigned long long> >char_pos_map;
for(int i=0;i<string_len;i++){
map<char,vector<unsigned long long> >::iterator char_pos_map_it=char_pos_map.find(s[i]);
if(char_pos_map_it==char_pos_map.end()) {
vector<unsigned long long> pos_list;
pos_list.push_back(i);
char_pos_map.insert(pair<char, vector<unsigned long long > >((char)s[i],pos_list));
} else {
vector<unsigned long long> & pos_list=char_pos_map_it->second;
pos_list.push_back(i);
}
} //map存储每个字符出现的位置
for(int index_head = 0;index_head<string_len;index_head++) {
std::map<char, vector<unsigned long long > >::iterator it = char_pos_map.find(s[index_head]);
if( it->second.size()==1) {
current_len = 1;
current_str = s[index_head];
if(current_len>longest_len) {
longest_str = current_str;
longest_len = current_len; //只出现一次的字符
}
} else {
vector<unsigned long long> & tmp_vec = it->second;
unsigned long long index_num = tmp_vec.size();
unsigned long long tmp_index_head = index_head;
for(long long j=(long long)(index_num-1);j>=0;j--) {
tmp_index_head = index_head;
unsigned long long tmp_index_tail = tmp_vec[j];
if(tmp_index_tail<tmp_index_head)
continue;
current_len = tmp_index_tail-tmp_index_head+1;
if( current_len==0 || current_len < longest_len)
continue;
current_str = s.substr(tmp_index_head, current_len); //取子字符串,验证是否为回文字符
while( ((long long)(tmp_index_tail-tmp_index_head)>=1) && (s[tmp_index_tail]==s[tmp_index_head]) ) {
tmp_index_head++;
tmp_index_tail--;
}
if( ((long long)(tmp_index_tail-tmp_index_head)==-1) || (tmp_index_tail-tmp_index_head==0) ){ //奇数 偶数个字符的情况
longest_len = current_len;
longest_str = current_str;
}
}
}
}
return longest_str;
}
};
2.2 动态规划
删除暴力解法中有很多重复的判断。很容易想到动态规划,时间复杂度O(n^2),空间O(n^2),动态规划方程如下:
- dp[i][j] 表示子串s[i…j]是否是回文
- 初始化:dp[i][i] = true (0 <= i <= n-1); dp[i][i-1] = true (1 <= i <= n-1); 其余的初始化为false
- dp[i][j] = (s[i] == s[j] && dp[i+1][j-1] == true)
在动态规划中保存最长回文的长度及起点即可
|
|
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
const int len = s.size();
if(len <= 1)return s;
bool dp[len][len]; //dp[i][j]表示s[i..j]是否是回文
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp)); //初始化为0
int resLeft = 0, resRight = 0;
dp[0][0] = true;
for(int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
dp[i][i] = true;
dp[i][i-1] = true; //这个初始化容易忽略,当k=2时要用到
}
for(int k = 2; k <= len; k++) //外层循环:枚举子串长度
for(int i = 0; i <= len-k; i++) //内层循环:枚举子串起始位置
{
if(s[i] == s[i+k-1] && dp[i+1][i+k-2])
{
dp[i][i+k-1] = true;
if(resRight-resLeft+1 < k)
{
resLeft = i;
resRight = i+k-1;
}
}
}
return s.substr(resLeft, resRight-resLeft+1);
}
};
|
2.3 从中间向两边展开,时间复杂度O(n^2),空间O(1)
回文字符串显然有个特征是沿着中心那个字符轴对称。比如aha沿着中间的h轴对称,a沿着中间的a轴对称。那么aa呢?沿着中间的空字符''轴对称。所以对于长度为奇数的回文字符串,它沿着中心字符轴对称,对于长度为偶数的回文字符串,它沿着中心的空字符轴对称。对于长度为N的候选字符串,我们需要在每一个可能的中心点进行检测以判断是否构成回文字符串,这样的中心点一共有2N-1个(2N-1=N-1 + N)。检测的具体办法是,从中心开始向两端展开,观察两端的字符是否相同
class
Solution {
public
:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
const
int
len = s.size();
if
(len <= 1)
return
s;
int
start, maxLen = 0;
for
(
int
i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
//寻找以i-1,i为中点偶数长度的回文
int
low = i-1, high = i;
while
(low >= 0 && high < len && s[low] == s[high])
{
low--;
high++;
}
if
(high - low - 1 > maxLen)
{
maxLen = high - low -1;
start = low + 1;
}
//寻找以i为中心的奇数长度的回文
low = i- 1; high = i + 1;
while
(low >= 0 && high < len && s[low] == s[high])
{
low--;
high++;
}
if
(high - low - 1 > maxLen)
{
maxLen = high - low -1;
start = low + 1;
}
}
return
s.substr(start, maxLen);
}
};
2.4 Manacher算法,时间复杂度O(n), 空间复杂度O(n)--------------????????????
该算法首先对字符串进行预处理,在字符串的每个字符前后都加入一个特殊符号,比如字符串 abcd 处理成 #a#b#c#d#,为了避免处理越界,在字符串首尾加上不同的两个特殊字符(c类型的字符串尾部不用加,因为自带‘\0’),这样预处理后最终变 成$#a#b#c#d#^,经过这样处理后有个好处是原来的偶数长度和奇数长度的回文在处理后的字符串中都是奇数长度。假设处理后的字符串为 s 本文地址
对于已经预处理好的字符串我们用数组p[i]来记录以字符S[i]为中心的最长回文子串向左/右扩张的长度(包括S[i]),以字符串“12212321”为例,p数组如下
s: $ # 1 # 2 # 2 # 1 # 2 # 3 # 2 # 1 # ^
p: 1 2 1 2 5 2 1 4 1 2 1 6 1 2 1 2 1
可以看出,P[i]-1正好是原字符串中回文串的总长度, 如果p数组已知,遍历p数组找到最大的p[i]就可以求出最长回文的长度,也可以求出回文的位置
下面给出求p[]数组的方法:
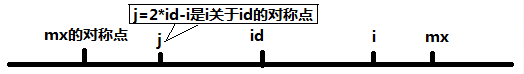
设id是当前求得的最长回文子串中心的位置,mx为当前最长回文子串的右边界(回文子串不包括该右边界),即mx = id + p[id]。记j = 2*id – i ,即 j 是 i 关于 id 的对称点。
1、 当i < mx 时,如下图。此时可以得出一个非常神奇的结论p[i] >= min(p[2*id - i], mx - i),下面我们来解释这个结论
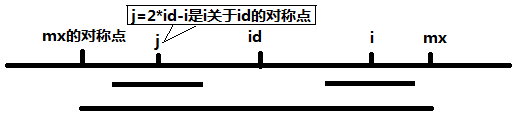
如何根据p[j]来求p[i]呢,又要分成两种情况
(1.1)当mx – i > p[j], 这时候以S[j]为中心的回文子串包含在以S[id]为中心的回文子串中,由于 i 和 j 对称,以S[i]为中心的回文子串必然包含在以S[id]为中心的回文子串中,所以 P[i] 至少等于 p[j], 后面的再继续匹配。如下图
注:这里其实p[i]一定等于p[j],后面不用再匹配了。因为如果p[i]后面还可以继续匹配,根据对称性,p[j]也可以继续扩展了
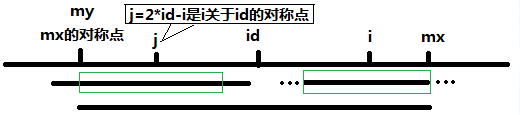
(1.2)当mx – i <= p[j], 以S[j]为中心的回文子串不完全包含于以S[id]为中心的回文子串中,但是基于对称性可知,下图中两个绿框所包围的部分是相同的,也就是说以S[i] 为中心的回文子串,其向右至少会扩张到mx的位置,也就是说 P[i] 至少等于 mx - i,至于mx之后的部分是否对称,就只能老老实实去匹配了。
注:如果mx – i < p[j] ,这时p[i]一定等于mx - i, 因为如果p[i]在mx之后还可以继续匹配,根据对称性,mx之后匹配的点(包括mx)一定会出现在my的前面,这说明p[id]也可以继续扩展了
2、当i >= mx, 无法对p[i]做更多的假设,只能p[i] = 1,然后再去匹配
算法复杂度分析:根据斜体字部分的注释,只有当mx-i = p[j]时 以及 i > mx时才要扩展比较,而mx也是在不断扩展的,总体而言每个元素比较次数是n的线性关系,所以时间复杂度为O(n)
class
Solution {
public
:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
const
int
len = s.size();
if
(len <= 1)
return
s;
//Manncher算法 ,o(n)
string str = preProcess(s);
int
n = str.size(), id = 0, mx = 0;
vector<
int
>p(n, 0);
for
(
int
i = 1; i < n-1; i++)
{
p[i] = mx > i ? min(p[2*id-i], mx-i) : 1;
//if(mx <= i || (mx > i && p[2*id-i] == mx - i)) //根据正文斜体部分的注释,这里可要可不要
while
(str[i+p[i]] == str[i-p[i]])p[i]++;
if
(i + p[i] > mx)
{
mx = i + p[i];
id = i;
}
}
//遍历p,寻找最大回文长度
int
maxLen = 0, index = 0;
for
(
int
i = 1; i < n-1; i++)
if
(p[i] > maxLen)
{
maxLen = p[i];
index = i;
}
return
s.substr((index - maxLen)/2, maxLen-1);
}
//预处理字符串,abc预处理后变成$#a#b#c#^
string preProcess(
const
string &s)
{
int
n = s.size();
string res;
res.push_back(
'$'
);
//把$放到字符串头部
res.push_back(
'#'
);
//以#作为原来字符串中每个字符的间隔
for
(
int
i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
res.push_back(s[i]);
res.push_back(
'#'
);
}
res.push_back(
'^'
);
//以^作为字符串的结尾
return
res;
}
};