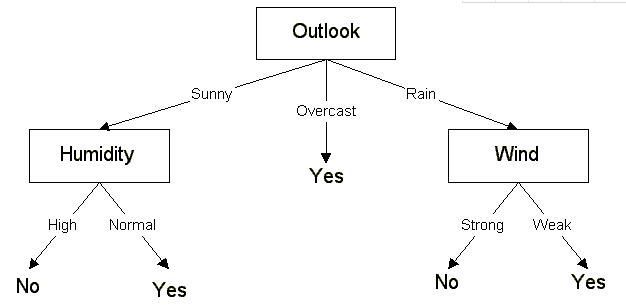
ID3决策树的仿真编程
function D = ID3(train_features, train_targets, params, region)
% Classify using Quinlan's ID3 algorithm
% Inputs:
% features - Train features
% targets - Train targets
% params - [Number of bins for the data, Percentage of incorrectly assigned samples at a node]
% region - Decision region vector: [-x x -y y number_of_points]
%
% Outputs
% D - Decision sufrace
[Ni, M] = size(train_features);
%Get parameters
[Nbins, inc_node] = process_params(params);
inc_node = inc_node*M/100;
%For the decision region
N = region(5);
mx = ones(N,1) * linspace (region(1),region(2),N);
my = linspace (region(3),region(4),N)' * ones(1,N);
flatxy = [mx(:), my(:)]';
%Preprocessing
[f, t, UW, m] = PCA(train_features, train_targets, Ni, region);
train_features = UW * (train_features - m*ones(1,M));;
flatxy = UW * (flatxy - m*ones(1,N^2));;
%First, bin the data and the decision region data
[H, binned_features]= high_histogram(train_features, Nbins, region);
[H, binned_xy] = high_histogram(flatxy, Nbins, region);
%Build the tree recursively
disp('Building tree')
tree = make_tree(binned_features, train_targets, inc_node, Nbins);
%Make the decision region according to the tree
disp('Building decision surface using the tree')
targets = use_tree(binned_xy, 1:N^2, tree, Nbins, unique(train_targets));
D = reshape(targets,N,N);
%END
function targets = use_tree(features, indices, tree, Nbins, Uc)
%Classify recursively using a tree
targets = zeros(1, size(features,2));
if (size(features,1) == 1),
%Only one dimension left, so work on it
for i = 1:Nbins,
in = indices(find(features(indices) == i));
if ~isempty(in),
if isfinite(tree.child(i)),
targets(in) = tree.child(i);
else
%No data was found in the training set for this bin, so choose it randomally
n = 1 + floor(rand(1)*length(Uc));
targets(in) = Uc(n);
end
end
end
break
end
%This is not the last level of the tree, so:
%First, find the dimension we are to work on
dim = tree.split_dim;
dims= find(~ismember(1:size(features,1), dim));
%And classify according to it
for i = 1:Nbins,
in = indices(find(features(dim, indices) == i));
targets = targets + use_tree(features(dims, :), in, tree.child(i), Nbins, Uc);
end
%END use_tree
function tree = make_tree(features, targets, inc_node, Nbins)
%Build a tree recursively
[Ni, L] = size(features);
Uc = unique(targets);
%When to stop: If the dimension is one or the number of examples is small
if ((Ni == 1) | (inc_node > L)),
%Compute the children non-recursively
for i = 1:Nbins,
tree.split_dim = 0;
indices = find(features == i);
if ~isempty(indices),
if (length(unique(targets(indices))) == 1),
tree.child(i) = targets(indices(1));
else
H = hist(targets(indices), Uc);
[m, T] = max(H);
tree.child(i) = Uc(T);
end
else
tree.child(i) = inf;
end
end
break
end
%Compute the node's I
for i = 1:Ni,
Pnode(i) = length(find(targets == Uc(i))) / L;
end
Inode = -sum(Pnode.*log(Pnode)/log(2));
%For each dimension, compute the gain ratio impurity
delta_Ib = zeros(1, Ni);
P = zeros(length(Uc), Nbins);
for i = 1:Ni,
for j = 1:length(Uc),
for k = 1:Nbins,
indices = find((targets == Uc(j)) & (features(i,:) == k));
P(j,k) = length(indices);
end
end
Pk = sum(P);
P = P/L;
Pk = Pk/sum(Pk);
info = sum(-P.*log(eps+P)/log(2));
delta_Ib(i) = (Inode-sum(Pk.*info))/-sum(Pk.*log(eps+Pk)/log(2));
end
%Find the dimension minimizing delta_Ib
[m, dim] = max(delta_Ib);
%Split along the 'dim' dimension
tree.split_dim = dim;
dims = find(~ismember(1:Ni, dim));
for i = 1:Nbins,
indices = find(features(dim, :) == i);
tree.child(i) = make_tree(features(dims, indices), targets(indices), inc_node, Nbins);
end