精通Mybatis之结果集处理流程与映射体系(联合查询与嵌套映射)(四)
前言
上篇博客小编将懒加载详细的讲解完毕,今天将结果集处理和映射体系全部结束,进入下一篇章。在映射体系中大家是否觉得还少了什么东西,记得精通Mybatis之结果集处理流程与映射体系(MetaObJect工具以及嵌套子查询)(一)的结果集查询后转换流程图中,遍历结果集是说简单,也就是之后的嵌套还是循环依赖以及懒加载细节都是以简单转换为基础的,当然还有遍历结果集为联合查询,即使用join(left,right,inner)查询,然后映射成对应的结果集。今天小编就讲解一下在联合查询的时候mysql是如何很好的映射成相应的结果。
联合查询
联合查询结构
嵌套映射我们一样用公司,法人,和部门来说一下,一个公司一个法人多个部门,配置仍然可用嵌套的配置适用association以及collection表示,咱们先看他的结构图,然后小编简单写个示例:
结构图
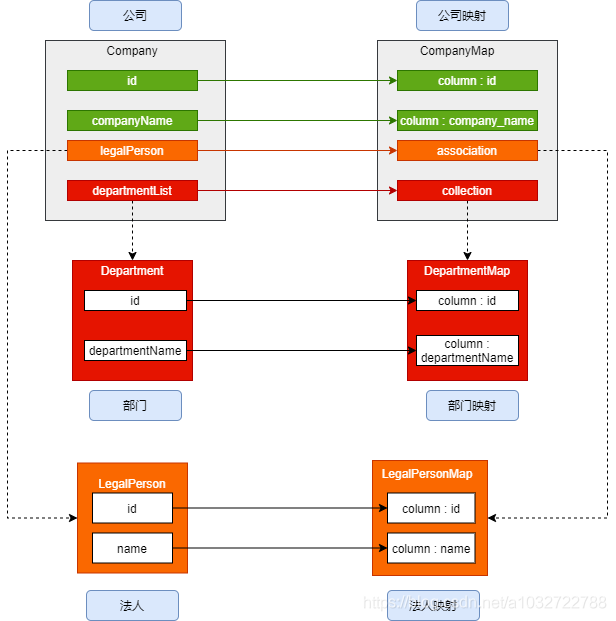
在配置方式上可以直接配置子映射,也以引入外部映射和自动映射。共有两类嵌套结构分别是一对多 与多对多 。

关于映射使用方式与属性的配置,大家也可以参考官方文档:结果映射,文章写得特别详细。
配置示例:
小编写了一个:公司与法人一对一自动映射xml配置以及公司与部门一对多xml配置:
<resultMap id="CompanyMap" type="entity.Company">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="companyName" column="company_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<association property="legalPerson" autoMapping="true" columnPrefix="legalPerson_"/>
resultMap>
<select id="selectCompanyAndLegalById" resultMap="CompanyMap" parameterType="java.lang.Long">
select co.id,co.company_name,lp.id as legalPerson_id,lp.name as legalPerson_name from company co left join legal_person lp on co.id = lp.company_id where co.id = #{companyId}
select>
<resultMap id="CompanyDepartmentMap" type="entity.Company">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="companyName" column="company_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<collection property="departmentList" ofType="entity.Department" autoMapping="true" columnPrefix="department_"/>
resultMap>
<select id="selectCompanyAndDepartById" resultMap="CompanyDepartmentMap" parameterType="java.lang.Long">
select co.id,co.company_name,de.id as department_id,de.department_name as department_name from company co left join department de on co.id = de.company_id where co.id = #{companyId}
select>
代码
public class JoinTest {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
Configuration configuration;
@Before
public void init() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
configuration = sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration();
}
@Test
public void joinSelectTest() {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.REUSE)) {
CompanyMapper companyMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CompanyMapper.class);
Company company = companyMapper.selectCompanyAndLegalById(1L);
System.out.println(company.getLegalPerson());
}
}
@Test
public void joinCollectionTest() {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.REUSE)) {
CompanyMapper companyMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CompanyMapper.class);
Company company = companyMapper.selectCompanyAndDepartmentById(1L);
System.out.println(company.getDepartmentList());
}
}
}
联合查询一对多流程
这里小编直接讲解一对多的处理流程,因为一对一是一对多的简化版,咱们将数据库查询的结果图放在下面:
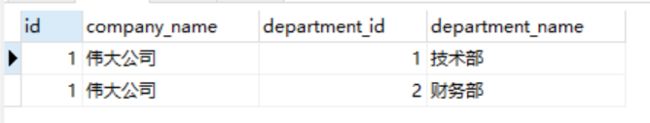
查询出来为两条记录,那mybatis怎么将两条数据变成只有一个company对象,且对象下面有两个部门的呢。上面的话company的resultMap中指定了id,所以company根据id去分组,id值一样认为是同一个,当然假如不设置id,就以result中的所有属性相同进行分组,当然id也可设置多个,根据多个id的属性值分组:
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="companyName" column="company_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
解析流程图(DefaultResultSetHandler.handleRowValuesForNestedResultMap()这个方法里面):
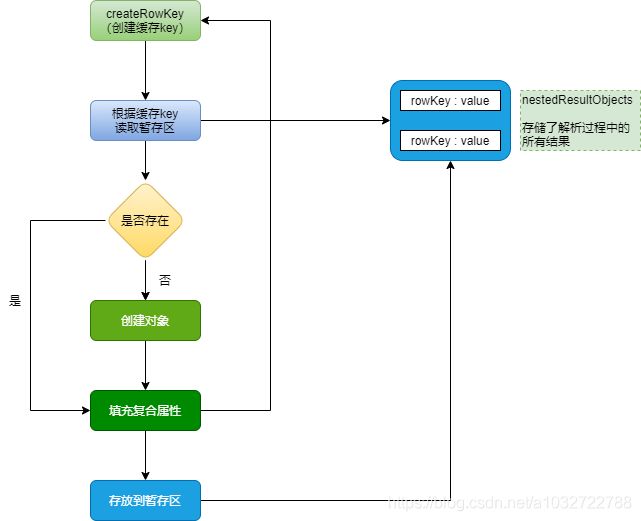
流程说明:
所有映射流程的解析都是在DefaultResultSetHandler当中完成。主要方法如下:
- handleRowValuesForNestedResultMap()
- 嵌套结果集解析入口,在这里会遍历结果集中所有行。并为每一行创建一个RowKey对象。然后调用getRowValue()获取解析结果对象。最后保存至ResultHandler中。
注:调用getRowValue前会基于RowKey获取已解析的对象,然后作为partialObject参数发给getRowValue - getRowValue()
该方法最终会基于当前行生成一个解析好对象。具体职责包括,1.创建对象、2.填充普通属性 3.填充嵌套属性。在解析嵌套属性时会以递归的方式在调用getRowValue获取子对象。最后一步4.基于RowKey 暂存当前解析对象。
如果partialObject参数不为空 只会执行 第3步。因为1、2已经执行过了。 - applyNestedResultMappings()
解析并填充嵌套结果集映射,遍历所有嵌套映射,然后获取其嵌套ResultMap。接着创建RowKey 去获取暂存区的值。然后调用getRowValue 获取属性对象。最后填充至父对象。
如果通过RowKey能获取到属性对象,它还是会去调用getRowsValue,因为有可能属下还存在未解析的属性。
源码阅读:
小编根据上面流程图带大家看一下源代码:
private void handleRowValuesForNestedResultMap(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
final DefaultResultContext<Object> resultContext = new DefaultResultContext<>();
ResultSet resultSet = rsw.getResultSet();
skipRows(resultSet, rowBounds);
Object rowValue = previousRowValue;
while (shouldProcessMoreRows(resultContext, rowBounds) && !resultSet.isClosed() && resultSet.next()) {
final ResultMap discriminatedResultMap = resolveDiscriminatedResultMap(resultSet, resultMap, null);
//获取缓存key
final CacheKey rowKey = createRowKey(discriminatedResultMap, rsw, null);
//根据缓存key读取暂存区的值
Object partialObject = nestedResultObjects.get(rowKey);
// issue #577 && #542
if (mappedStatement.isResultOrdered()) {
if (partialObject == null && rowValue != null) {
nestedResultObjects.clear();
storeObject(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue, parentMapping, resultSet);
}
rowValue = getRowValue(rsw, discriminatedResultMap, rowKey, null, partialObject);
} else {
//解析值
rowValue = getRowValue(rsw, discriminatedResultMap, rowKey, null, partialObject);
if (partialObject == null) {
storeObject(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue, parentMapping, resultSet);
}
}
}
if (rowValue != null && mappedStatement.isResultOrdered() && shouldProcessMoreRows(resultContext, rowBounds)) {
storeObject(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue, parentMapping, resultSet);
previousRowValue = null;
} else if (rowValue != null) {
previousRowValue = rowValue;
}
}
private Object getRowValue(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, CacheKey combinedKey, String columnPrefix, Object partialObject) throws SQLException {
final String resultMapId = resultMap.getId();
Object rowValue = partialObject;
if (rowValue != null) {
//第二次的时候rowValue != null
final MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(rowValue);
putAncestor(rowValue, resultMapId);
//直接将department放入company的departmentList中
applyNestedResultMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix, combinedKey, false);
ancestorObjects.remove(resultMapId);
} else {
//第一次为空
final ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader = new ResultLoaderMap();
//创建java映射的对象
rowValue = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, lazyLoader, columnPrefix);
if (rowValue != null && !hasTypeHandlerForResultObject(rsw, resultMap.getType())) {
//包装成metaObject 方便属性赋值
final MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(rowValue);
boolean foundValues = this.useConstructorMappings;
if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, true)) {
//自动解析
foundValues = applyAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix) || foundValues;
}
//手动映射解析,这里只是company的基本属性值
foundValues = applyPropertyMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, lazyLoader, columnPrefix) || foundValues;
//放入祖先map中用于引用循环
putAncestor(rowValue, resultMapId);
//嵌套映射中的值解析 然后赋值company的department值,看下面的代码
foundValues = applyNestedResultMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix, combinedKey, true) || foundValues;
ancestorObjects.remove(resultMapId);
foundValues = lazyLoader.size() > 0 || foundValues;
rowValue = foundValues || configuration.isReturnInstanceForEmptyRow() ? rowValue : null;
}
if (combinedKey != CacheKey.NULL_CACHE_KEY) {
//放入暂存区
nestedResultObjects.put(combinedKey, rowValue);
}
}
return rowValue;
}
private boolean applyNestedResultMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject, String parentPrefix, CacheKey parentRowKey, boolean newObject) {
boolean foundValues = false;
//遍历三个resultMap,第三个映射会进去
//联合查询一对多循环引用
小编先将xml配置写出来,什么是循环引用(这次使用公司对应法人,法人下面有公司):
<resultMap id="CompanyMap" type="entity.Company">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="companyName" column="company_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<association property="legalPerson" autoMapping="true" columnPrefix="legalPerson_">
<association property="company" javaType="entity.Company" resultMap="CompanyMap"/>
association>
resultMap>
<select id="selectCompanyAndLegalById" resultMap="CompanyMap" parameterType="java.lang.Long">
select co.id,co.company_name,lp.id as legalPerson_id,lp.name as legalPerson_name
from company co left join legal_person lp on co.id = lp.company_id
where co.id = #{companyId}
select>
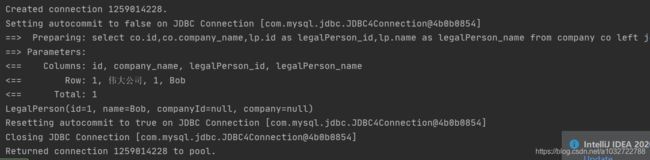
上面companyMap中,company下面有legalPerson,legalPerson中有company。有了mybatis循环调用依赖之后,小伙伴肯定没有疑惑认为这个引用会报错了吧。下面是小编的测试结果:

DefaultResultSetHandler 在解析复合映射之前都会在上下文中填充当前解析对象(使用resultMapId做为Key)。如果子属性又映射引用了父映射ID,就可以直接获取不需要在去解析父对象。具体流程如下:
循环引用流程:

源代码阅读:
上面小编也讲过了,这边贴出重要代码即可:
//将父映射id对应值扔进去 comany扔进去
putAncestor(rowValue, resultMapId);
//嵌套映射中的值解析 然后赋值company的department值,看下面的代码
foundValues = applyNestedResultMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix, combinedKey, true) || foundValues;
ancestorObjects.remove(resultMapId);
//legalPerson关联company
if (resultMapping.getColumnPrefix() == null) {
// try to fill circular reference only when columnPrefix
// is not specified for the nested result map (issue #215)
Object ancestorObject = ancestorObjects.get(nestedResultMapId);
if (ancestorObject != null) {
if (newObject) {
linkObjects(metaObject, resultMapping, ancestorObject); // issue #385
}
continue;
}
}
总结
到这儿mybatis的结果处理以及结果集映射体系就完毕了,希望大家都有所收获,也希望小编已经讲清楚了。接下来是mybatis的动态sql解析,configuration配置体系以及插件体系。这样mybatis就告一段落了,一起加油努力吧!