张量之拼接切分操作
张量操作
1. 张量拼接与切分
1.1 torch.cat()
作用:将张量按维度dim进行拼接
- tensor:张量序列
- dim:要拼接的维度
代码示例:
import torch
import numpy as np
# ************example1***********
t = torch.ones((2,3))
t_0 = torch.cat([t,t],dim=0)
t_1 = torch.cat([t,t],dim=1)
print("t_0:{} shape:{}\nt_1:{} shape:{}".format(t_0, t_0.shape,t_1,t_1.shape))运行:
可以看到在第一个维度拼接的时候,生成一个4*3的全1张量,第二个维度的时候生成一个2*6的全1张量
1.2 torch.stack()
作用:在新创建的维度dim上进行拼接
- tensor:张量序列
- dim:要拼接的维度
和torch.cat()不同,用torch.stack()会创建一个新维度
代码示例:
t = torch.ones((2,3))
t_stack = torch.stack([t,t],dim=2)
print("t_stack:{}\nshape:{}".format(t_stack,t_stack.shape))结果发现新创建了一个第三维度
若在第一个维度创建,则原来的维度往后移动一个位子,比如:
t = torch.ones((2,3))
t_stack = torch.stack([t,t],dim=0)
print("t_stack:{}\nshape:{}".format(t_stack,t_stack.shape))运行结果:生成2*2*3的张量
1.3 torch.chunk()
作用:将张量按维度dim进行平均切分
返回值:张量列表
注意:如果不能整除,最后一份张量小于其他张量
- input:要切分的张量
- chunks:要切分的份数
- dim:要切分的维度
代码示例:
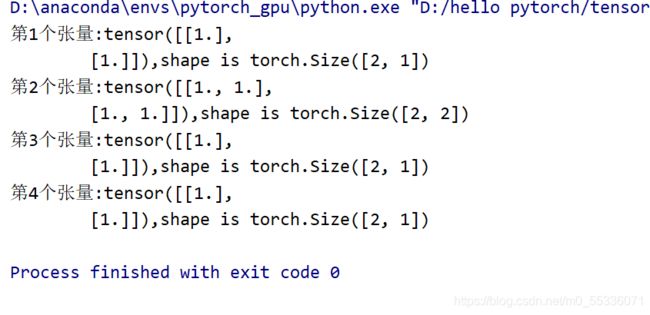
a = torch.ones((2,3))
list_of_tensors = torch.chunk(a, dim=1, chunks=3)
for idx,t in enumerate(list_of_tensors):
print("第{}个张量:{},shape is {}".format(idx+1,t, t.shape))运行:
1.4 torch.split()
作用:将张量按维度dim进行切分
返回值:张量列表
- tensor:要切分的张量
- split_size_or_sections:为int时,表示每一份的长度;为list时,按list元素切分
- dim:要切分的维度
代码:split_size_or_sections为int时
t = torch.ones((2,5))
list_of_tensors = torch.split(t, 2,dim=1)
for idx,t in enumerate(list_of_tensors):
print("第{}个张量:{},shape is {}".format(idx+1,t, t.shape))结果:
当split_size_or_sections为list时,list的数字加起来要等于指定维度的长度,否则会报错
改成
list_of_tensors = torch.split(t, [1,2,1,1],dim=1)结果:
2. 张量索引
2.1 torch.index_select()
作用:在维度dim上,按index索引数据
返回值:依据index索引数据拼接的张量
- input:要索引的张量
- dim:要索引的维度
- index:要索引数据的序号
代码:注意idx的数据类型是torch.long(如果是其他类型会报错)
t = torch.randint(0,9,size=(3,3))
idx = torch.tensor([0,2],dtype=torch.long)
t_select = torch.index_select(t,dim=0,index=idx)
print("t:\n{}\nt_select:\n{}".format(t,t_select))运行
2.2 torch.masked_select()
作用:按mask中的True进行索引
返回值:一维张量
- input:要索引的张量
- mask:与input同形状的布尔类型张量
代码实现
t = torch.randint(0,9,size=(3,3))
mask = t.ge(5)
t_select = torch.masked_select(t,mask) #ge表示大于等于
print("t:\n{}\nmask:\n{}\nt_select:\n{}".format(t,mask,t_select))运行结果
3. 张量变换
3.1 torch.reshape()
作用:变换张量形状
注意:当张量在内存中是连续的时候,新张量与input共享数据内存
- input:要变换的张量
- shape:新张量的形状
代码:
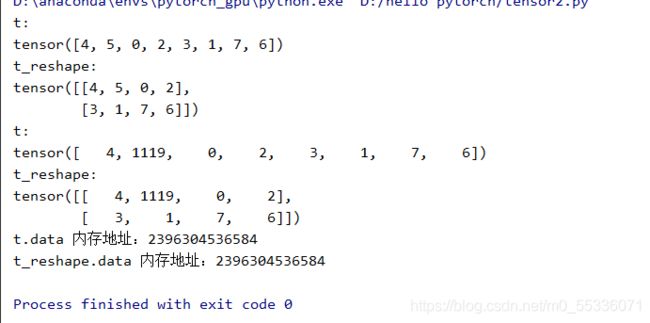
t = torch.randperm(8)
t_reshape = torch.reshape(t,(2,4))
print("t:\n{}\nt_reshape:\n{}".format(t,t_reshape))运行
注意reshape前后的张量是共享内存的,这里可以用代码示例:
t[1] = 1119
print("t:\n{}\nt_reshape:\n{}".format(t,t_reshape))
print("t.data 内存地址:{}".format(id(t.data)))
print("t_reshape.data 内存地址:{}".format(id(t_reshape.data)))运行可以看到t和t_reshape的第二个元素都变成了1119,而且数据的内存地址也是相同的
3.2 torch.transpose()
作用:交换张量的两个维度
- input:要交换的张量
- dim0:要交换的维度
- dim1:要交换的维度
代码示例:
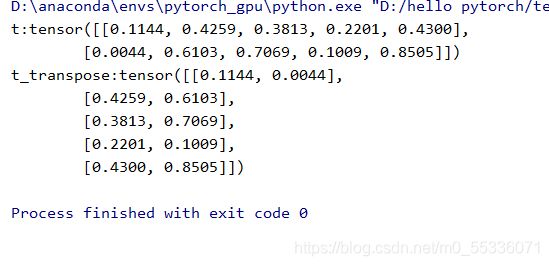
t = torch.rand((2,2,4))
t_transpose = torch.transpose(t,dim0=1,dim1=2)
print("t:{} \nt_transpose:{}".format(t,t_transpose))运行
3.3 torch.t()
作用:2维张量转置,对矩阵而言,等价torch.transpose(input, 0, 1)
代码示例:
t = torch.rand((2,5))
t_t = torch.t(t)
print("t:{} \nt_transpose:{}".format(t,t_t))运行:
3.4 torch.squeeze()
作用:压缩长度为1的维度
- dim:若为none,移除所有长度为1的轴,若指定维度,当且仅当该轴长度为1时,可以被移除
用代码理解一下:
t = torch.rand((1,1,3,4))
t_sq = torch.squeeze(t)
t_0 = torch.squeeze(t,dim=0)
t_1 = torch.squeeze(t,dim=1)
t_2 = torch.squeeze(t,dim=2)
t_3 = torch.squeeze(t,dim=3)
print(t.shape,
t_sq.shape,
t_0.shape,
t_1.shape,
t_2.shape,
t_3.shape)结果如下:
3.5 torch.unsqueeze()
作用:依据dim扩展维度
- dim:扩展的维度
在t_sq = torch.squeeze(t)后面加上t_unsq = torch.unsqueeze(t_sq,dim=1)
t_sq = torch.squeeze(t)
t_unsq = torch.unsqueeze(t_sq,dim=1)结果