Spring boot jdbcTemplate
文章目录
- Spring boot jdbcTemplate
-
- 上一节 Spring boot lombok
- 源码
-
- jdbcTemplate
- jdbcTemplate crud 使用
-
- jdbcTemplate.update()
- jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate()
- jdbcTemplate.queryForObject()
- jdbcTemplate.query()
- jdbcTemplate.queryForList()
- jdbcTemplate.execute()
- NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
-
- update 示例
- 自动装配类
-
- JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration
- 总结
- 下一节 Spring boot 数据库连接池
Spring boot jdbcTemplate
上一节 Spring boot lombok
Spring boot lombok
源码
springboot学习指南
jdbcTemplate
简介
spring 提供了好的的template类 简化和封装了一些便利的操作,例如 jdbcTemplte, redisTemplate,kafkaTemplate, rabbitTemplate 等等;
现在使用 jdbcTemplate 进行对数据库的操作。虽然没有mybatis 和jpa,hibernate等orm框架更先进,
不过在小型项目中偶尔还是可以使用的。
1. 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<!--创建web项目-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 配置文件中配置数据源信息
server:
port: 8989
spring:
application:
name: test-jdbcTemplate
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mytest?useSSL=false&charsetEncoding=utf8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
logging:
level:
org.springframework.jdbc.core: debug
3. 创建数据库表结构
创建user表
drop table t_user;
commit;
create table t_user
(
u_id varchar(64) not null
primary key,
u_name varchar(32) not null,
password varchar(32) not null,
money int(10) null,
create_time timestamp default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null
);
commit ;
创建表实体类
@ToString
public class UserEntity {
private String uId;
private String uName;
private String password;
private Long money;
private Date createTime;
public String getuId() {
return uId;
}
public void setuId(String uId) {
this.uId = uId;
}
public String getuName() {
return uName;
}
public void setuName(String uName) {
this.uName = uName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Long getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Long money) {
this.money = money;
}
public Date getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
}
使用 jdbcTemplate 进行crud 操作
jdbcTemplate 在springboot项目中已经被自动装配,在 类 JdbcTemplateConfiguration或者自动装配类JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration 中jdbcTemplate 被创建,所以可以直接引入使用:
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
jdbcTemplate crud 使用
jdbcTemplate.update()
insert
@PostMapping({
"", "add"})
public String addUser(UserEntity userEntity) throws Exception {
String id = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", "");
Object[] params = new Object[]{
id,
userEntity.getuName(),
userEntity.getPassword(),
userEntity.getMoney(),
new Date()};
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into t_user(u_id,u_name,password,money,create_time) values(?,?,?,?,?)", params);
return id;
}
jdbcTemplate.update 可以执行 update ,insert,和delete语句;
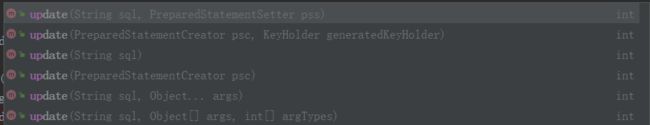
update 语句提供了以上几种重载方法;
update(String sql, @Nullable Object… args) 接收一个sql语句, 和参数;sql语句中的占位符 ? 和 参数一一对应不能有null值
update(String sql, @Nullable PreparedStatementSetter pss) 接收sql语句 和 PreparedStatementSetter;
PreparedStatementSetter 中可以使用PreparedStatement进行参数的设置
update(String sql, Object[] args, int[] argTypes) 接收一个sql语句,参数,参数类型;参数对应的数据库类型;一般情况下我们使用默认的即可,所以此方法一般不使用。
update(final String sql) 直接接收一个sql, 可以没有条件或者参数是直接拼接好了的
update
jdbcTemplate.update("update t_user set u_name = ?, password = ? where u_id = ?", new Object[]{
userEntity.getuName(), userEntity.getPassword(), userEntity.getuId()})
delete
@DeleteMapping("{id}")
public void del(@PathVariable String id) throws Exception {
Objects.requireNonNull(id);
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from t_user where u_id = ?", new Object[]{
id});
}
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate()
batch insert
批量操作 和单条操作方法基本是一致的,批量操作我们使用 BatchPreparedStatementSetter 进行参数的设置;当然不使用批量操作也可以传入参数PreparedStatementSetter
@PostMapping({
"/batch"})
public List<String> batchAddUser(@RequestBody List<UserEntity> userEntityList) {
List<UserEntity> collect = userEntityList.stream().map(u -> {
u.setuId(UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", ""));
u.setCreateTime(new Date());
return u;
}).collect(toList());
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("insert into t_user(u_id,u_name,`password`,money,create_time) values(?,?,?,?,?)", new BatchPreparedStatementSetter() {
@Override
public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps, int i) throws SQLException {
ps.setString(1, collect.get(i).getuId());
ps.setString(2, collect.get(i).getuName());
ps.setString(3, collect.get(i).getPassword());
ps.setLong(4, collect.get(i).getMoney());
ps.setDate(5, new java.sql.Date(collect.get(i).getCreateTime().getTime()));
}
@Override
public int getBatchSize() {
return collect.size();
}
});
return collect.stream().map(UserEntity::getuId).collect(toList());
}
collect 是我们插入的一组数据, 参数BatchPreparedStatementSetter 是我们给参数进行赋值操作,ps 这个不用说了 数据库底层的PreparedStatement , i 是 批量操作的语句的索引,也就是给索引是 i 的sql语句参数设置值;
jdbcTemplate.queryForObject()
select
使用 jdbcTemplate.queryForObject 进行查询操作
@GetMapping({
"{id}"})
public UserEntity getUser(@PathVariable String id) throws Exception {
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from t_user where u_id = ?", new Object[]{
id}, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(UserEntity.class));
}
如果我们想要返回一个实体类,必须使用 beanPropertyRowMapper 进行映射;
queryForObject(String sql, Class requiredType) 的 requiredType 不是返回的映射实体类。
注意
queryForObject如果没有查询出来数据会报错
org.springframework.dao.EmptyResultDataAccessException: Incorrect result size: expected 1, actual 0
如果使用的是queryForObject(String sql, Class requiredType) 方法或其他带requiredType参数的方法;
这里的requiredType 是数据库的单个字段表,并不是实体类映射
所以如果 映射为 UserEntity.class 就会报错如下:
org.springframework.jdbc.IncorrectResultSetColumnCountException: Incorrect column count: expected 1, actual 5
正常使用应该为 jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select u_id from t_user where u_id = ?", new Object[]{id}, String.class); 查询数据单字段信息
例如查询用户名称
// 获取用户名
jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select u_name from t_user where u_id = ?", new Object[]{
id}, String.class);
// count
jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(u_id) from t_user", Long.class);
jdbcTemplate.query()
batch select
@GetMapping("batch")
public List<UserEntity> getBatchUser(@RequestParam(name = "ids") String[] ids) throws Exception {
String params = Stream.generate(() -> "?").limit(ids.length).collect(Collectors.joining(",", "", ""));
return jdbcTemplate.query("select * from t_user where u_id in (" + params + ")", ids, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(UserEntity.class));
}
jdbcTemplate.queryForList()
jdbcTemplate.queryForList("select * from t_user where u_id in (" + params + ")", ids);
queryForList 方法不能直接返回映射的实体对象;
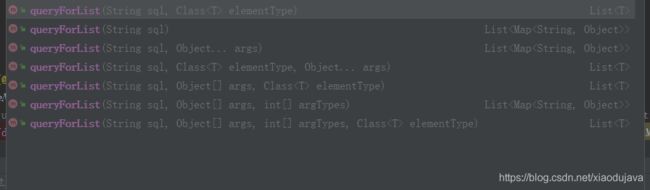
参数elementType 和.queryForObject 方法的requiredType 参数一样;是单列行结果映射,就是返回只有单列数值的时候使用, 直接映射为实体bean ;则也会报错
org.springframework.jdbc.IncorrectResultSetColumnCountException: Incorrect column count: expected 1, actual 5
#### jdbcTemplate.queryForMap()
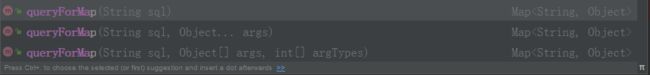
和queryForObject 方法基本一致;只不过返回的是个map; 不能映射为实体bean
@GetMapping({
"v2/{id}"})
public Map<String, Object> getUser2(@PathVariable String id) throws Exception {
return jdbcTemplate.queryForMap("select * from t_user where u_id = ?", new Object[]{
id}, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(UserEntity.class));
}
jdbcTemplate.execute()
batch delete
使用jdbcTemplate.execute(String sql, PreparedStatementCallback action) 方法;
execute 方法 是jdbcTemplate 的核心;所有的数据库操作方法都是调用的execute 方法;
@DeleteMapping("batch")
public void del(@RequestBody List<String> ids) throws Exception {
String collect = Stream.generate(() -> "?").limit(ids.size()).collect(Collectors.joining(",", "", ""));
jdbcTemplate.execute("delete from t_user where u_id in (" + collect + ")", new PreparedStatementCallback<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer doInPreparedStatement(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException, DataAccessException {
for (int i = 0; i < ids.size(); i++) {
ps.setString(i + 1, ids.get(i));
}
return ps.executeUpdate();
}
});
}
NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
namedParameterJdbcTemplate 和 jdbcTemplate 都是对数据库进行操作的工具;
namedParameterJdbcTemplate 维护了一个jdbcTemplate实例; 委托给jdbcTemplate 进行操作;
使用上 是对参数 占位符 ‘?’ 进行了改变; 使用 :param 这样的形式
update 示例
@PutMapping()
public void update(@RequestBody UserEntity userEntity) throws Exception {
Objects.requireNonNull(userEntity.getuId());
namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update("update t_user set u_name = :uName, password = :password where u_id = :uId", new ObjectMapper().convertValue(userEntity, Map.class));
}
其他操作和jdbctempalte 基本一致;
自动装配类
JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({
DataSource.class, JdbcTemplate.class })
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(JdbcProperties.class)
public class JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration
static class JdbcTemplateConfiguration {
private final DataSource dataSource;
private final JdbcProperties properties;
JdbcTemplateConfiguration(DataSource dataSource, JdbcProperties properties) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.properties = properties;
}
@Bean
@Primary
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(JdbcOperations.class)
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate() {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(this.dataSource);
JdbcProperties.Template template = this.properties.getTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setFetchSize(template.getFetchSize());
jdbcTemplate.setMaxRows(template.getMaxRows());
if (template.getQueryTimeout() != null) {
jdbcTemplate.setQueryTimeout((int) template.getQueryTimeout().getSeconds());
}
return jdbcTemplate;
}
}
@Configuration
@Import(JdbcTemplateConfiguration.class)
static class NamedParameterJdbcTemplateConfiguration {
@Bean
@Primary
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(JdbcTemplate.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(NamedParameterJdbcOperations.class)
public NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
return new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(jdbcTemplate);
}
}
}
总结
jdbcTemplate 相对是封装了一下jdbcConnection原生的操作;使用上还不是很便捷,更多的我们会选择mybatis jpa 这样更抽象的
下一节 Spring boot 数据库连接池
Spring boot 数据库连接池