0x00 前言
CPU版的TensorFlow安装还是十分简单的,也就是几条命令的时,但是GPU版的安装起来就会有不少的坑。在这里总结一下整个安装步骤,以及在安装过程中遇到的问题和解决方法。
整体梳理
安装GPU版的TensorFlow和CPU版稍微有一些区别,这里先做一个简单的梳理,后面有详细的安装过程。
- Python
- NVIDIA Cuda
- cuDNN
- TensorFlow
- 测试
0x01 安装Python
这里有两种安装的方法:
- 安装基本的Python环境,需要什么再继续安装。
- 安装Anaconda,基本上能用到的包都有包含。
笔者都是直接安装Anaconda了,省事,直接在官网下载安装即可,没什么写的。
下面给出安装基本Python环境的命令。
apt-get install python-pip python-dev python-virtualenv
0x02 安装NVIDIA Cuda
整体参考说明:http://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-installation-guide-linux/index.html#runfile
安装Cuda主要有下面几个步骤:
- 确认电脑的显卡支持cuda
- 确认Linux版本是否支持cuda
- 确认gcc是否安装
- 确认kernel版本
- 禁用开源驱动
- 关闭x server
- 下载cuda
- 安装cuda
前面几个步骤,主要是做各种前置条件验证的。本文的操作基于Ubuntu16.04,而且电脑本来就是双显卡,基本没什么问题。
主要的坑在安装cuda
1. 验证安装环境
友情提示: 这几步笔者基本上就跳过了,基本上没什么问题,感兴趣或者对自己系统不了解的可以验证一下。
- 确认电脑的显卡支持cuda
- 确认Linux版本是否支持cuda
- 确认gcc是否安装
- 确认kernel版本
2.1. Verify You Have a CUDA-Capable GPU
To verify that your GPU is CUDA-capable, go to your distribution's equivalent of System Properties, or, from the command line, enter:
$ lspci | grep -i nvidia
If you do not see any settings, update the PCI hardware database that Linux maintains by entering update-pciids (generally found in /sbin) at the command line and rerun the previous lspci command.
If your graphics card is from NVIDIA and it is listed in http://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-gpus, your GPU is CUDA-capable.
The Release Notes for the CUDA Toolkit also contain a list of supported products.
2.2. Verify You Have a Supported Version of Linux
The CUDA Development Tools are only supported on some specific distributions of Linux. These are listed in the CUDA Toolkit release notes.
To determine which distribution and release number you're running, type the following at the command line:
$ uname -m && cat /etc/*release
You should see output similar to the following, modified for your particular system:
x86_64
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Workstation release 6.0 (Santiago)
The x86_64 line indicates you are running on a 64-bit system. The remainder gives information about your distribution.
2.3. Verify the System Has gcc Installed
The gcc compiler is required for development using the CUDA Toolkit. It is not required for running CUDA applications. It is generally installed as part of the Linux installation, and in most cases the version of gcc installed with a supported version of Linux will work correctly.
To verify the version of gcc installed on your system, type the following on the command line:
$ gcc --version
If an error message displays, you need to install the development tools from your Linux distribution or obtain a version of gcc and its accompanying toolchain from the Web.
2.4. Verify the System has the Correct Kernel Headers and Development Packages Installed
The CUDA Driver requires that the kernel headers and development packages for the running version of the kernel be installed at the time of the driver installation, as well whenever the driver is rebuilt. For example, if your system is running kernel version 3.17.4-301, the 3.17.4-301 kernel headers and development packages must also be installed.
While the Runfile installation performs no package validation, the RPM and Deb installations of the driver will make an attempt to install the kernel header and development packages if no version of these packages is currently installed. However, it will install the latest version of these packages, which may or may not match the version of the kernel your system is using. Therefore, it is best to manually ensure the correct version of the kernel headers and development packages are installed prior to installing the CUDA Drivers, as well as whenever you change the kernel version.
The version of the kernel your system is running can be found by running the following command:
$ uname -r
This is the version of the kernel headers and development packages that must be installed prior to installing the CUDA Drivers. This command will be used multiple times below to specify the version of the packages to install. Note that below are the common-case scenarios for kernel usage. More advanced cases, such as custom kernel branches, should ensure that their kernel headers and sources match the kernel build they are running.
RHEL/CentOS
The kernel headers and development packages for the currently running kernel can be installed with:
$ sudo yum install kernel-devel-$(uname -r) kernel-headers-$(uname -r)
Fedora
The kernel headers and development packages for the currently running kernel can be installed with:
$ sudo dnf install kernel-devel-$(uname -r) kernel-headers-$(uname -r)
OpenSUSE/SLES
Use the output of the uname command to determine the running kernel's version and variant:
$ uname -r
3.16.6-2-default
In this example, the version is 3.16.6-2 and the variant is default. The kernel headers and development packages can then be installed with the following command, replacing and with the variant and version discovered from the previous uname command:
$ sudo zypper install kernel--devel=
Ubuntu
The kernel headers and development packages for the currently running kernel can be installed with:
$ sudo apt-get install linux-headers-$(uname -r)
Read more at: http://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-installation-guide-linux/index.html#ixzz4b1TabLmw
Follow us: @GPUComputing on Twitter | NVIDIA on Facebook
2. 禁用开源驱动
注意:有些教程会有更多需要禁用的驱动,这里遵循官网的说明,没有问题。
新建一个文件
vim /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conf
文件内容为
blacklist nouveau
options nouveau modeset=0
update一下
sudo update-initramfs -u
3. 关闭X server
当我们安装 NVIDIA 的驱动程序时,需要先关闭 X server,关闭的方式有两种:
- 关闭gdm
- 关闭lightdm
第一种不行时,尝试用第二种。 本文使用的是第二种关闭方式。
方法1
sudo /etc/init.d/gdm stop
sudo /etc/init.d/gdm status
方法2
sudo /etc/init.d/lightdm stop
sudo /etc/init.d/lightdm status
注意:后面显卡驱动程序安装完毕后,应首先重启 gdm 或者 lightdm。
4. 下载cuda
官网下载即可。 目前这种方式是最靠谱的。
https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads
注意:这里在选择下载文件时选择的是.run后缀的文件。用别的遇到了一些坑,最后发现这个最稳定。
5. 安装cuda
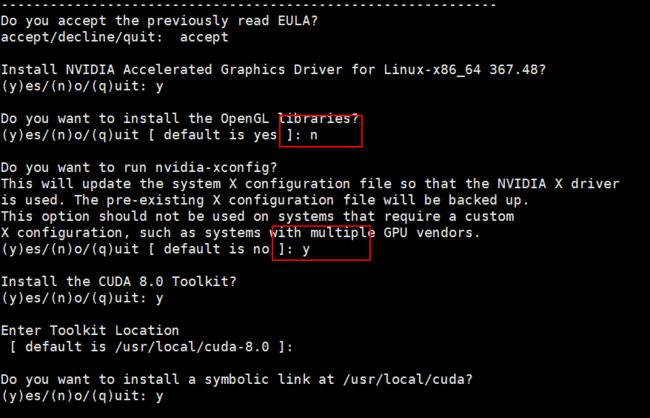
注意:安装过程中有坑,请重视下面的说明,否则安装后的ubuntu可能会出现无法进入图形界面的情况。因为这个原因,笔者重做了一晚上的操作系统,尝试了3个Ubuntu的版本和两个Centos的版本。
其它的步骤,跟着说明点就行,主要注意图中框的地方。
安装cuda时一定不要安装OpenGL;切记,否则有可能在安装完之后无法启动图形化桌面。
显卡驱动程序安装完毕后,应首先重启 gdm 或者 lightdm。
6. 添加环境变量
在官网里面需要配置环境变量。
在terminal根目录中输入以下命令:
$ sudo vim ~/.bash_profile
在打开的文本末尾加入:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/cuda/lib64:/usr/local/cuda/extras/CUPTI/lib64"
export CUDA_HOME=/usr/local/cuda
0x03 安装cuDNN
下面是下载地址,需要提前注册。 注册一下就好。
注意下载的版本。
https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-download
下载下来的文件就deb包,直接dpkg -i 安装即可。
0x04 安装TensorFlow
Tensorflow官网中有很详细的说明。笔者建议无论是Anaconda还是原生Python环境,都使用pip安装,最为简便,版本也很新。
pip install tensorflow
另外,如果使用Anaconda的conda安装,有一个好处就是可以为Tensorflow单独建一个虚拟环境,但要注意输入正确的Tensorflow包地址(gpu还是cpu版本、操作系统、Python版本等)。
在https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/里有所有Tensorflow包的列表(XML格式)。
建一个虚拟环境
$ conda create -n tensorflow
Activate虚拟环境
$ source activate tensorflow
(tensorflow)$ # Your prompt should change
安装tensorflow
(tensorflow)$ pip install --ignore-installed --upgrade \
https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/linux/gpu/tensorflow-1.0.1-cp27-cp27m-linux_x86_64.whl
0x05 验证安装
这里跑一个小例子来验证一下。
$ python
Then, enter the following short program inside the python interactive shell:
>>> import tensorflow as tf
>>> hello = tf.constant('Hello, TensorFlow!')
>>> sess = tf.Session()
>>> print(sess.run(hello))
If the system outputs the following, then you are ready to begin running TensorFlow programs:
Hello, TensorFlow!
作者:cathyxlyl | | GITHUB
个人主页:http://cathyxlyl.github.io/
文章可以转载, 但必须以超链接形式标明文章原始出处和作者信息