java管理系统 修改密码_狂神说Java【SMBMS】——SMBMS超市订单管理系统(四) ——密码修改...
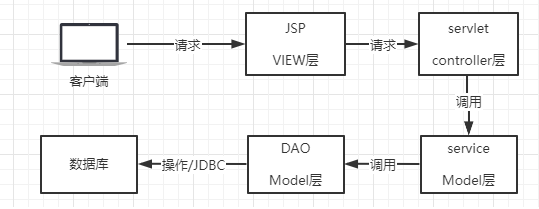
分析:很明显,要修改用户密码我们还是需要和数据库交互,那么就还是前面我们写登陆功能的代码编写步骤 —— DAO层、service层、servlet层,前端页面直接使用现成的,但是注意servlet中使用的地址和servlet的地址映射注意和前端页面保持一致
为什么要按照DAO层、service层、servlet层,JSP页面的顺序来编写呢?
原因在上图展示的很清楚,开发JSP需要填写servlet在服务器上的映射路径,开发servlet需要调用service中的方法完成业务逻辑,开发service需要调用Dao中对数据库的操作来操作数据库,而只有Dao中使用的JDBC我们是数据库厂商实现了的,所以我们可以直接使用;所以为了开发的完整性,我们就应该从Dao开始-->service-->servlet-->JSP
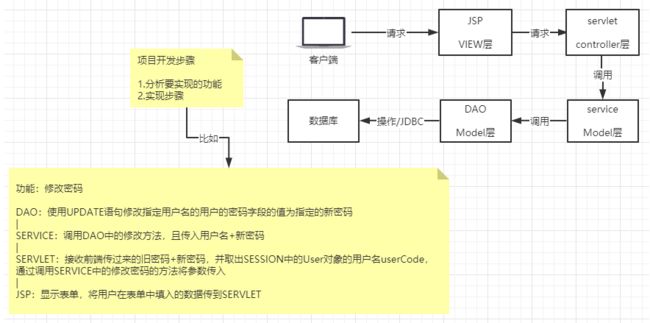
分析实现步骤/模块功能划分(很重要)
只有我们先想好了怎么做,然后再去编写代码才会快,且有条不紊,切忌看完要求之后马上开始写代码
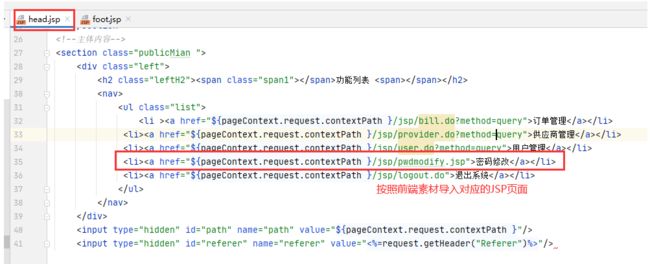
1.导入前端素材
2.Dao接口
package com.thhh.dao.user;
import com.thhh.pojo.User;
import java.sql.Connection;
public interface UserDao {
/**
* 得到要进行登陆的用户
* @param conn:数据库连接对象
* @param userCode:通过用户的用户名userCode查询用户数据
* @return
*/
public User getLoginUserInfo(Connection conn,String userCode);
/**
* 修改用户密码
* @param conn:数据库连接对象
* @param id:修改密码的用户的ID
* @param newPwd:新密码
* @return:影响行数
*/
public int updatePwd(Connection conn,String newPwd,int id);
}
只需要看方法2
3.Dao接口实现
package com.thhh.dao.user;
import com.thhh.dao.BaseDao;
import com.thhh.pojo.User;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
//1、获取要进行登陆的用户对象
@Override
public User getLoginUserInfo(Connection conn, String userCode) {
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
User user = null;
if (conn!=null){
String sql = "SELECT * FROM smbms_user WHERE userCode = ?";
Object[] params = {userCode};
rs = BaseDao.executeQuery(sql,params,conn,pstmt,rs);//调用项目搭建阶段准备的公共查询方法
try {
while (rs.next()){
user = new User();
user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
user.setUserCode(rs.getString("userCode"));
user.setUserName(rs.getString("userName"));
user.setUserPassword(rs.getString("userPassword"));
user.setGender(rs.getInt("gender"));
user.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday"));
user.setPhone(rs.getString("phone"));
user.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
user.setUserRole(rs.getInt("userRole"));
user.setCreatedBy(rs.getInt("createdBy"));
user.setCreationDate(rs.getTimestamp("creationDate"));
user.setModifyBy(rs.getInt("modifyBy"));
user.setModifyDate(rs.getTimestamp("modifyDate"));user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
user.setUserCode(rs.getString("userCode"));
user.setUserName(rs.getString("userName"));
user.setUserPassword(rs.getString("userPassword"));
user.setGender(rs.getInt("gender"));
user.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday"));
user.setPhone(rs.getString("phone"));
user.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
user.setUserRole(rs.getInt("userRole"));
user.setCreatedBy(rs.getInt("createdBy"));
user.setCreationDate(rs.getTimestamp("creationDate"));
user.setModifyBy(rs.getInt("modifyBy"));
user.setModifyDate(rs.getTimestamp("modifyDate"));
}
//关闭资源
BaseDao.close(null,pstmt,rs);//因为数据库的连接可能不只是这一个操作,所以我们不应该做完一件事就把数据库连接对象销毁,所以conn处传的null
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
return user;
}
//2、修改用户密码
@Override
public int updatePwd(Connection conn, String newPwd, int id) {
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
int rs = 0;
User user = null;
if (conn!=null){
String sql = "UPDATE smbms_user SET userPassword = ? WHERE id = ?";
Object[] params = {newPwd,id};//按照sql语句的占位符的顺序来传递数据,使用的时候需要注意
rs = BaseDao.executeUpdate(sql,params,conn,pstmt);
BaseDao.close(null,pstmt,null);//把这次使用的sql语句发送器关掉,连接不要关,service还可能有其他用
}
return rs;
}
}
只需要看方法2
4.service接口
package com.thhh.service.user;
import com.thhh.pojo.User;
import java.sql.Connection;
public interface UserService {
/**
* 1、获取登陆用户对象,对用户登陆身份进行验证
* @param userCode:用户账号
* @param userPassword:用户密码,注意,密码判断我们在service层进行;
* 在Dao层只是简单的操作数据库,没有其他的逻辑代码;在servlet层中只是接收和转发请求以及控制视图跳转
* 而对于业务层(service)就是用来实现业务逻辑代码的
* @return
*/
public User login(String userCode,String userPassword);
/**
* 2、根据用户ID修改用户密码
* @param newPwd:新密码
* @param id:用户ID
* @return
*/
public boolean updatePwd(String newPwd, int id);
}
只看方法2
5.service接口实现
package com.thhh.service.user;
/**
* 业务层主要就是编写业务代码,在编写业务代码的时候经常会调用数据库
* 所以在业务层中需要使用到我们一开始编写好的DAO的代码
*/
import com.thhh.dao.BaseDao;
import com.thhh.dao.user.UserDao;
import com.thhh.dao.user.UserDaoImpl;
import com.thhh.pojo.User;
import java.sql.Connection;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
private UserDao userDao;//业务层需要使用Dao,所以直接将Dao作为一个成员变量来使用
public UserServiceImpl() {
this.userDao = new UserDaoImpl();//在业务层被实例化的时候就让它得到Dao对象,后面就可以直接去用
}
/**
* 1、判断登陆用户的用户名+密码是否合法,并将用户对象返回
* @param userCode:用户账号
* @param userPassword:用户密码,注意,密码判断我们在service层进行;
* 在Dao层只是简单的操作数据库,没有其他的逻辑代码;在servlet层中只是接收和转发请求以及控制视图跳转
* 而对于业务层(service)就是用来实现业务逻辑代码的
* @return
*/
@Override
public User login(String userCode, String userPassword) {
Connection conn = null;
User user = null;
User error = null;
conn = BaseDao.getConnection();//获取数据库连接对象
//通过业务层调用Dao层
user = userDao.getLoginUserInfo(conn,userCode);//调用userDao中的获取用户信息的方法
BaseDao.close(conn,null,null);
if (user.getUserPassword().equals(userPassword)){
return user;
}
return error;
}
/**
* 2、通过已经登陆用户的ID修改新密码,并将数据库中受影响的行数返回
* @param newPwd:新密码
* @param id:用户ID
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean updatePwd(String newPwd, int id) {
Connection conn = null;
int rs = 0;
boolean flag = false;
conn = BaseDao.getConnection();//获取数据库连接对象
//通过业务层调用Dao层
if (userDao.updatePwd(conn,newPwd,id)>0){//数据库修改成功
flag = true;
}
BaseDao.close(conn,null,null);
return flag;
}
}
只看方法2
6.servlet编写
package com.thhh.servlet.user;
import com.mysql.jdbc.StringUtils;
import com.thhh.pojo.User;
import com.thhh.service.user.UserService;
import com.thhh.service.user.UserServiceImpl;
import com.thhh.utils.Constants;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
//实现servlet复用
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
boolean flag = false;
Object user = req.getSession().getAttribute(Constants.USER_SESSION);
String newpassword = req.getParameter("newpassword");
if (user!=null && !StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(newpassword)){//获取到了这个用户对象且获取到的新密码不为空
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
flag = userService.updatePwd(newpassword,((User)user).getId());//servlet调用业务层
if (flag){//修改成功
req.setAttribute("message","密码修改成功!请使用新密码重新登陆");
//移除用户的session,利用过滤器阻止用户再进行操作,直接跳转error.jsp页面
req.getSession().removeAttribute(Constants.USER_SESSION);
}else{
req.setAttribute("message","密码修改失败");
}
}else {
//用户可以进行密码修改,则user一定不是null,所以跳入这个分支的原因一定是newpassword = NULL
req.setAttribute("message","密码设置有误,请重新输入!");
}
//无论是修改成功还是失败,都重定向到密码修改页面,就是在刷新页面,否则我们设置在req中的message属性不会被前端读到
req.getRequestDispatcher("pwdmodify.jsp").forward(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
7.注册servlet
UserServlet
com.thhh.servlet.user.UserServlet
UserServlet
/jsp/user.do
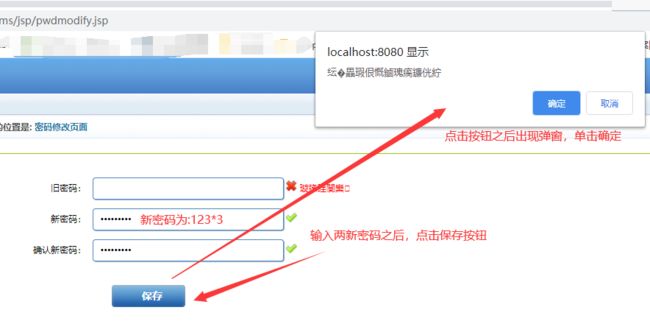
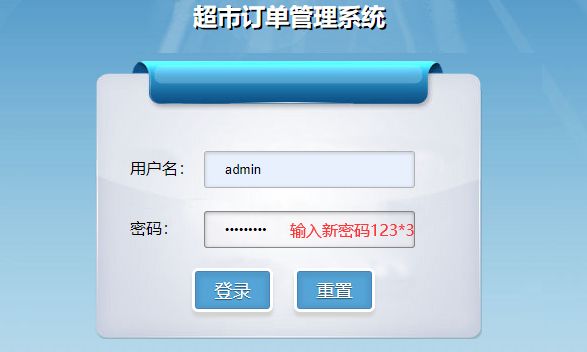
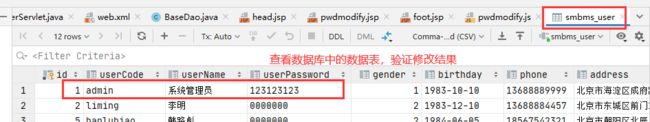
8.测试
bug1:
//1、在编写servlet的时候,要判断前端传过来的新密码是否为空,这里ZB用了一个工具类,但是这个工具类是isNullOrEmpty,即它的作用判断"是空",所以使用的时候注意在前面加上一个"!"
//或者我们就是要常见的方法:newpassword!=null&&newpassword.length!=0
if (user!=null && !StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(newpassword))
bug2:
//2、在编写BaseDao即基本公共数据库操作方法的时候,设置PreparedStatement对象中sql占位符的值时要注意
//PreparedStatement的占位符index从1开始,而数组的下标从0开始,所以我们使用的i=1,但是要注意控制循环次数的时候使用的是params.length,所以我们需要取"=",否则数组中的参数是取不完的,取不完就会出现SQL错误
for (int i=1;i<= params.length;i++){//循环遍历参数数组,并将参数设入SQL中
pstmt.setObject(i,params[i-1]);//注意:数组的index从0开始,而PreparedStatement中设置占位符的值的index从1开始
}
bug3:
//前端页面上,编写的时候要求输入旧密码,但是实际测试的时候输入旧密码有BUG,我们直接不使用输入旧密码,使用新密码+重复新密码输入框来修改密码
//但是前端使用的JS控制了提交表单的按钮,即需要3个输入框输入都满足要求的时候才能提交表单数据,所以我们需要把判断旧密码输入框的判断语句注释了
//这样才能只通过新密码+重复新密码实现密码修改
saveBtn.on("click",function(){
oldpassword.blur();
newpassword.blur();
rnewpassword.blur();
// oldpassword.attr("validateStatus") == "true"
// &&
if( newpassword.attr("validateStatus") == "true"
&& rnewpassword.attr("validateStatus") == "true"){
if(confirm("确定要修改密码?")){
$("#userForm").submit();
}
}
});
9.优化servlet代码,实现servlet复用
通过测试,功能完全相同,且修改密码正确!