一、前言
最近关注了一下《爱情公墓》的票房,所以下载了猫眼app,发现他的下拉刷新动画甚是好看:
所以想着仿着做一个,最终实现效果:
二、分析
猫眼的下拉头部动画是最具有美感的一个动画效果。拆开来看,是由四个弧形,加一个中间的图片组成,下拉的时候,有一个水位上涨的效果,水位到顶后,开启动画,外面的圈旋转,里面的图片保持不动。
画圆弧画图片很简单,但是这个水位上涨和旋转的动画有点麻烦。
如果不想在一个View里面处理两个动画,实际上可以用一个组合的FrameLayout解决,底下是圆弧的View,上面是图片Logo的ImageView,功能能实现,但是不够优雅,这里就是用一个自定义View解决两个动画问题。
三、代码实现
3.1 自定义View的模板
public class RefreshImageView extends View {
public RefreshImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public RefreshImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView(context, attrs);
}
private void initView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
}
}
3.2 onMeasure 处理
自定义第一步,你要知道自己的这个View需要多大的手机屏幕面积,也就是告诉手机我这个View的宽高。一般来说,是有固定的写法的,先判断是不是wrap_content的,是的话有两种处理
1.给一个默认的值
2.看子View需要多大空间计算得出 (当然这里View没有子类)
所以这里简化一点,不考虑wrap_content的情况了,直接认为使用的时候要么是match_parent的要么就是100dp这种确认的值,所以计算代码如下:
public class RefreshImageView extends View {
private int width;
public RefreshImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public RefreshImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView(context, attrs);
}
private void initView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(width, width);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
}
}
这样得到的View就是一个正方形。
3.3 圆弧Rect计算
我们知道,画一段圆弧,一定要知道圆弧所在的正方形区域,而且,圆弧是画在View的边框上的,如果圆弧的宽度特别大的时候,实际上有一半的弧形是画到边界外面的,所以这里我们需要计算圆弧的区域。
public class RefreshImageView extends View {
private int width;
private int borderWidth = 10;
private RectF rectF;
public RefreshImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public RefreshImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView(context, attrs);
}
private void initView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
rectF = new RectF(borderWidth, borderWidth, width - borderWidth, width - borderWidth);
setMeasuredDimension(width, width);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
}
}
在确认了View的宽度width之后,直接在View内部减去一个弧形宽度的正方形区域内画圆弧,这样是不会超出View边界的。
3.4 onDraw 画弧形
public class RefreshImageView extends View {
private int width;
private int borderWidth = 10;
private RectF rectF;
private Paint borderPaint;
public RefreshImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public RefreshImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView(context, attrs);
}
private void initView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
borderPaint = new Paint();
borderPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
borderPaint.setStrokeWidth(borderWidth);
borderPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
borderPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
borderPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#999999"));
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
rectF = new RectF(borderWidth, borderWidth, width - borderWidth, width - borderWidth);
setMeasuredDimension(width, width);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
canvas.drawArc(rectF, -40 + 90 * i, 80, false, borderPaint);
}
}
}
四段弧形,直接一个for循环,默认是每画80度灰色弧形,开一个10度的弧形空隙,继续下一个弧形,这样图案就出来了:
3.5 onDraw 画水位
这里是根据进度来确定水位的高度的,所以需要从使用的地方传递进来一个浮点型progress。重要的一点是怎么给进度以下的部分上色?这里需要了解 图像混合模式
我们在View的底部绘制一个逐渐上涨的水位矩形图,但是由于设置了图像混合模式,只会显示两个图案并集的部分,于是就实现了这种逐渐渲染的效果:
public class RefreshImageView extends View {
private int width;
private int borderWidth = 10;
private RectF rectF;
private Paint borderPaint;
private float progress = 0.5f;
private Paint progressPaint;
private PorterDuffXfermode mXfermode;
public RefreshImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public RefreshImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView(context, attrs);
}
private void initView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
borderPaint = new Paint();
borderPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
borderPaint.setStrokeWidth(borderWidth);
borderPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
borderPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
borderPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#999999"));
progressPaint = new Paint();
progressPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
progressPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#eb1c42"));
//最重要的一点,选择合适的图片重叠模式
mXfermode = new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_ATOP);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
rectF = new RectF(borderWidth, borderWidth, width - borderWidth, width - borderWidth);
setMeasuredDimension(width, width);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
int sc = canvas.saveLayer(0, 0, width, width, null, Canvas.ALL_SAVE_FLAG);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
canvas.drawArc(rectF, -40 + 90 * i, 80, false, borderPaint);
}
progressPaint.setXfermode(mXfermode);
canvas.drawRect(0, width - width * progress, width, width, progressPaint);
progressPaint.setXfermode(null);
canvas.restoreToCount(sc);
}
public void setProgress(float progress) {
this.progress = progress;
invalidate();
}
}
首先我们需要在离屏缓存的canvas上绘制两者混合的图案,否则没有混合的效果。初始我们定的progress为50%,效果已经出来了:
3.6 绘制Logo
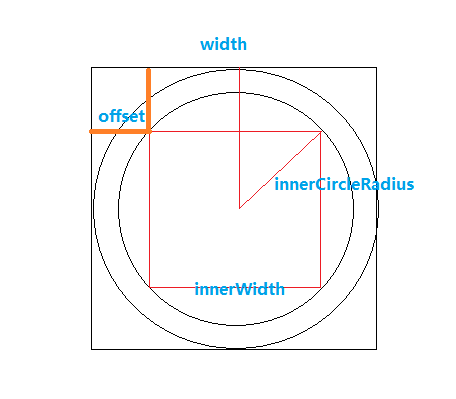
中间的logo的矩形应该比border的矩形更小,否则会重合border,这里需要通过勾股定理计算,也不复杂,不理解可以画一个图形帮助理解:
public class RefreshImageView extends View {
private int width;
private int borderWidth = 10;
private RectF rectF;
private Paint borderPaint;
private float progress = 0.5f;
private Paint progressPaint;
private PorterDuffXfermode mXfermode;
private RectF bitmapRectF;
private Paint bitmapPaint;
private Bitmap srcBitmap;
private int innerWidth;
private int offset;
public RefreshImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public RefreshImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView(context, attrs);
}
private void initView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
borderPaint = new Paint();
borderPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
borderPaint.setStrokeWidth(borderWidth);
borderPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
borderPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
borderPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#999999"));
progressPaint = new Paint();
progressPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
progressPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#eb1c42"));
//最重要的一点,选择合适的图片重叠模式
mXfermode = new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_ATOP);
bitmapPaint = new Paint();
bitmapPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
srcBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.riv_test);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
rectF = new RectF(borderWidth, borderWidth, width - borderWidth, width - borderWidth);
setMeasuredDimension(width, width);
//此处计算logo的矩形位置
int innerCircleRadius = width / 2 - borderWidth * 2;
innerWidth = (int) (Math.sqrt(2) * innerCircleRadius);
offset = width / 2 - innerWidth / 2;
bitmapRectF = new RectF(offset, offset, width - offset, width - offset);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
int sc = canvas.saveLayer(0, 0, width, width, null, Canvas.ALL_SAVE_FLAG);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
canvas.drawArc(rectF, -40 + 90 * i, 80, false, borderPaint);
}
progressPaint.setXfermode(mXfermode);
canvas.drawRect(0, width - width * progress, width, width, progressPaint);
progressPaint.setXfermode(null);
canvas.restoreToCount(sc);
canvas.drawBitmap(srcBitmap, null, bitmapRectF, bitmapPaint);
}
public void setProgress(float progress) {
this.progress = progress;
invalidate();
}
}
3.7 border 动画
如果没有logo图案,可以让View rotate实现旋转,但是有了logo这样导致logo也在旋转,不合理,所以需要不断的改变border的起始绘制位置,这样就很容易想到属性动画,0到360度的数值变化:
public void startAnim() {
progress = 1;
animator = ValueAnimator.ofInt(0, 360);
animator.setDuration(1000);
animator.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);
animator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
animator.start();
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
dAngle = (Integer) animation.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
});
}
public void stopAnim() {
if (animator != null) {
animator.cancel();
dAngle = 0;
progress = 0;
invalidate();
}
}
开启动画之前,设置progress为1,确保水位是满的,0度到360度的变化,增加一个变量dAngle,记录变化的角度,所以onDraw的代码也要做出变化:
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
canvas.drawArc(rectF, -40 + 90 * i + dAngle, 80, false, borderPaint);
}
每一段弧形加上变化的角度。
四、总结
到这里就全部结束了,剩下的就是代码的优化了,将border宽度和颜色什么的都写到属性文件里,可以在xml里方便的设置上。
附上完整代码
public class RefreshImageView extends View {
private int width;
private int borderWidth = 10;
private RectF rectF;
private Paint borderPaint;
private float progress;
private Paint progressPaint;
private PorterDuffXfermode mXfermode;
private RectF bitmapRectF;
private Paint bitmapPaint;
private Bitmap srcBitmap;
private int innerWidth;
private int offset;
private ValueAnimator animator;
//变化的角度
private int dAngle;
private int borderColor;
private int borderCoverColor;
private int gapAngle;
public RefreshImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public RefreshImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView(context, attrs);
}
private void initView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
if (attrs != null) {
TypedArray array = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.RefreshImageView);
borderWidth = (int) array.getDimension(R.styleable.RefreshImageView_refresh_iv_border_width, 10);
borderColor = array.getColor(R.styleable.RefreshImageView_refresh_iv_border_color, Color.GRAY);
borderCoverColor = array.getColor(R.styleable.RefreshImageView_refresh_iv_cover_color, Color.RED);
gapAngle = array.getInt(R.styleable.RefreshImageView_refresh_iv_gap_angle, 10);
int srcId = array.getResourceId(R.styleable.RefreshImageView_refresh_iv_src, R.drawable.riv_test);
srcBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), srcId);
}
borderPaint = new Paint();
borderPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
borderPaint.setStrokeWidth(borderWidth);
borderPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
borderPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
borderPaint.setColor(borderColor);
progressPaint = new Paint();
progressPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
progressPaint.setColor(borderCoverColor);
//最重要的一点,选择合适的图片重叠模式
mXfermode = new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_ATOP);
bitmapPaint = new Paint();
bitmapPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
srcBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.riv_test);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
rectF = new RectF(borderWidth, borderWidth, width - borderWidth, width - borderWidth);
setMeasuredDimension(width, width);
int innerCircleRadius = width / 2 - borderWidth * 2;
innerWidth = (int) (Math.sqrt(2) * innerCircleRadius);
offset = width / 2 - innerWidth / 2;
bitmapRectF = new RectF(offset, offset, width - offset, width - offset);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
int sc = canvas.saveLayer(0, 0, width, width, null, Canvas.ALL_SAVE_FLAG);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int sweepAngle = 90 - gapAngle;
canvas.drawArc(rectF, -sweepAngle / 2 + 90 * i + dAngle, sweepAngle, false, borderPaint);
}
progressPaint.setXfermode(mXfermode);
canvas.drawRect(0, width - width * progress, width, width, progressPaint);
progressPaint.setXfermode(null);
canvas.restoreToCount(sc);
canvas.drawBitmap(srcBitmap, null, bitmapRectF, bitmapPaint);
}
public void setProgress(float progress) {
this.progress = progress;
invalidate();
}
public void startAnim() {
progress = 1;
animator = ValueAnimator.ofInt(0, 360);
animator.setDuration(1000);
animator.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);
animator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
animator.start();
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
dAngle = (Integer) animation.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
});
}
public void stopAnim() {
if (animator != null) {
animator.cancel();
dAngle = 0;
progress = 0;
invalidate();
}
}
}
附上github地址