第二章:Java基本语法
目录:
1. 关键字 & 标识符
2. 变量
- 基本数据类型
- 基本数据类型转换
3. 运算符
4. 程序流程控制
- 4.1 分之结构
- 4.2 循环结构
- 4.3 break&continue
5. 数组
- 二维数组
- 数组的常见异常
- 数组的常用的算法问题
关键字 & 标识符
关键字
关键字的定义和特点:
定义:被Java语言赋予了特殊含义,用做专门用途的字符串(单词)
特点:关键字中所有字母都为小写
用于定义数据类型的关键字:
class 、interface、enum、byte、short、int、long、float、double、char、boolean、void
用于定义数据类型值的关键字:
true、false、null
用于定义流程控制的关键字:
if、else、switch、case、default、while、do、for、break、continue、return
用于定义访问权限修饰符的关键字:
private、protected、public
用于定义类,函数,变量修饰符的关键字:
abstract、final、static、synchronized
用于定义类与类之间关系的关键字:
extends、implements
用于定义建立实例及引用实例,判断实例的关键字:
new、this、super、instanceof
用于异常处理的关键字:
try、catch、finally、throw
用于包的关键字:
package、import
其他修饰符关键字:
native、strictfp、transient、volatile
保留字
Java保留字:现有Java版本尚未使用,但以后版本可能会作为关键字使用。自己命名标识符时要避免使用这些保留字
byValue、cast、future、generic、inner、operator、outer、rest、var、goto、const
标识符
Java 对各种变量、方法和类等要素命名时使用的字符系列成为标识符。
凡是自己可以起名字的地方都叫标识符。
- 定义合法标识符规则:
- 由26个英文字母大小写,0-9,_或$组成
- 数字不可以开头
- 不可以使用关键字和保留字,但能包含关键字和保留字
- Java中严格区分大小写,长度无限制
- 标识符不能包含空格
注意:在起名字时,为了提高阅读性,要尽量有意义,“见名知意”。
Java中的名称命名规范:(不遵守,也不会出现编译的错误)
包名:多单词组成时所有字母都小写:xxxyyyzzz
类名、接口名:多单词组成时,所有单词的首字母大写:XxxYyyZzz
变量名、方法名:多单词组成时,第一个单词首字母小写,第二个单词开始每个单词首字母大写:xxxYyyZzz
常量名:所有字母都大写。多单词时每个单词用下划线连接:XXX_YYY_ZZZ
变量
java中变量按照数据类型来分类:基本数据类型 vs 引用数据类型(数组 类 接口)
基本数据类型:整型:byte(8 bit) short int(默认类型) long
浮点型:float double (默认类型)
字符型:char(‘ ’)
布尔类型: boolean(只能取值为true 或false,不能取null)补充:按照在类中存在的位置的不同:成员变量 vs 局部变量
进制(了解)
十进制 二进制 八进制 十六进制
二进制:计算机底层都是用二进制来存储、运算。- 二进制 与十进制之间的转换。
- 二进制在底层存储:正数、负数都是以补码的形式存储的。(原码、反码、补码)
- 四种进制间的转换
变量的运算:
- ①自动类型转换:容量小的数据类型自动转换为容量大的数据类型。
short s = 12;
int i = s + 2;
注意:byte short char之间做运算,结果为int型! - ②强制类型转换:是①的逆过程。使用“()”实现强转。
- ①自动类型转换:容量小的数据类型自动转换为容量大的数据类型。
运算符
运算符是一种特殊的符号,用以表示数据的运算、赋值和比较等。
算术运算符:
+ - + - * / % ++ – +
注意:1) /: int i = 12; i = i / 5;
2) %:最后的符号只跟被模数相同
3)前++:先+1,后运算 后++:先运算,后+1
4)+:String字符串与其他数据类型只能做连接运算,且结果为String类型。sysout(‘’ + ‘\t’ + ‘‘); vs sysout(“” + ‘\t’ + ‘‘);
赋值运算符:
= += -= *= /= %=
int i= 12;
i = i * 5;
i *= 5;//与上一行代码同样的意思
【特别地】
short s = 10;
s = s + 5;//报编译的异常
s = (short)(s + 5);
s += 5;//s = s + 5,但是结果不会改变s的数据类型。
比较运算符(关系运算符):
== > < >= <= instanceof
【注意】区分== 与 = 区别。
进行比较运算操作以后,返回一个boolean类型的值
4>=3 表达的是4 > 3或者 4 = 3.结果是true。
if(i > 1 && i < 10){ }
不能写为:if(1 < i < 10){}
逻辑运算符(运算符的两端是boolean值):
& && | || ^ !
【注意】区分 & 与 && 的区别,以及 | 与 || 的区别
我们使用的时候,选择&& , ||
位运算符(两端是数值类型的数据):
<< >> >>> & | ^ ~
【例子】1.如何交换m = 12和n = 5的值
2.将60转换为十六进制输出。
三元运算符:
(条件表达式)? 表达式1 : 表达式2;
1)既然是运算符,一定会返回一个结果,并且结果的数据类型与表达式1,2的类型一致
2)表达式1与表达式2 的数据类型一致。
3)使用三元运算符的,一定可以转换为if-else。反之不一定成立。
例子:获取两个数的较大值;获取三个数的最大值。
程序流程控制
4.1 顺序结构
程序从上到下逐行地执行,中间没有任何判断和跳转。
4.2 分支结构
根据条件,选择性地执行某段代码。
有 if…else 和 switch…case两种分支语句。
if-else语句
![]()
例如:
实现:
/*
score>=90 等级为:A
70<=score<90 等级为:B
60<=score<70 等级为C
score<60 等级为:D
/*
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestScore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入学生成绩:");
int score = s.nextInt();
char level;
if (score >= 90) {
level = 'A';
System.out.println("等级为:"+level);
}
if (score >= 70 && score < 90) {
level = 'B';
System.out.println("等级为:"+level);
}
if (score >= 60 && score < 70) {
level = 'C';
System.out.println("等级为:"+level);
}
if (score < 60) {
level = 'D';
System.out.println("等级为:"+level);
}
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestScore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入学生成绩:");
int score = s.nextInt();
char level;
if (score > 90) {
level = 'A';
} else if (score >= 70) {
level = 'B';
} else if (score >= 60) {
level = 'C';
} else {
level = 'D';
}
System.out.println("等级为:" + level);
}
}switch-case语句
![]()
- 没有写 break; 语句,则在找到对应case语句后,还会继续向下执行。
- 其中变量可以是哪些类型? 可以是char,byte,short,int,枚举,String(jdk1.7),double、float等不可以。
- case 条件:其中条件只能是值,不能是取值范围。
4.3 循环结构
根据循环条件,重复性的执行某段代码。
有while、do…while、for三种循环语句。
注:JDK1.5提供了 foreach 循环,方便的遍历集合、数组元素。
①初始化条件 ②循环条件 ③迭代条件 ④循环体
for循环
- 格式:
for(①;②;③){
//④
}- 执行过程:①-②-④-③-②-④-③-….-④-③-②
while循环
格式:
①
while(②){
④
③
}
do-while循环
格式:
do{
④
③
}while(②)
另:
无限循环:
for( ; ; ){}
或者
while(true){
}
说明:一般情况下,在无限循环内部要有程序终止的语句,使用break实现,若没有,那就是死循环。
public class TestFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//上半部分
for(int i = 0;i < 5; i++){
for(int k = 0; k < 4-i; k++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int j = 0;j < i+1; j++){
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
//下半部分
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
for(int k =0;k < i+1; k++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int j = 0; j < 4-i; j++){
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}2)实现九九乘法表
![]()
public class TestJiuJiu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 1;i <= 9; i++){
//一共有九行
for(int j = 1;j <= i; j++){
//每行有 i 个等式
System.out.print(i + "*" + j + "=" + i*j + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}break和continue关键字
break:使用在switch-case中或者循环中
如果使用在循环中,表示:结束“当前”循环continue:使用在循环结构中,表示:结束“当次”循环
关于break和continue中标签的使用。
public class TestBreakContinue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//break和continue中标签的使用
label:for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j++) {
if(j % 4 == 0){
//break;
//continue;
continue label;
}
System.out.print(j);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}数组
数组:相同数据类型的数据的组合。
1.一维数组
如:
int score = 72;
int score = 90;
int score = 58;
使用数组:
1. 静态初始化:在声明并初始化与给数组相应的元素赋值操作同时进行。
int[] score1 = new int[]{72, 90, 58};//int[] score1 = {72, 90, 58};
2. 动态初始化:在声明并初始化与给数组相应的元素赋值操作分开进行。
int score2 = new int[3];
score[0] = 72;
score[1] = 90;
score[2] = 58;注:数组长度一旦创建后数组长度不可变。
声明数组的错误写法:
1)String names = new String[5]{“AA”,”BB”,”CC”};
2)int a[10];
3)int i = new int[];
另外
1. 对于byte、short、int、long数组元素值默认为0
2. 对于float、double数组元素值默认为0.0
3. 对于char数组元素值默认为空格
4. 对于boolean数组元素值默认为false
5. 对于引用类型的变量构成的数组而言,默认初始化为null,以String为例
2.二维数组
- 静态初始化:
int[][] scores;
scores = new int[][]{
{
1, 2,3},{
3, 4, 5},{
6}};- 动态初始化:
String[][] names;
names = new String[3][2];//动态初始化之一
或者
names = new String[4][];//动态初始化之二(不指定二维的长度)
names[0] = new String[5];
names[1] = new String[4];
namse[2] = new String[7];错误的初始化:
names = new String[][];
names = new String[][5];
都是未指定第一维长度。
Q:二维数组如何遍历?
for(int m = 0;m < score.length;m++ ){
for(int n = 0;n < score[m].length;n++){
System.out.println(score[m][n]);
}
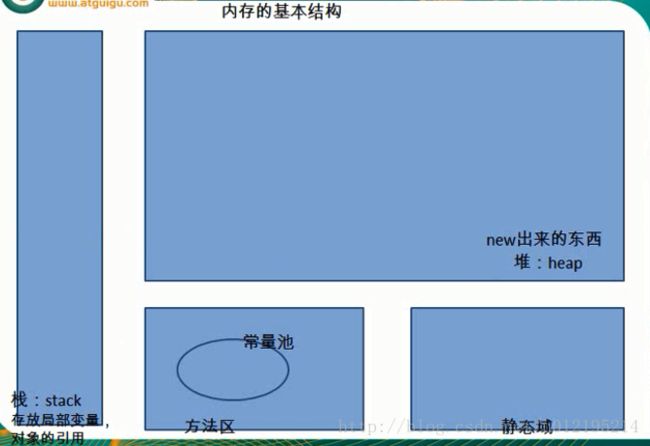
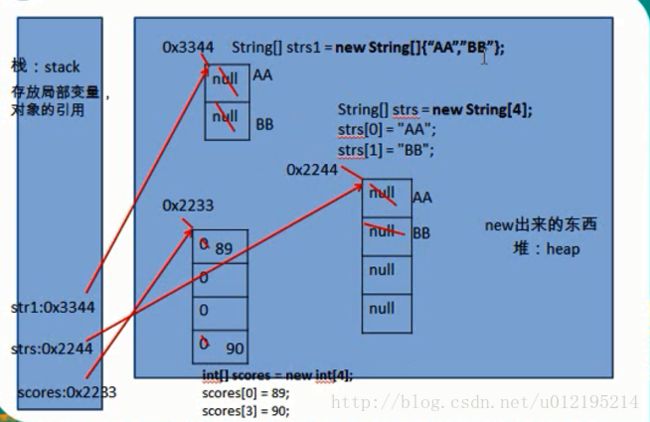
}内存结构
一维数组练习:
/*
从键盘读入学生成绩,找出最高分,并输出学生成绩。
成绩>=最高分-10 等级为A
成绩>=最高分-20 等级为B
成绩>=最高分-30 等级为C
其余 等级为D
提示:先读入学生人数,根据人数创建int数组,存放学生成绩
*/
public class TestStudentScore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1,创建Scanner的对象,并从键盘获取学生的个数n
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入学生的个数:");
int count = s.nextInt();// count记录学生的个数
// 2,根据输入的学生个数n,创建一个长度为n的int型数组
int[] scores = new int[count];
int maxScore = 0;
// 3,依次从键盘获取n个学生的成绩,并赋给相应的的数组元素,并获取n个学生中的最高分
System.out.println("请输入" + count + "个数学生成绩:");
for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {
int score = s.nextInt();// 依次从键盘获取学生的成绩
scores[i] = score;
if (scores[i] > maxScore) {
maxScore = scores[i];
}
}
System.out.println("最高分为:" + maxScore);
// 4,遍历学生成绩的数组,并根据学生成绩与最高分的差值,赋予相应的等级,并输出
for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {
char level;
if (scores[i] >= maxScore - 10) {
level = 'A';
} else if (scores[i] >= maxScore - 20) {
level = 'B';
} else if (scores[i] >= maxScore - 30) {
level = 'C';
} else {
level = 'D';
}
System.out.println("Student " + (i + 1) + " score is " + scores[i]
+ " level is " + level);
}
}
}
数组的常见异常
//1.数组下标越界的异常:java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int[] i = new int[10];
// i[0] = 90;
// i[10] = 99;
// for(int m = 0;m <= i.length;m++){
// System.out.println(i[m]);
// }
//2.空指针的异常:NullPointerException
//第一种:
// boolean[] b = new boolean[3];
// b = null;
// System.out.println(b[0]);
//第二种:
// String[] str = new String[4];
// //str[3] = new String("AA");//str[3] = "AA";
// System.out.println(str[3].toString());
//第三种:
int[][] j = new int[3][];
j[2][0] = 12;