SpringBoot Security的介绍
1.SpringBoot security框架的简介
SpringBoot security是基于spring框架的,提供了一套Web应用安全性完整的解决方案。
SpringBoot重要的核心功能:
用户认证和用户授权:
2.SpringBoot+spring security
入门的案例:
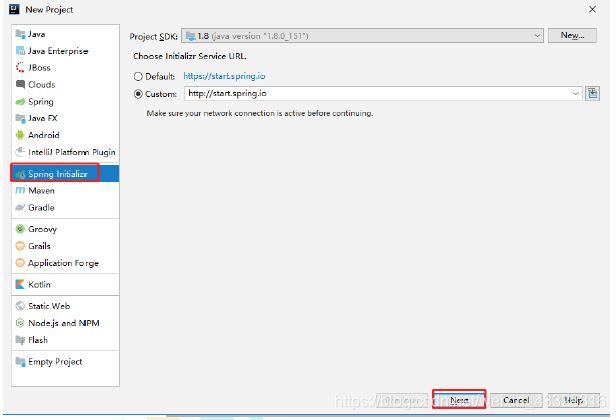
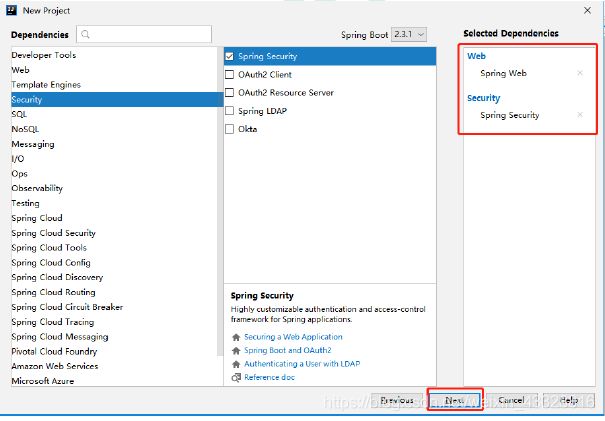
1.创建一个springboot的项目
编写一个controller:
package com.lsy.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author:lsy
* @Date:
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello security!";
}
}
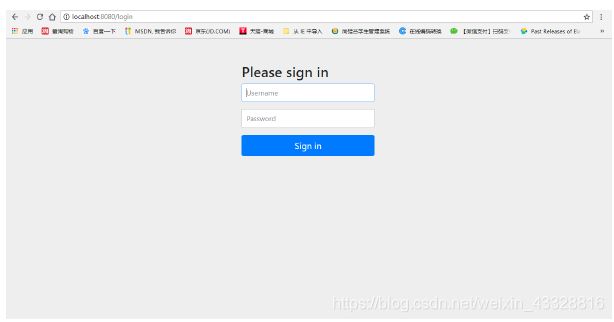
启动之后,输入:localhost:8080/test/hello
出现以下的界面:
由于没有进行配置所以系统是默认的用户名和密码:
输入用户名和密码就可以访问localhost:8080/test/hello
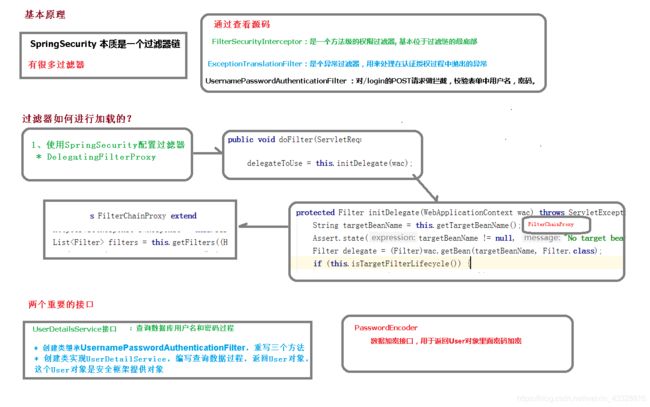
3.SpringBoot的基本原理
4.Web的权限方案:
认证和授权:
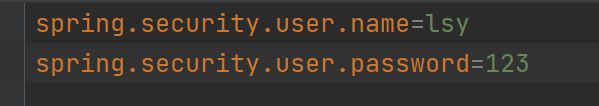
设置登录的用户名和密码:
方式一:通过配置文件。
方式二:通过配置类
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
/* 对密码进行加密 */
BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
String encode = bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("123");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("lsy").password(encode).roles("admin");
}
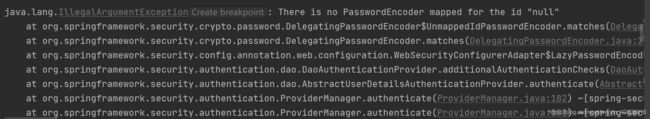
}出现了一个错误:
因为要先创建BCryptPasswordEncoder的实例。并注入容器中
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}就可以进行登录。
方式三:自定义编写实现类
在配置类中注入UserDetailsService
package com.lsy.config;
import com.lsy.service.MyUserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author:lsy
* @Date:
*/
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfigUser extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
MyUserDetailsService myUserDetailsService;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(myUserDetailsService).passwordEncoder(password());
}
@Bean
PasswordEncoder password() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
编写UserDetailsService的实现类,在实现类中定义相应的用户名和密码
@Service
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//定义一个权限角色
List auth= AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("role");
return new User("mary",new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123"),auth);
}
} 5.实现数据库认证来完成用户登录
整合MybatisPlus完成数据库操作
第一步:引入相关的依赖
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.0.5
mysql
mysql-connector-java
8.0.11
第二步:在数据库中创建相应的数据表
第三步:创建相应的实体类:
package com.lsy.bean;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.ToString;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author:lsy
* @Date:
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class Users {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
}第四步:整合mybatis-plus,继承mybatis-plus的接口BaseMapper
package com.lsy.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.lsy.bean.Users;
/**
* @Description:mybatis-plus中的BaseMapper风咋混了很多对数据库的操作
* @Author:lsy
* @Date:
*/
public interface UsersMapper extends BaseMapper {
} 第五步:在MyUserDetailsService中调用Mapper中的方法对数据库进行查询。
package com.lsy.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.lsy.bean.Users;
import com.lsy.mapper.UsersMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.AuthorityUtils;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author:lsy
* @Date:
*/
@Service
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
UsersMapper usersMapper;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//调用USerMapper中的方法去调用数据库
//使用mybatis-plus中的一个条件构造器。
QueryWrapper wrapper=new QueryWrapper<>();
//根据用户名到数据库中进行查询。
//相当于是在数据库查询语句中的where username=?
wrapper.eq("username",username);
//通过用户名查询数据库中的一条记录
Users users = usersMapper.selectOne(wrapper);
//进行判断
if(users==null){
//表示数据库中没有该用户名,认证失败
//可以直接抛异常
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户名不存在");
}
//如果不等于空的话。就表示认证成功。
//定义一个权限角色
List auth= AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("role");
//根据从数据库中返回的用户的用户
return new User(users.getUsername(),new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123"),auth);
}
}
第六步:在启动类中添加注解MapperScan
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.lsy.mapper")
public class SpringbootSecurityApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootSecurityApplication.class, args);
}
}第七步:在配置文件中进行数据库的配置
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=lsy可以使用数据库的用户名和密码进行登录了
6.一般情况下,我们的登录页面都是自己编写的
自定义的登录页面
//自定义页面的登录过程
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()//自定义自己编写的登录页面
.loginPage("/login.html")//具体的登录页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/user/login")// 登录访问路径,也就是controller
.defaultSuccessUrl("/test/index").permitAll() //登录成功之后,跳转路径
.and().authorizeRequests()//授权访问
.antMatchers("/","/test/hello","/user/login").permitAll() //设置哪些路径可以直接访问,不需要认证
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护
}
xx
表单提交
7.基于角色或者权限进行访问控制
1.hasAuthority方法:之争对有一个权限角色
//自定义页面的登录过程
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()//自定义自己编写的登录页面
.loginPage("/login.html")//具体的登录页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/user/login")// 登录访问路径,也就是controller
.defaultSuccessUrl("/test/index").permitAll() //登录成功之后,跳转路径或者是页面
.and().authorizeRequests()//授权访问
.antMatchers("/","/test/hello","/user/login").permitAll() //设置哪些路径可以直接访问,不需要认证
// 当前登录用户,只有具有admins权限才可以访问这个路径
// 1 hasAuthority方法
.antMatchers("/test/index").hasAuthority("admins")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护
}在MyUserDetailsService中增加相应的角色
//定义一个权限角色
List auth= AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admins"); 如果在MyUserDetailsService中增加的角色不是admins,则会出现以下错误
2.hasAnyAuthority方法:可以设置多个权限,只要符合其中一个就可以
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()//自定义自己编写的登录页面
.loginPage("/login.html")//具体的登录页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/user/login")// 登录访问路径,也就是controller
.defaultSuccessUrl("/test/index").permitAll() //登录成功之后,跳转路径或者是页面
.and().authorizeRequests()//授权访问
.antMatchers("/","/test/hello","/user/login").permitAll() //设置哪些路径可以直接访问,不需要认证
// 当前登录用户,只有具有admins权限才可以访问这个路径
// 1 hasAuthority方法
// .antMatchers("/test/index").hasAuthority("admins")
//2 hasAnyAuthority方法
.antMatchers("/test/index").hasAnyAuthority("admins,manager")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护
}3.方法三:hasRole方法:如果当前主题具有指定的角色,则返回true,否则返回false。
//自定义页面的登录过程
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()//自定义自己编写的登录页面
.loginPage("/login.html")//具体的登录页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/user/login")// 登录访问路径,也就是controller
.defaultSuccessUrl("/test/index").permitAll() //登录成功之后,跳转路径或者是页面
.and().authorizeRequests()//授权访问
.antMatchers("/","/test/hello","/user/login").permitAll() //设置哪些路径可以直接访问,不需要认证
// 当前登录用户,只有具有admins权限才可以访问这个路径
// 1 hasAuthority方法
// .antMatchers("/test/index").hasAuthority("admins")
//2 hasAnyAuthority方法
// .antMatchers("/test/index").hasAnyAuthority("admins,manager")
//3 hasRole方法 ROLE_sale
.antMatchers("/test/index").hasRole("sale")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护
}hasRole的源码:
private static String hasRole(String role) {
Assert.notNull(role, "role cannot be null");
Assert.isTrue(!role.startsWith("ROLE_"), () -> {
return "role should not start with 'ROLE_' since it is automatically inserted. Got '" + role + "'";
});
return "hasRole('ROLE_" + role + "')";
}
//定义一个权限角色
List auth= AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("ROLE_sale");
4.方法4:hasAnyRole:可以设置多个权限,只要符合其中一个就可以
8.自定义403页面:当用户没有权限进行访问的时候,返回的就是403
在配置类中进行配置
//自定义页面的登录过程
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//配置没有权限访问跳转的403页面
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("unauth.html");
}
Title
没有访问权限!
9.用户的授权:注解的使用
1.@Secured:判断是否具有角色,另外需要注意的是这里匹配的字符串需要议案家前缀“ROLE_”
使用注解前要先开启注解功能!
在配置类或者启动类上添加注解
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)在controller中设置该注解
@Secured("ROLE_sale")
@GetMapping("/update")
public String update(){
return "hello update!";
}在UserDetailsService中设置相应的角色
List auth= AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("ROLE_sale,ROLE_manager");
在浏览器输入:http://localhost:8080/test/update。登录就可以进行访问
2.@PreAuthorize:适合进入方法前的权限验证,可以将登录用户的roles/permissions参数传到方法中。
现在启动类上添加prePostEnable=true
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true,prePostEnabled = true)在controller的方法上添加相应的注解
在注解中可以使用hasAnyAuthority,hasAuthority,hasRole,hasAnyRoles
在进入方法之前进行访问:
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('ROLE_manager')")
@GetMapping("/update")
public String update(){
return "hello update!";
}
3.@PostAuthorize:在方法执行之后进行校验,适合验证带有返回值的权限(使用不多)
@PostAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('ROLE_manager')")
@GetMapping("/update")
public String update(){
return "hello update!";
}方法没有访问权限也会执行这个方法,因为是在执行方法之后才会进行校验
以下两个方法使用较少:
4.PostFilter:权限验证之后对数据进行过滤,也就是方法事务返回数据进行过滤。
5.PreFilter:进入控制器方法之前对参数进行过滤
10.用户注销
在配置类中添加一个退出的配置:
http.logout().logoutUrl("/logout").logoutSuccessUrl("/test/hello").permitAll();测试:
1.登录成功之后,跳转到成功的页面
2.在成功页面中添加一个注销登录的超链接
3.登录成功之后,在成功页面点击了注销之后,就不能进行访问了
//在配置类中添加一个退出的配置:
http.logout().logoutUrl("/logout").logoutSuccessUrl("/test/hello").permitAll();
//配置没有权限访问跳转的403页面
http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/unauth.html");
http.formLogin()//自定义自己编写的登录页面
.loginPage("/login.html")//具体的登录页面
.loginProcessingUrl("/user/login")// 登录访问路径,也就是controller
.defaultSuccessUrl("/success.html").permitAll() //登录成功之后,跳转路径或者是页面
}
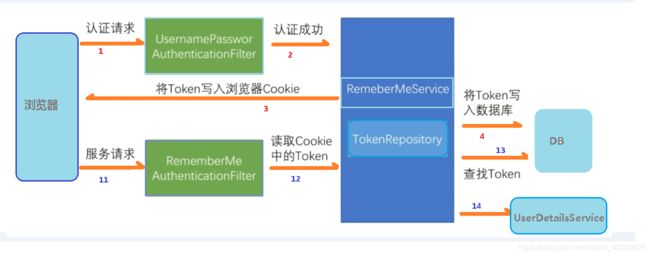
11.用户的自动登录
自动登录的原理:
实现用户登录的过程:
第一步:现在数据库中创建相应的表:表的字段名称和表名都是固定的
create table persistent_logins (
username varchar(64) not null,
series varchar(64) primary key,
token varchar(64) not null,
last_used timestamp not null)第二步:修改配置类
//注入数据源
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;
//配置对象
//添加容器,并且注入相应的数据源
@Bean
public PersistentTokenRepository persistentTokenRepository(){
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl jdbcTokenRepository=new JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl();
jdbcTokenRepository.setDataSource(dataSource);
//也可以自动创建数据库的表,不需要单独在数据库中创建相应的表
// jdbcTokenRepository.setCreateTableOnStartup(true);
return jdbcTokenRepository;
}
第三步:在配置类中配置自动登录
.antMatchers("/test/index").hasRole("sale")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
//传入操作数据库的对象
.and().rememberMe().tokenRepository(persistentTokenRepository())
//设置相应的保存的有效时长,单位是秒。
.tokenValiditySeconds(60)
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService)
.and().csrf().disable(); //关闭csrf防护第四步:在登录页上添加自动登录的复选框name必须为remember-me
自动登录12.cfrf跨站请求伪造
解决方案就是:
1.在登录页面添加一个隐藏域:
2.开启防护