接上一节十四、spring aop之创建代理,我们这节分析spring是如何把Advisor(增强器)封装成调用链,并且是如何逐一调用的,这里我们以JDk动态代理为例,这块逻辑jdk和cglib是一样的。代码在JdkDynamicAopProxy#invoke方法中。
List我们先来分析如何生成拦截器链。
public ListgetInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice方法只分析其中的一部分,就是把Advisor转换成MethodInterceptor。
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
List interceptors = new ArrayList(3);
Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
//通知本身就是MethodInterceptor对象,就不需要再转换
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);
}
//如果通知不是MethodInterceptor对象对象,使用适配器转换
for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
}
}
if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
}
return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[interceptors.size()]);
}
adapters对象有三个值
private final List adapters = new ArrayList(3);
public DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry() {
//对前置通知的代理
registerAdvisorAdapter(new MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter());
//返回通知代理
registerAdvisorAdapter(new AfterReturningAdviceAdapter());
//异常通知代理
registerAdvisorAdapter(new ThrowsAdviceAdapter());
}
这里以MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter作为例子分析
class MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter implements AdvisorAdapter, Serializable {
@Override
public boolean supportsAdvice(Advice advice) {
return (advice instanceof MethodBeforeAdvice);
}
@Override
public MethodInterceptor getInterceptor(Advisor advisor) {
MethodBeforeAdvice advice = (MethodBeforeAdvice) advisor.getAdvice();
return new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(advice);
}
}
MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter把前置通知转换成MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor对象。
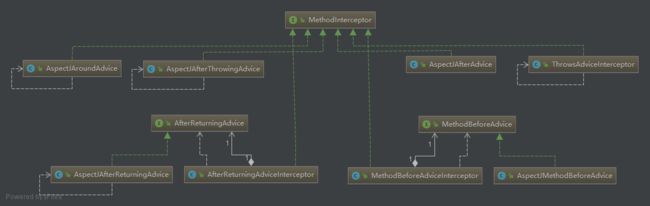
所以我们再来看下几种通知的类图:
从类图可以看出
AspectJAfterAdvice、AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice、AspectJAroundAdvice是实现了MethodInterceptor接口,AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice和AspectJAfterReturningAdvice是需要使用适配器适配,才能生成MethodInterceptor对象。
把拦截器生成MethodInterceptor拦截器链后,接下来又如何去调用呢?这个逻辑在ReflectiveMethodInvocation的proceed()上。
@Override
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
//拦截器链全部调用完,再调用目标方法
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
//增加计数器,得到下一个通知或者拦截器
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
//调用拦截器中方法
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
在proceed方法中,或许代码逻辑并没有我们想象的那么复杂,ReflectiveMethodInvocation中的主要职责是维护了链接调用的计数器,记录着当前调用链接的位置,以便链接可以有序地进行下去,在这个方法中并没有维护调用链的顺序,而是将此工作委拖给各个增强器,在各个增强器的内部进行逻辑实现。
我们再来分析MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor和AspectJAfterAdvice执行逻辑。
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
private MethodBeforeAdvice advice;
public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis() );
return mi.proceed();
}
}
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
protected Object invokeAdviceMethodWithGivenArgs(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object[] actualArgs = args;
if (this.aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterTypes().length == 0) {
actualArgs = null;
}
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.aspectJAdviceMethod);
// TODO AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection
//调用通知的方法
return this.aspectJAdviceMethod.invoke(this.aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectInstance(), actualArgs);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopInvocationException("Mismatch on arguments to advice method [" +
this.aspectJAdviceMethod + "]; pointcut expression [" +
this.pointcut.getPointcutExpression() + "]", ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor的invoke方法是调用了前置通知的before方法,前置通知before通过反射调用通知方法,然后再调用proceed()执行调用链。
public class AspectJAfterAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice
implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
}
}
AspectJAfterAdvice调用逻辑与前置通知不一样,它是直接实现MethodInterceptor,它的invoke方式是先调用执行链,然后再执行invokeAdviceMethod(),这种调用方式利用的是方法调用的入桟出栈。调用图如下: