你必须掌握的Java类库工具包Hutool,真甜!(高级篇)
Hutool高级篇,企业级应用实例
- 前言
- 一、安装
-
- 1.1 导入Maven依赖
- 二、使用
-
- 2.1 HashMap扩展-Dict
-
- 2.1.1 获取单个对象
- 2.1.2 获取List集合对象
- 2.2 JSONUtil
-
- 2.2.1 toXXX
- 2.2.2 parseXXX
- 2.3 BeanUtil
-
- 2.3.1 是否为Bean对象
- 2.3.2 内省 Introspector
- 2.4 使用Map填充bean
-
- 2.4.1 Map填充bean(fillBeanWithMap)
- 2.4.2 忽略大小写(fillBeanWithMapIgnoreCase)
- 2.4.3 设置别名方式一(BeanUtil.toBean)
- 2.4.3 设置别名方式二(BeanUtil.toBeanIgnoreCase)
- 2.4.4 Bean转为Map
- 2.4.5 Bean转Bean
- 2.4.6 Alias注解
- 2.5 CompareUtil
- 2.6 IO工具类
-
- 2.6.1 拷贝
- 2.6.2 读取流中的内容 (read)
- 2.6.3 写入到流(write)
- 2.7 StrBuilder
- 2.7 Convert
-
- 2.7.1 时间转换
- 2.7.3 金额大小写转换
- 总结
前言
Hutool是一个Java工具包类库,对文件、流、加密解密、转码、正则、线程、XML等JDK方法进行封装,组成各种Util工具类。
一、安装
1.1 导入Maven依赖
在项目的pom.xml的dependencies中加入以下内容:
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.6.3</version>
</dependency>
二、使用
下面我们演示一下企业常用的函数、不做全面的demo演示,例子使用类Employee ,并且还是简单的SpringBoot + MybatisPlus项目demo:
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = false)
@TableName("t_employee")
public class Employee implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double salary;
private Integer departmentId;
}
2.1 HashMap扩展-Dict
Dict继承HashMap,其key为String类型,value为Object类型,通过实现BasicTypeGetter接口提供针对不同类型的get方法,同时提供针对Bean的转换方法,大大提高Map的灵活性。
2.1.1 获取单个对象
接口方法:
/**
* 根据id查询员工信息
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/getById/{id}")
@ResponseBody
public CommonResult<Dict> getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
Dict emp = employeeService.getEmpById(id);
// 获取指定类型的值
Integer integer = emp.getInt("id");
String str = emp.getStr("name");
// 打印输出
System.out.println(integer);
System.out.println(str);
return CommonResult.success(emp);
}
Mapp.xml
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="cn.hutool.core.lang.Dict">
SELECT * FROM t_employee WHERE id = #{id}
select>
获取指定类型的值:
其实就和Map用法一样,根据key获取value。
Integer integer = emp.getInt("id");
String str = emp.getStr("name");
2.1.2 获取List集合对象
接口方法:
/**
* 查询员工信息
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/list")
@ResponseBody
public CommonResult<List<Dict>> listEmp(){
List<Dict> empList = employeeService.listEmp();
empList.forEach(emp->{
Integer id = emp.getInt("id");
System.out.println(id);
});
return CommonResult.success(empList);
}
Mapp.xml
<select id="listEmp" resultType="cn.hutool.core.lang.Dict">
SELECT * FROM t_employee
select>
2.2 JSONUtil
JSONUtil是针对JSONObject和JSONArray的静态快捷方法集合.
2.2.1 toXXX
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee employee = new Employee(1,"张三",18,100d,1);
// toJsonStr将对象转化为字符串
String str = JSONUtil.toJsonStr(employee);
System.out.println("str>>>"+str);
// 将json字符串转换为Bean对象
Employee bean = JSONUtil.toBean(str, Employee.class);
System.out.println("bean>>>"+bean.toString());
}
2.2.2 parseXXX
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
employeeList.add(new Employee(1,"张三",18,100d,1));
employeeList.add(new Employee(2,"李四",19,150d,2));
// toJsonStr将集合对象转化为字符串
String str = JSONUtil.toJsonStr(employeeList);
System.out.println("str>>>"+str);
// parseArray将json字符串转化为json集合
JSONArray array = JSONUtil.parseArray(str);
for (JSONObject jsonObj : array.jsonIter()) {
System.out.println(jsonObj.getInt("id"));
System.out.println(jsonObj.getStr("name"));
}
System.out.println("array>>>"+array);
}
2.3 BeanUtil
2.3.1 是否为Bean对象
BeanUtil.isBean方法根据是否存在只有一个参数的setXXX方法或者public类型的字段来判定是否是一个Bean对象。这样的判定方法主要目的是保证至少有一个setXXX方法用于属性注入。
public class TestBean {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean isBean = BeanUtil.isBean(TestBean.class);
System.out.println(isBean); // false
}
2.3.2 内省 Introspector
生成get、set等方法,加入@Data注解:
@Data
public class TestBean {
private Integer id;
private String name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获得Bean类指定属性描述,必须为一个Bean(拥有get、set方法)
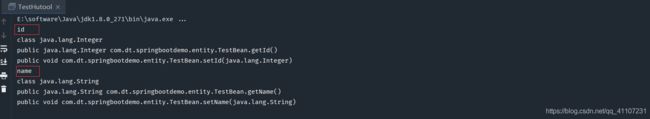
PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = BeanUtil.getPropertyDescriptors(TestBean.class);
for (int i = 0; i < propertyDescriptors.length; i++) {
// 获得属性名称
String proName = propertyDescriptors[i].getName();
System.out.println(proName);
// 获得属性的对象
Class<?> type = propertyDescriptors[i].getPropertyType();
System.out.println(type);
// 获得用于读取属性值的方法
Method readMethod = propertyDescriptors[i].getReadMethod();
System.out.println(readMethod);
// 获得用于写入属性值的方法
Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptors[i].getWriteMethod();
System.out.println(writeMethod);
}
}
hashCode() //获取对象的哈希值;
setReadMethod(Method readMethod) //设置用于读取属性值的方法;
setWriteMethod(Method writeMethod) //设置用于写入属性值的方法。
2.4 使用Map填充bean
2.4.1 Map填充bean(fillBeanWithMap)
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = CollUtil.newHashMap();
map.put("id", 1);
map.put("name", "张三");
TestBean testBean = BeanUtil.fillBeanWithMap(map, new TestBean(), false);
System.out.println(testBean);
}
2.4.2 忽略大小写(fillBeanWithMapIgnoreCase)
使用Map填充bean,忽略大小写。
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = CollUtil.newHashMap();
map.put("Id", 1);
map.put("Name", "张三");
TestBean testBean = BeanUtil.fillBeanWithMapIgnoreCase(map, new TestBean(), false);
System.out.println(testBean);
}
2.4.3 设置别名方式一(BeanUtil.toBean)
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = CollUtil.newHashMap();
map.put("a_id", 1);
map.put("b_name", "张三");
// 设置别名,用于对应bean的字段名
HashMap<String, String> mapping = CollUtil.newHashMap();
mapping.put("a_id", "id");
mapping.put("b_name", "name");
TestBean bean = BeanUtil.toBean(map, TestBean.class, CopyOptions.create().setFieldMapping(mapping));
System.out.println(bean);
}
2.4.3 设置别名方式二(BeanUtil.toBeanIgnoreCase)
map的key与属性对应,可以直接转:
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = CollUtil.newHashMap();
map.put("id", 1);
map.put("name", "张三");
// toBeanIgnoreCase map的key与属性对应,可以直接转
TestBean bean = BeanUtil.toBeanIgnoreCase(map, TestBean.class, false);
System.out.println(bean);
}
2.4.4 Bean转为Map
BeanUtil.beanToMap方法则是将一个Bean对象转为Map对象。
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestBean testBean = new TestBean(1,"张三");
Map<String, Object> map = BeanUtil.beanToMap(testBean);
System.out.println(map);
}
2.4.5 Bean转Bean
Bean之间的转换主要是相同属性的复制,因此方法名为copyProperties,此方法支持Bean和Map之间的字段复制。
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestBean testBean = new TestBean(1,"张三");
Map<String, Object> map = MapUtil.newHashMap();
BeanUtil.copyProperties(testBean, map);
System.out.println(map);
}
2.4.6 Alias注解
5.x的Hutool中增加了一个自定义注解:@Alias,通过此注解可以给Bean的字段设置别名。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class TestBean {
private Integer id;
// 设置别名:aliasSubName
@Alias("aliasSubName")
private String name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
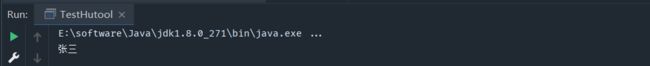
TestBean bean = new TestBean(1,"张三");
// Bean转换为Map时,自动将subName修改为aliasSubName
Map<String, Object> map = BeanUtil.beanToMap(bean);
// 通过别名(key)获取信息
String name = (String) map.get("aliasSubName");
System.out.println(name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Object> map = MapUtil.newHashMap();
map.put("id", 1);
map.put("aliasSubName", "张三");
TestBean testBean = BeanUtil.mapToBean(map, TestBean.class, false);
String name = testBean.getName();
System.out.println(name);
}
2.5 CompareUtil
在JDK提供的比较器中,对于null的比较没有考虑,Hutool封装了相关比较,可选null是按照最大值还是最小值对待。
当传入的第一个参数是null的时候,当我们设置isNullGreater为true时,null始终最大
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 当传入的第一个参数是null的时候,当我们设置isNullGreater为true时,null始终最大
int compare = CompareUtil.compare(null, 99, true);
System.out.println(compare);
}
当传入的第一个参数是null的时候,当我们设置isNullGreater为false时,null始终最小
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 当传入的第一个参数是null的时候,当我们设置isNullGreater为false时,null始终最小
int compare = CompareUtil.compare(null, 99, false);
System.out.println(compare);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 大于的时候返回1,小于的时候返回-1,等于的时候返回0
int compare = CompareUtil.compare(99, 99, true);
System.out.println(compare);
}
2.6 IO工具类
IO工具类的存在主要针对InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer封装简化,并对NIO相关操作做封装简化。总体来说,Hutool对IO的封装,主要是工具层面,我们努力做到在便捷、性能和灵活之间找到最好的平衡点。
2.6.1 拷贝
流的读写可以总结为从输入流读取,从输出流写出,这个过程我们定义为拷贝。这个是一个基本过程,也是文件、流操作的基础。
abc
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedInputStream in = FileUtil.getInputStream("E:\\ydffile\\hutool\\test1.txt");
BufferedOutputStream out = FileUtil.getOutputStream("E:\\ydffile\\hutool\\test2.txt");
long copySize = IoUtil.copy(in, out, IoUtil.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
System.out.println("写入大小>>>"+copySize);
}
1、重复拷贝,内容相同,不会覆盖。
2、如果text1.txt 文件内容更新为:abcdefg,再次拷贝,则text2.txt也会得到新的数据 。
3、如果text2.txt文件内容更新为:abcdefghijk ,再次拷贝,则text1.txt会覆盖掉text2.txt的内容。
2.6.2 读取流中的内容 (read)
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
// 创建一个FileInputStream对象,并绑定一个数据源文件
//FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("E:\\ydffile\\hutool\\test1.txt");
BufferedInputStream in = FileUtil.getInputStream("E:\\ydffile\\hutool\\test1.txt");
// 两个参数,第一个:FileInputStream,第二个:用完是否关闭输入流
FastByteArrayOutputStream read = IoUtil.read(in, true);
String string = read.toString();
System.out.println(string);
}
2.6.3 写入到流(write)
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
// 写入到哪个文件
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("E:\\ydffile\\hutool\\test1.txt");
// 写入的内容
String string = "This is the text content";
// 得到内容字节
byte[] content = string.getBytes();
// 开始写入
IoUtil.write(out,true, content);
System.out.println("写入结束");
}
一个直接调用OutputStream.write方法,另一个用于将对象转换为字符串(调用toString方法),然后写入到流中。
列化对象序列化后写入到流中:
IoUtil.writeObjects 用于将可序列化对象序列化后写入到流中。write方法并没有提供writeXXX,需要自己转换为String或byte[]。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 写入到哪个文件
File file = new File("E:\\ydffile\\hutool\\test1.txt");
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
// 写入序列化的对象的内容
TestBean testBean = new TestBean(1,"abc");
// 开始写入
IoUtil.writeObjects(out,true,testBean.toString());
System.out.println("写入结束");
}
2.7 StrBuilder
StrBuilder和StringBuilder使用方法基本一致,只是多了reset方法可以重新构建一个新的字符串而不必开辟新内存。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StrBuilder builder = StrBuilder.create();
StrBuilder append = builder.append("aaa").append("你好").append('r');
System.out.println(append);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//StringBuilder
TimeInterval timer = DateUtil.timer();
StringBuilder b2 = new StringBuilder();
for(int i =0; i< 1000000; i++) {
b2.append("test");
b2 = new StringBuilder();
}
Console.log(timer.interval());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//StrBuilder
TimeInterval timer = DateUtil.timer();
StrBuilder builder = StrBuilder.create();
for(int i =0; i< 1000000; i++) {
builder.append("test");
builder.reset();
}
Console.log(timer.interval());
}
2.7 Convert
2.7.1 时间转换
Convert.convertTime方法主要用于转换时长单位,比如一个很大的毫秒,我想获得这个毫秒数对应多少分:
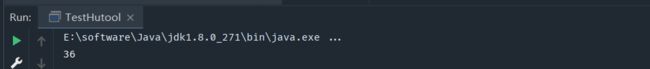
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
long a = 4535345;
long minutes = Convert.convertTime(a, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
System.out.println(minutes);
}
2.7.3 金额大小写转换
比如一些财务需求场景,将金钱数转换为大写形式:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
double money = 9000.56;
String digitUppercase = Convert.digitToChinese(money);
System.out.println("您的工资为:"+digitUppercase);
}
总结
Hutool工具封装了很多好用的方法,特别适用,代码一下子变得高大尚很多,这里我只做了部分讲解,其他简单的工具类方法就不说了,因为一看就懂了,Hutool中的工具类很多,可以参考:https://www.hutool.cn/docs