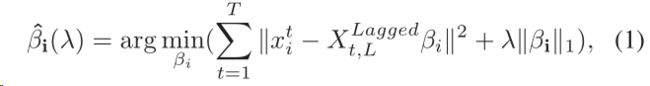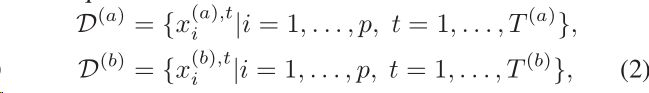Granger Causality for Time-Series Anomaly Detection
摘要中用于工业数据异常检测,可借鉴。用多维时间序列级联成的序列(一维)去拟合目标时间序列xi(一维),系数为βi,用lasso求解βi,见式(1)。这样是线性关系。
I. I NTRODUCTION
In this paper, we propose to investigate Granger graphical models, which uncover the temporal dependencies between variables in multivariate time-series data, as a novel and effective approach to detect dependency anomalies in time series data.
II. GRANGER G RAPHICAL M ODELS FOR A NOMALY DETECTION
Granger-lasso algorithm for uncovering temporal dependencies between time series。
A. Granger-Lasso Algorithm
Granger causality has gained tremendous success across many domains due to its simplicity, robustness, and ex-tendibility [7], [4].Most existing algorithms for detecting Granger causality are based on statistical significance tests, which is time-consuming and sensitive to the number of observations in the autoregression.
representing whether and how much each variable contributes to the difference between the two data sets.表示是否多少每个变量有助于两个数据集之间的差异。Univariate anomaly detection using Granger graphical models is a simple step:单因素异常检测用格兰杰图形模型是一个简单的一步:
Step 1. Learning temporal causal graphs by regularization.
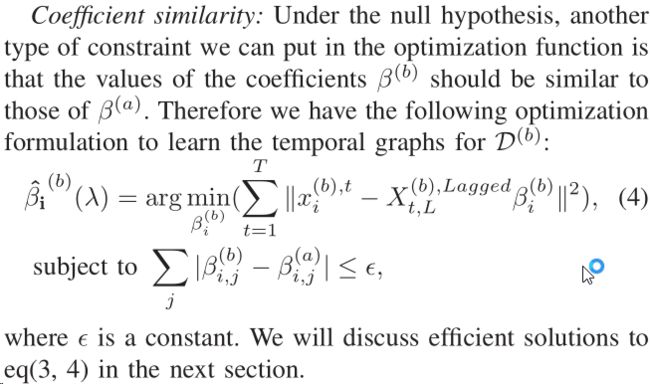
we can use the null hypothesis as an additional constraint in the optimization algorithm outlined in Granger-lasso algorithm.我们使用的零假设作为在格兰杰套索算法的优化算法的附加约束。
Neighborhood similarity
Coefficient similarity
We can determinethe temporal dependence between time series i and othersby the following regularized regression
We can determinethe temporal dependence between time series i and othersby the following regularized regression
where X j Granger causes X i if and only if at least one ofthe corresponding coefficients of X j is nonzero. The majorcontribution of their work is to introduce L 1 regularized regression as an efficient method to recover the sparse Gangercausality relations from highdimensional time series.
B. Granger Graphical Models for Anomaly Detection
Before delving into the details of our proposed algorithm,we first formally define the task of anomaly detection formultivariate timeseries data: given p number of time series,X 1 ,...,X p , we aim to find data points (indexed by timestamp) that significantly deviate from the normal patternof the data sequence. Without loss of generality, we cantransform the task into the following formulation: given twodata sequences