Linux_多线程与锁
文章目录
- 1 .常见锁的概念
-
- 1.1 死锁
- 1.2 死锁四个必要条件
- 1.3 避免死锁
- 2. Linux线程同步
-
- 2.1 条件变量
- 2.2 同步概念与竞态条件
- 2.3 编码实现方式
- 2.4 相关接口函数
-
- 2.4.1 初始化条件变量
- 2.4.2 销毁条件变量
- 2.4.3 等待条件满足
- 2.4.4 唤醒等待
- 2.5 代码示例
- 3. 生产者消费者模型
-
- 3.1 图示详解
- 3.2 代码示例
- 4. POSIX 信号量
-
- 4.1 POSIX概念
- 4.2 POSIX函数
-
- 4.2.1 初始化信号量
- 4.2.2 销毁信号量
- 4.2.3 等待信号量
- 4.2.4 发布信号量
- 4.3 基于环形队列的生产消费模型
- 4.3 代码示例
- 在前面的博客【Linux_深究多线程—>link】中已经讲了有关多线程操作的有关操作和锁的基本概念。这章将接着上一章的内容对线程与锁的有关概念和操作继续深究。
1 .常见锁的概念
1.1 死锁
- 死锁是指在
一组进程中的各个进程均占有不会释放的资源,但因互相申请被其他进程所站用不会释放的资源而处于的一种永久等待状态。
1.2 死锁四个必要条件
互斥条件:一个资源每次只能被一个执行流使用请求与保持条件:一个执行流因请求资源而阻塞时,对已获得的资源保持不放不剥夺条件:一个执行流已获得的资源,在末使用完之前,不能强行剥夺循环等待条件:若干执行流之间形成一种头尾相接的循环等待资源的关系
注意:要形成死锁,四个条件缺一不可。所以解决死锁的方法就是破坏四个必要条件中的一个以上,常见有银行家算法/死锁检测算法等。
1.3 避免死锁
- 破坏死锁的四个必要条件
- 加锁顺序一致
- 避免锁未释放的场景
- 资源一次性分配
问题:
2. Linux线程同步
2.1 条件变量
- 当一个线程互斥地访问某个变量时,它可能发现在其它线程改变状态之前,它什么也做不了。
- 同步存在是为了多线程协同高效完成某些事情。
- 例如一个线程访问队列时,发现队列为空,它只能等待,只到其它线程将一个节点添加到队列中,这种情况就需要用到条件变量。
2.2 同步概念与竞态条件
同步:在保证数据安全的前提下,让线程能够按照某种特定的顺序访问临界资源,从而有效避免饥饿问题,叫做同步。竞态条件:因为时序问题,而导致程序异常,我们称之为竞态条件。在线程场景下,这种问题也不难理解。
2.3 编码实现方式
- 如果条件不满足,等待,释放锁。
- 通知机制。
2.4 相关接口函数
2.4.1 初始化条件变量
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
参数:
- cond:要初始化的条件变量
- attr:NULL
2.4.2 销毁条件变量
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond)
2.4.3 等待条件满足
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
参数:
- cond:要在这个条件变量上等待
- mutex:互斥量。
2.4.4 唤醒等待
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
2.5 代码示例
#include为什么pthread_cond_wait()需要互斥量呢?- 答:
- 条件等待是线程间同步的一种手段,如果只有一个线程,条件不满足,一直等下去都不会满足所以必须要有一个线程通过某些操作,改变共享变量,使原先不满足的条件变得满足,并且友好的通知等待在条件变量上的线程。
- 条件不会无缘无故的突然变得满足了,必然会牵扯到共享数据的变化。所以一定要用互斥锁来保护。没有互斥锁就无法安全的获取和修改共享数据。
- 简单来说,pthread_cond_wait()中还要带上锁是因为,如果该线程在等待时,此时应该将临界区进行解锁,让另外的线程在该线程等待时,可以进入到临界区,要不然它在等待时还一直加锁状态,就没意义。当别的进程给该进程发信号,唤醒它,这个时候从新加锁,访问临界区,保证其原子性。
3. 生产者消费者模型
问题:
- 为何要使用生产者消费者模型 ?
- 生产者消费者模式就是通过一个容器来解决生产者和消费者的强耦合问题。生产者和消费者彼此之间不直接通讯,而通过阻塞队列来进行通讯,所以生产者生产完数据之后不用等待消费者处理,直接扔给阻塞队列,消费者不找生产者要数据,而是直接从阻塞队列里取,阻塞队列就相当于一个缓冲区,平衡了生产者和消费者的处理能力。这个阻塞队列就是用来给生产者和消费者解耦的。
生产者消费者模型优点:
- 解耦
- 支持并发
- 支持忙闲不均
3.1 图示详解
- 基于BlockingQueue的生产者消费者模型 ,BlockingQueue 在多线程编程中阻塞队列(Blocking Queue)是一种常用于实现生产者和消费者模型的数据结构。
- 其与普通的队列区别在于,当队列为空时,从队列获取元素的操作将会被阻塞,直到队列中被放入了元素;当队列满时,往队列里存放元素的操作也会被阻塞,直到有元素被从队列中取出(以上的操作都是基于不同的线程来说的,线程在对阻塞队列进程操作时会被阻塞)。
生产者消费者“321”- 3->
3种关系:生产者&消费者(互斥/同步),生产者&生产者(互斥),消费者&消费者(互斥) - 2->
2种角色:生产者,消费者 - 3->
一个交易场所
3.2 代码示例
ps.h
#ifndef __QUEUE_BLOCK_H__
#define __QUEUE_BLOCK_H__
#includeps.cpp
#include "block.h"
using namespace std;
void *consumer_run(void *arg)
{
//int num=(int)arg;
pthread_mutex_t lock;
BlockQueue *bq=(BlockQueue*)arg;
while(true)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
//int data;
Task t;
bq->Get(t);
//t.Run();
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
cout<<"consumer"<<t.x<<"+"<<t.y<<"="<<t.Run()<<endl;
sleep(1);
}
//pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
void *productor_run(void *arg)
{
//int num=(int)arg;
pthread_mutex_t lock;
sleep(1);
BlockQueue *bq=(BlockQueue*)arg;
//int count=0;
while(true)
{
int x=rand()%10+1;
int y=rand()%100+1;
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
Task t(x,y);
bq->Put(t);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
cout<<"productor "<<x<<"+"<<y<<"=?"<<endl;
}
//pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
int main()
{
BlockQueue *bq = new BlockQueue(5);
pthread_t con1,pro1;
pthread_create(&con1,nullptr,consumer_run,(void*)bq);
pthread_create(&pro1,nullptr,productor_run,(void*)bq);
//pthread_create(&con2,nullptr,consumer_run,(void*)bq);
//pthread_create(&pro2,nullptr,productor_run,(void*)bq);
pthread_join(con1,nullptr);
//pthread_join(con2,nullptr);
pthread_join(pro1,nullptr);
//pthread_join(pro2,nullptr);
return 0;
}
4. POSIX 信号量
4.1 POSIX概念
4.2 POSIX函数
4.2.1 初始化信号量
#include 参数:
- pshared:0表示线程间共享,非零表示进程间共享
- value:信号量初始值
4.2.2 销毁信号量
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem)
4.2.3 等待信号量
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
功能:
- 等待信号量,会将信号量的值减1 //P()
4.2.4 发布信号量
int sem_post(sem_t *sem)//V()
功能:
- 发布信号量,表示资源使用完毕,可以归还资源了。将信号量值加1
上面生产者-消费者的例子是基于queue的,其空间可以动态分配,现在基于固定大小的环形队列重写这个程序(POSIX信号量):
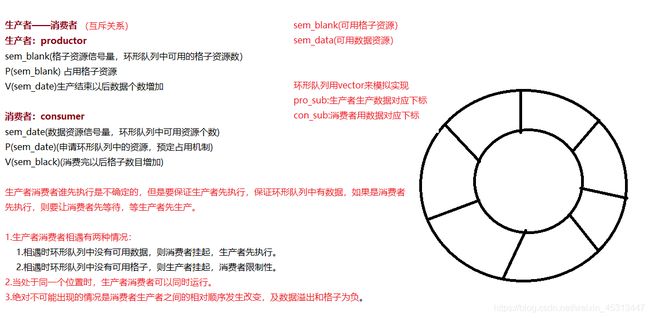
4.3 基于环形队列的生产消费模型
- 环形队列采用数组模拟,用模运算来模拟环状特性
- 环形结构起始状态和结束状态都是一样的,不好判断为空或者为满,所以可以通过加计数器或者标记位来判断满或者空。另外也可以预留一个空的位置,作为满的状态
- 但是我们现在有信号量这个计数器,就很简单的进行多线程间的同步过程
4.3 代码示例
// RingQueue.hpp
#pragma once
#include //main.cpp
#include "RingQueue.hpp"
pthread_mutex_t pro_lock;//生产者组内竞争锁
pthread_mutex_t con_lock;//消费者组内竞争锁
int count=0;//生产者数据
void Lock(pthread_mutex_t &lock)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
}
void ULock(pthread_mutex_t &lock)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
void *Get(void *arg)
{
RingQueue *q=(RingQueue*)arg;
while(1)
{
usleep(1);
int data=0;
Lock(con_lock);//组内竞争
q->Get(data);//获取数据
ULock(con_lock);
std::cout<<"consumer get data...:"<<data<<std::endl;
}
}
void *Put(void *arg)
{
RingQueue *q=(RingQueue*)arg;
while(1)
{
sleep(1);//增加系统调用
Lock(pro_lock);//组内竞争
int number = (++count)%10l;
q->Put(number);
ULock(pro_lock);
std::cout<<"productor put data...."<< number << std::endl;
}
}
int main()
{
//创建交易场所
RingQueue *q=new RingQueue(5);
//初始化锁
pthread_mutex_init(&con_lock,nullptr);
pthread_mutex_init(&pro_lock,nullptr);
//创建线程
pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3,tid4,tid5,tid6;
pthread_create(&tid1,nullptr,Put,q);
pthread_create(&tid2,nullptr,Put,q);
pthread_create(&tid3,nullptr,Put,q);
pthread_create(&tid4,nullptr,Get,q);
pthread_create(&tid5,nullptr,Get,q);
pthread_create(&tid6,nullptr,Get,q);
//等待线程、避免内存泄漏,不关心返回值
pthread_join(tid1,nullptr);
pthread_join(tid2,nullptr);
pthread_join(tid3,nullptr);
pthread_join(tid4,nullptr);
pthread_join(tid5,nullptr);
pthread_join(tid6,nullptr);
//销毁工作
pthread_mutex_destroy(&con_lock);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pro_lock);
delete q;
return 0;
}