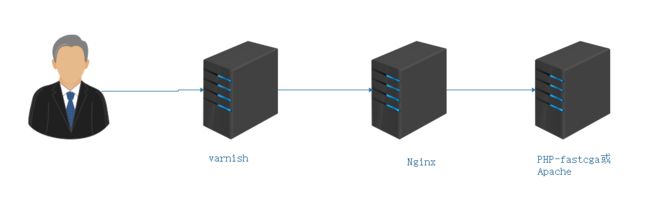
当网站访问量很大时,会导致后端处理程序响应超时而导致一些问题。所以运用一些手段去尽量避免这些问题。那么久用到了varnish。
varnish严格来说是可以当作一个代理服务器的软件,直接将HTTP请求转发到php-cgi,然后交给php处理,varnish会获取经过php处理后的数据,最后返回给浏览器
但是现在我们一般情况下不会使用php-fastcgi,那么我们不能直接将varnish与php组合,因为php-fpm的交互方式为socket,而不再是监听本机的9000端口
所以我们必须找一个的媒介,连接varnish和php-fpm,nginx可以扮演这个媒介。
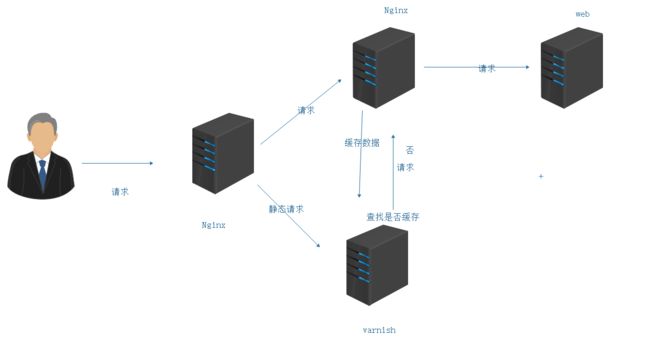
后来发现,varnish处理http请求不如nginx那么高效。所以对结构做出了改变。
模仿这个结构可以做架构
事先需要准备nginx,varnish,php-fpm,php这些软件,安装内容我就不多说了。测试内容可以用httpd服务提供也可以。
这里直接说主要配置
配置
Nginx
vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
http {
## proxy global setting
proxy_connect_timeout 5;
proxy_read_timeout 60;
proxy_send_timeout 5;
proxy_buffer_size 16k;
proxy_buffers 4 64k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 128k;
##END
## cache proxy pass
upstream cache {
server 127.0.0.1:6081;
}
##END
## php proxy pass
upstream php {
server 127.0.0.1:8080;
}
##END
# Basic Settings
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
server_tokens off;
#depend on nginx-extras 需要安装nginx-extras才能定义Server
more_set_headers 'Server: Bird-shark';
# server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
# server_name_in_redirect off;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
##
# SSL Settings
##
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; # Dropping SSLv3, ref: POODLE
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
##
# Logging Settings
##
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
##
# Gzip Settings
##
gzip on;
gzip_disable "msie6";
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_buffers 16 8k;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;
##
# Virtual Host Configs
##
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
}
vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
server_name localhost;
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|png|css|js|flv|ico|swf|html)$ {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass http://cache;
}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
location / {
proxy_pass http://php;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass_header Server;
}
}
server {
listen 8080;
root /var/www/html;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
location / {
if (!-e $request_filename){
rewrite ^(.*)$ /index.php?s=$1 last;
break;
}
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location ~ ^(.+\.php)(.*)$ {
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php5-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
fastcgi_buffers 8 128k;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
varnish
vim /etc/varnish/default.vcl
vcl 4.0;
# Default backend definition. Set this to point to your content server.
backend default {
.host = "127.0.0.1";
.port = "8080";
}
acl purgers {
"localhost";
#"103.22.188.169";
}
sub vcl_recv {
# Happens before we check if we have this in cache already.
#
# Typically you clean up the request here, removing cookies you don't need,
# rewriting the request, etc.
if (req.restarts == 0) {
unset req.http.X-Purger;
}
if(req.method == "PURGE"){
if(!client.ip ~ purgers){
return(synth(405,"Not Allowed."));
}
return (purge);
#ban("obj.http.x-url ~ " + req.url);
}
if(req.method == "GET" && req.url ~ "\.(js|css|jpg|png|gif|swf|jpeg|ico)$"){
unset req.http.cookie;
}
}
sub vcl_backend_response {
#set beresp.http.x-url = bereq.url;
if (bereq.url ~ "\.(js|css|jpg|png|gif|swf|jpeg|ico)$") {
unset beresp.http.Cache-Control;
unset beresp.http.set-cookie;
set beresp.ttl = 10h;
set beresp.http.Cache-Control = "max-age=36000";
set beresp.do_gzip = true;
}
if(bereq.url ~ "\.html$"){
set beresp.ttl = 10m;
set beresp.do_gzip = true;
unset beresp.http.Cache-Control;
unset beresp.http.Pragma;
set beresp.http.Cache-Control = "max-age=600";
unset beresp.http.Expires;
}
}
sub vcl_deliver {
if (obj.hits > 0) {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT from " + req.http.host;
#set resp.http.X-Cache-Hits = obj.hits;
} else {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "MISS from " + req.http.host;
}
if (req.http.X-Purger) {
set resp.http.X-Purger = req.http.X-Purger;
}
unset resp.http.X-Powered-By;
unset resp.http.Server;
unset resp.http.Via;
unset resp.http.X-Varnish;
unset resp.http.Age;
#unset resp.http.x-url; # Optional
}
sub vcl_hit {
if (req.method == "PURGE") {
return (synth(200,"Purged."));
}
}
sub vcl_miss {
if (req.method == "PURGE") {
return (synth(404,"Purged."));
}
}
sub vcl_purge {
if (req.method == "PURGE") {
#set req.http.X-Purge = "Purged";
ban("req.url ~ "+req.url);
#return (restart);
set req.method = "GET";
set req.http.X-Purger = "Purged";
return (restart);
}
}
sub vcl_hash {
hash_data(req.url);
if (req.http.host) {
hash_data(req.http.host);
} else {
hash_data(server.ip);
}
if (req.http.cookie) {
hash_data(req.http.cookie);
}
if (req.http.Accept-Encoding ~ "gzip") {
hash_data("gzip");
} elseif (req.http.Accept-Encoding ~ "deflate") {
hash_data("deflate");
}
}
测试&分析
在不使用缓存模块的情况下
vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
#location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|png|css|js|flv|ico|swf|html)$ {
# proxy_set_header Host $host;
# proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
# proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
# proxy_pass http://cache;
#}
也就是把静态的跳转关闭。
如果要是把注释去掉就意味着可以跳转。当系统拥有缓存时,把源文件删除,服务器仍然可以相应其请求,除非重启或者将缓存清除但是对PURGE显然是不对外公开的,以下是服务器端用curl清除varnish缓存的命令。
curl -v -k -X PURGE http://localhost/Public/Home/css/t_navigation.css
varnish是一款内存类型的缓存软件,而非nginx扩展proxy_cache那种物理缓存类型的软件,存取速度比较快,但是也有弊端,重启后所有缓存得重写。