SpringBoot Http getMapping、postMaping等详细解析
背景
一直以来对http各种请求controller层该如何处理,总是弄不大明白。于是决定自己写一些测试来总结一下。
项目环境:springBoot、swagger。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2artifactId>
<version>2.9.2version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>swagger-modelsartifactId>
<groupId>io.swaggergroupId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-uiartifactId>
<version>2.9.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.swaggergroupId>
<artifactId>swagger-modelsartifactId>
<version>1.5.24version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>swagger-annotationsartifactId>
<groupId>io.swaggergroupId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
总结的内容:
方法上的注解:@postMapping、@GetMapping、@PutMapping、@DeleteMapping、@PatchMapping(部分修改时使用,但基本不用这个)。
参数上的注解:@PathVariable、@RequestBody、@RequestPart。
决定从实际需求出发来说明用法。
参数上的注解
@PathVariable
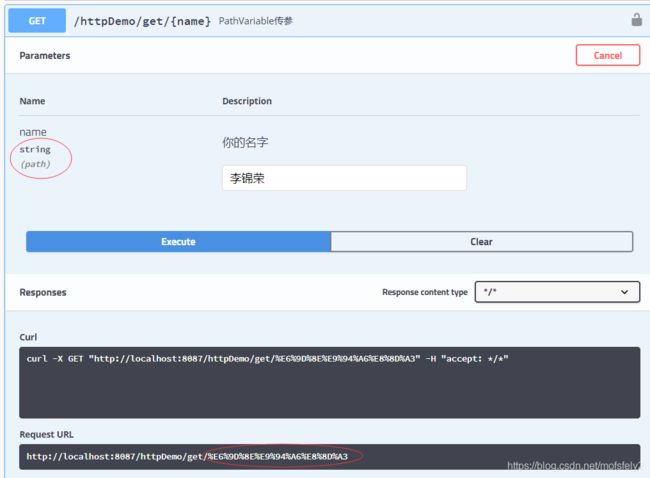
中文翻译过来就是路径参数。@PathVariable 注解可以将 URL 中占位符参数绑定到控制器处理方法的入参中;主要用于接收http://host:port/path/{参数值}数据,实现了实现了RestFul的风格,将中文参数转成16进制。
/**
* 主要用于接收http://host:port/path/{参数值}数据
* 实现了RestFul的风格
* 中文参数会转成16进制
* @param name
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation("PathVariable传参")
@GetMapping("/get/{name}")
public ResponseVo<String> pathVariable(@ApiParam(value = "你的名字") @PathVariable String name ){
return ResponseFactory.success(name);
}
注:参数下显示的是“path”;李锦荣转成了%E6%9D%8E%E9%94%A6%E8%8D%A3;PathVariable的优点除了实现了restFul风格,暂时不知道有什么好处(如有知道的评论区告诉我,谢谢)
猜想:如果参数中存在特殊字符,比方/是否会影响?
参数如数“/李锦荣”,返回错误信息—HTTP Status 400 – Bad Request:
<html lang="en"><head><title>HTTP Status 400 – Bad Requesttitle><style type="text/css">body {
font-family:Tahoma,Arial,sans-serif;} h1, h2, h3, b {
color:white;background-color:#525D76;} h1 {
font-size:22px;} h2 {
font-size:16px;} h3 {
font-size:14px;} p {
font-size:12px;} a {
color:black;} .line {
height:1px;background-color:#525D76;border:none;}style>head><body><h1>HTTP Status 400 – Bad Requesth1>body>html>
证明@pathVariable不适合传入特殊字符,如果一定要用,可以参考文章“关于@PathVariable你需要知道的事”。地址:https://www.jianshu.com/p/1a1384b9cd34
猜想:能否实现对参数的非空校验?
1.尝试加入@PathVariable(required = true)
controller层:
/**
* PathVariable能否实现对参数的非空校验
* 1.尝试加入@PathVariable(required = true)
* @param name
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation("PathVariable传参")
@GetMapping("/get/{name}/1")
public ResponseVo<String> pathVariable2(
@ApiParam(value = "你的名字") @PathVariable(required = true) String name ){
return ResponseFactory.success(name);
}
swagger不输入参数,点击执行
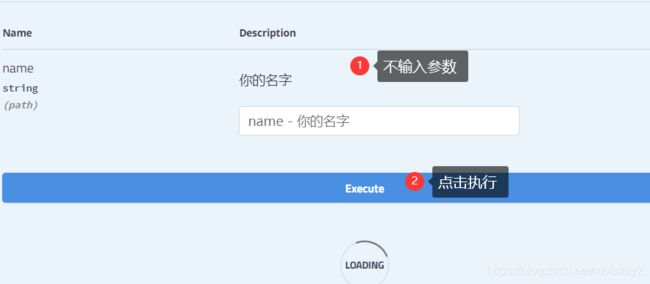
成功进入方法内,参数为undefined,说明@PathVariable(required = true)起不到校验作用
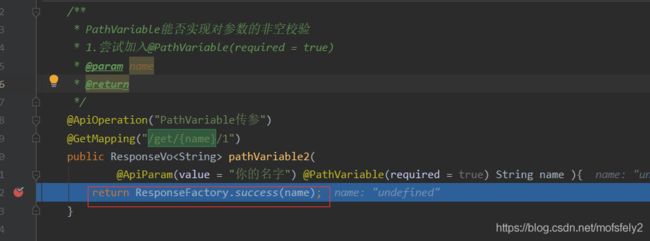
2.尝试加入@NotNull
/**
* PathVariable能否实现对参数的非空校验
* 2.尝试加入@NotNull
* @param name
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation("PathVariable传参")
@GetMapping("/get/{name}/2")
public ResponseVo<String> pathVariable3(
@ApiParam(value = "你的名字") @PathVariable(required = true) @NotNull String name ){
return ResponseFactory.success(name);
}
结果。仍然是undefined:
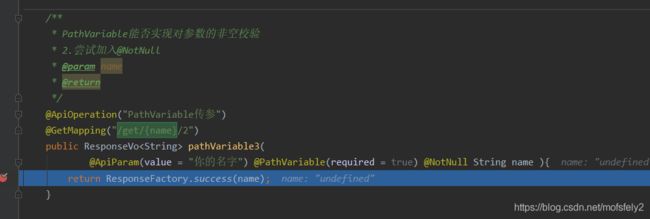
加入@NotEmpty ——无效;加入@Length(max = 3)——有效
结论:以上测试得出的结论,@PathVariable无法对参数进行非空校验。
RequestParam
主要用于接收http://host:port/path?参数名=参数值数据(与@PathVariable格式不同)
@RequestParam注解的参数在url中传递。
@RequestParam适用于注解int和string,因为前端传给后台,最终就这两个类型。也可以理解为只注解键值对的参数格式。
@RequestParam不适用注解实体(DTO等)。
/**
* 主要用于接收http://host:port/path?参数名=参数值数据(与@PathVariable格式不同)
* 适用于注解int和string,因为前端传给后台,最终就这两个类型
* 不适用注解实体(DTO等)
* @param name
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation("RequestParam传参")
@GetMapping("/get/requestParam")
public ResponseVo<String> requestParam(
@ApiParam(value = "你的名字") @RequestParam(required = true) String name ){
return ResponseFactory.success(name);
}
swagger中显示:
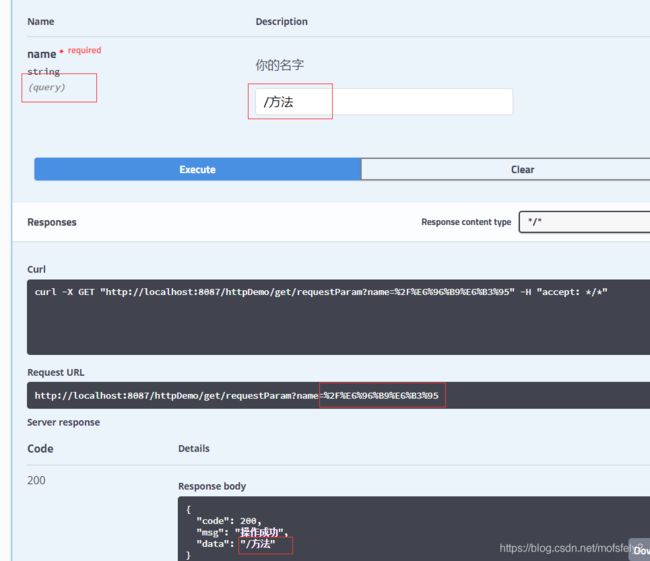
注:这里可以看到RequestParam显示的是query,而且没有特殊字符的问题。@RequestParam(required = true)默认就是true,会校验非空。就不演示了,应该都知道的。
验证@RequestParam不适用注解实体(DTO等)
/**
* RequestParam注解DTO实体会报String无法转为DTO的错误
* @param dogDTO
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation("RequestParam传参")
@GetMapping("/get/requestParam1")
public ResponseVo<String> requestParam1(
@ApiParam(value = "你的名字") @RequestParam DogDTO dogDTO ){
return ResponseFactory.success(dogDTO.getDogName());
}
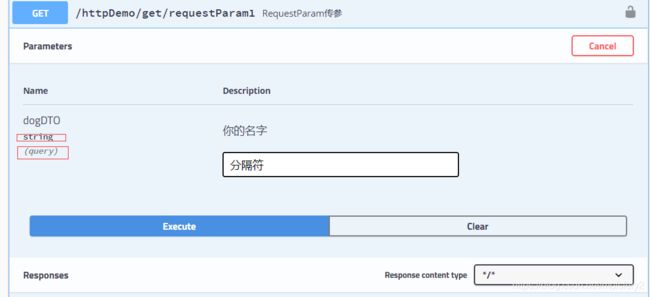
执行后报错:Cannot convert value of type ‘java.lang.String’ to required type ‘com.aliyu.entity.demo.dto.DogDTO’:
注:从swagger图中看到 参数类型是string 而不是对应的dto实体。
@RequestBody
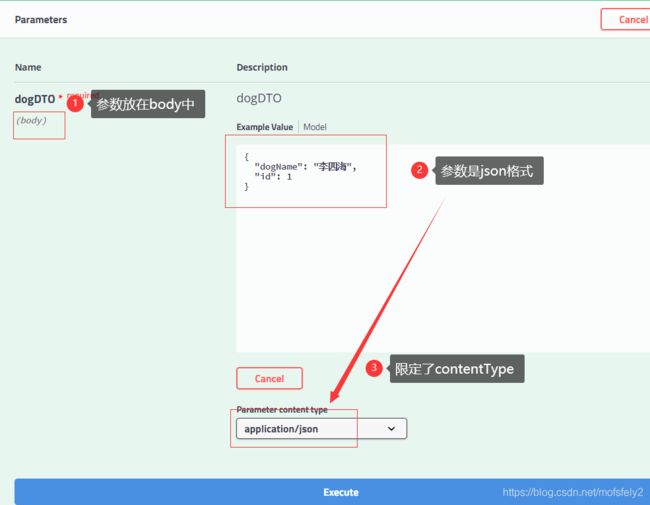
1.参数放在body中,默认前端提交的Content-Type就是application/json;
2.Content-Type为application/x-www-form-urlencoded,正常情况不支持。当然有别的解决方式,但要需要加东西。参考地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_32836221/article/details/112111893 ;
3.其他格式包括application/json, application/xml等。这些格式的数据必须使用@RequestBody来处理;
4.不能处理multipart/form-data,处理它的是@RequestPart,待会讲到。
简单来说就是,如果参数是json就用@RequestBody;如果用了@RequestBody,就规定了参数是json。
@ApiOperation("post请求-DTO实体-RequestBody传参数")
@PostMapping("/post/requestBody")
public ResponseVo requestBody(@RequestBody DogDTO dogDTO) {
return ResponseFactory.success(dogDTO.getDogName());
}
证明Content-Type为application/x-www-form-urlencoded正常情况不支持
要证明这个,涉及到一个知识点,如何限制前端传入参数的contentType。
/**
* 反例:Content-Type为application/x-www-form-urlencoded,正常情况不支持
* 报错Content type 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8' not supported
* consumes设置前端传入的参数的contentType
* produces设置返回的contentType
* @param dogDTO
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation("RequestBody接收contentType为application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
@PostMapping(value="/post/requestBody2", consumes = {
MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED_VALUE} )
public ResponseVo requestBody2(@RequestBody DogDTO dogDTO) {
return ResponseFactory.success(dogDTO.getDogName());
}
注:postMapper中有两个配置,一个consumes设置前端传入的参数的contentType,produces设置返回的contentType。返回的默认就是json不需要设置。
接下来看swagger中的展示:
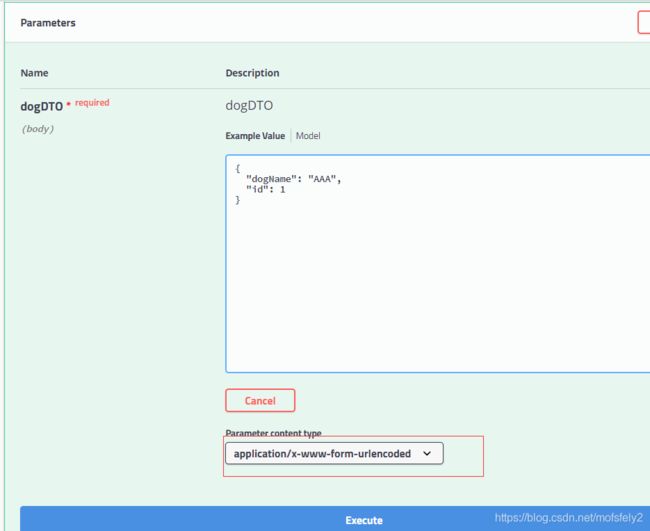
成功设置了contentType为application/x-www-form-urlencoded,请求看看:
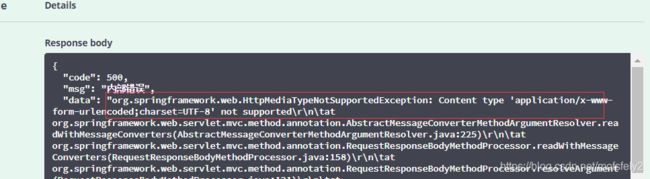
报错Content type ‘application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8’ not supported。
证明不能处理multipart/form-data
/**
* 反例子
* 证明RequestBody不支持接收contentType为multipart/form-data
* @param dogDTO
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation("RequestBody接收contentType为multipart/form-data")
@PostMapping(value = "/post/requestBody3",consumes = {
MediaType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA_VALUE})
public ResponseVo requestBody3(@RequestBody DogDTO dogDTO) {
return ResponseFactory.success(dogDTO.getDogName());
}
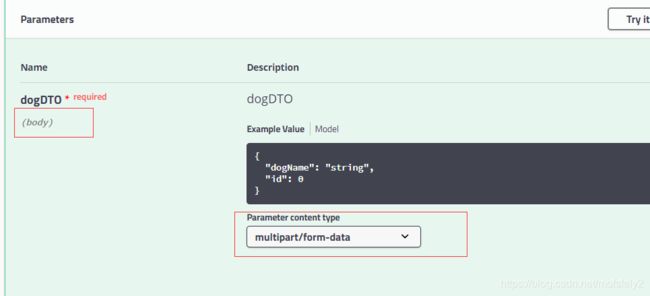
成功设置了contentType为multipart/form-data,请求看看:
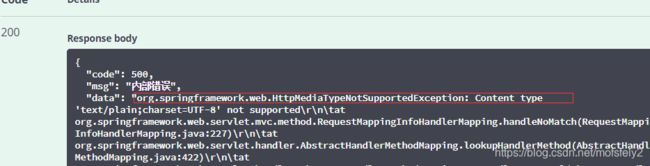
@RequestPart
这个注解设定contentType为multipart/form-data, 适用于文件上传
同时上传文件和输入json参数的话,也必须用这个。但是@RequestPart用于注解json参数时正常情况会报错。
注解int或string、注解文件:
/**
* 这个注解设定contentType为multipart/form-data,适用于文件上传
* @param dogName
* @param file
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation("RequestPart上传文件,@RequestPart注解string或int参数")
@PostMapping("/post/requestPart")
public ResponseVo requestPart(@RequestPart String dogName,
@RequestPart MultipartFile file) {
return ResponseFactory.success(dogName);
}
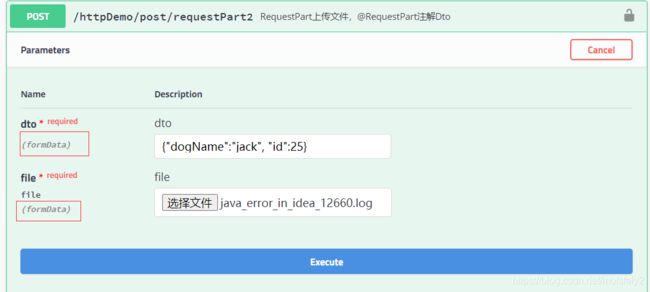
@RequestPart对应显示的是formData:
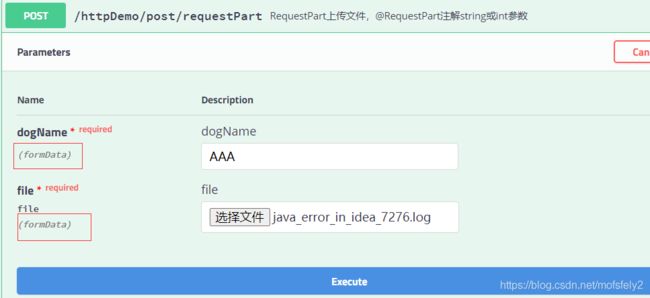
contentType为multipart/form-data:
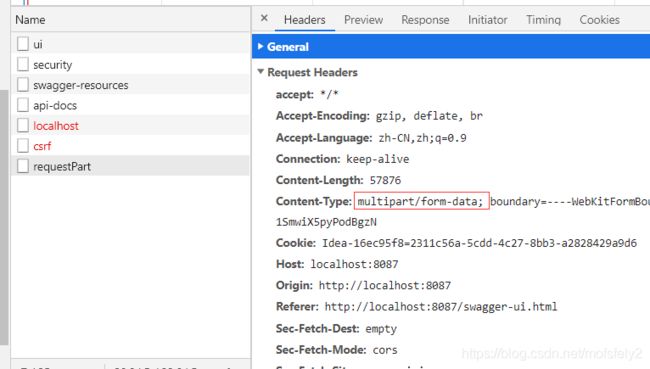
点击执行后,后端报错:
com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonParseException: Unrecognized token ‘AAA’: was expecting (JSON String, Number, Array, Object or token ‘null’, ‘true’ or ‘false’)
at [Source: (PushbackInputStream); line: 1, column: 4]
意思是无法解析此参数类型,它支持的类型是“JSON String, Number, Array, Object or token ‘null’, ‘true’ or ‘false’”。也就是controller层的@RequestPart String dogName不能用 string,还是得用DTO。
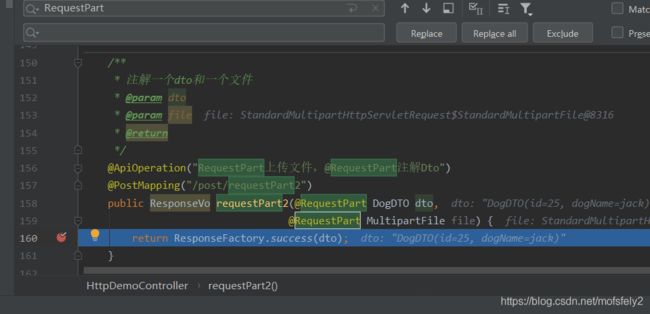
如果注解的参数是DTO加文件
/**
* 注解一个dto和一个文件
* @param dto
* @param file
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation("RequestPart上传文件,@RequestPart注解string或int参数")
@PostMapping("/post/requestPart2")
public ResponseVo requestPart2(@RequestPart DogDTO dto,
@RequestPart MultipartFile file) {
return ResponseFactory.success(dto);
}
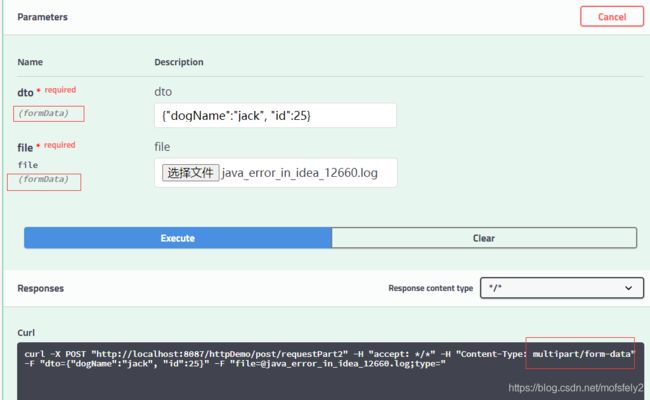
点击执行,报错:HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException: Content type ‘application/octet-stream’ not supported
参考地址:https://blog.csdn.net/gao_grace/article/details/96431269
大概的意思是:使用swagger调用的api,查看swagger生成的curl命令发现,请求中file这个参数指定了content-type,但是dto却并没有。后端的找不到contentType,只好使用默认的application/octet-stream。但是又没有对应类型的消息转换器,所以就报不支持了。
我觉得说法上可能不准确,因为一个请求只能有一个contentType,并不是一个参数配一次。不过DTO需要设置它的dataType为json,这样才行。但是swagger目前没有支持的配置,实际的前端是有的(前端代码不熟,有知道的可以提供一下示例)。
解决的方案是写一个@component注解转换器的类,如下:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.converter.json.AbstractJackson2HttpMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
/**
*@author: aliyu
*@create: 2021/1/14 10:35
*@description: 增加对application/octet-stream的消息转换器
* 用@RequestPart同时上传文件和json时,传入的contentType为null,导致使用默认的application/octet-stream
* 而application/octet-stream没有对应的消息转换器
*/
@Component
public class MultipartJackson2HttpMessageConverter extends AbstractJackson2HttpMessageConverter {
protected MultipartJackson2HttpMessageConverter(ObjectMapper objectMapper) {
super(objectMapper, MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM);
}
@Override
public boolean canWrite(Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean canWrite(Type type, Class<?> clazz, MediaType mediaType) {
return false;
}
@Override
protected boolean canWrite(MediaType mediaType) {
return false;
}
}
重启项目后,可以正常传递参数。
查询——@GetMapping
主要用于查询。
get请求特点:
a. 请求参数会添加到请求资源路径的后面,只能添加少量参数(因为请求行只有一行,大约只能存放2K左右的数据)
b. 请求参数会显示在浏览器地址栏,路由器会记录请求地址 (极为的不安全)
极少参数的查询,查询参数不包含实体类(只是基本类型)
查询参数不超过3个,最多的情况是通过id获取详情。如果超过3个,建议新建一个DTO来存放。
@ApiOperation("基本类型参数,少量参数传参")
@GetMapping("/get/getMapping")
public ResponseVo<String> getMapping(
@ApiParam(value = "你的名字") @RequestParam String name,
@ApiParam(value = "性别") @RequestParam String sex,
@ApiParam(value = "年龄") @RequestParam Integer age){
return ResponseFactory.success(name);
}
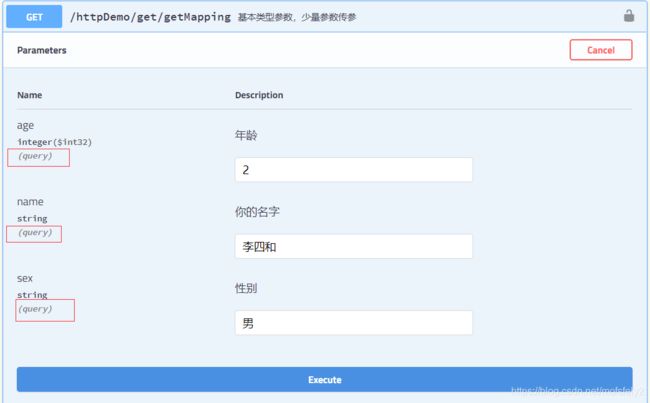 注:执行后可以正常获取参数,至于为什么不使用@PathVariable?因为前面说到它不支持参数非空校验,还有就是不能输入像“/”这样的特殊字符。如果参数不加@RequestParam 也是可以的,不过就是参数都非必输了(因为RequestParam 默认就是必输)。如果参数非空的话,这个注解就必须加上了。
注:执行后可以正常获取参数,至于为什么不使用@PathVariable?因为前面说到它不支持参数非空校验,还有就是不能输入像“/”这样的特殊字符。如果参数不加@RequestParam 也是可以的,不过就是参数都非必输了(因为RequestParam 默认就是必输)。如果参数非空的话,这个注解就必须加上了。
查询参数为DTO
业务场景上,一个模块的查询一般都是某一个实体类的部分字段,如果字段比较多,或者考虑到扩展性。就应该建一个DTO来传递。对于get请求,是不能使用@ResponseBody的。这时候这个dto其实啥注解也不加就可以了。
/**
* get请求dto传参。
* @param dto
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation("dto传参")
@GetMapping("/get/getMapping2")
public ResponseVo<String> getMapping2(DogDTO dto){
return ResponseFactory.success(dto.getDogName());
}
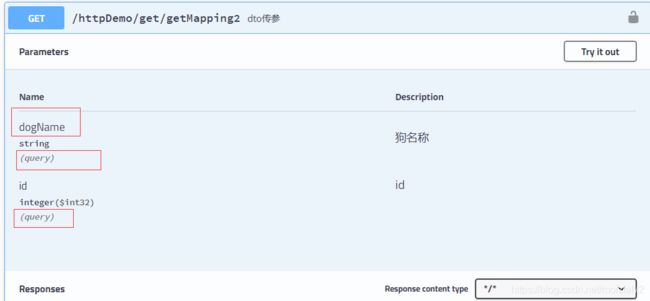
注:不加默认也是query传参,至于dto参数的校验是通过在dto实体类中为各个属性加校验注解的方式实现的(可以参考我的另一篇校验的文章)
新增——@PostMapping
幂等性:是指一次和多次请求某一个资源对于资源本身应该具有同样的结果(网络超时等问题除外)。
也就是说,其任意多次执行对资源本身所产生的影响均与一次执行的影响相同,
http协议明确规定,put、get与delete请求都是具有幂等性的,而post为非幂等性请求。
偏向于添加时使用
a. 请求参数添加到实体内容里面,可以添加大量的参数(也解释了为什么浏览器地址栏不能发送post请求,在地址栏里我们只能填写URL,并不能进入到Http包的实体当中)
b. 相对get安全,但是,post请求不会对请求参数进行加密处理(可以使用https协议来保证数据安全)。
极少参数的新增(参数只是基本类型,不建议)
这种情况,比较少见。一般新增都会新增一条数据。表字段一般不会太少,所以新增时要录入的参数一般也不会太少。
@ApiOperation("post请求-少量参数-RequestParam传参")
@PostMapping("/post/postMappring")
public ResponseVo postMappring(@ApiParam(value = "你的名字") @RequestParam String dogName,
@ApiParam(value = "年龄") @RequestParam int age,
@ApiParam(value = "性别") @RequestParam String sex) {
return ResponseFactory.success(dogName);
}
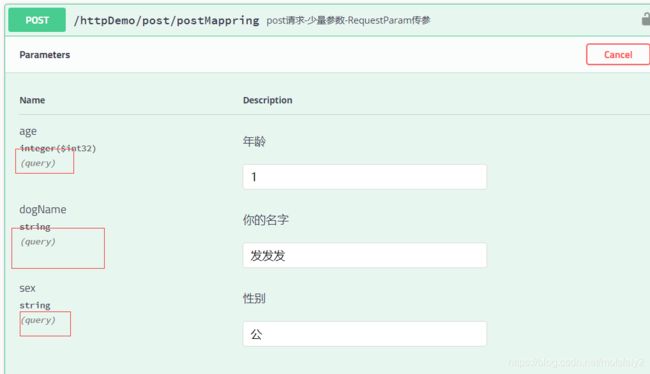
注:可以看到,这样的参数其实是存在url中的,和get差不多了。。。所以不建议这样写。
另外如果一个参数建一个@RequestBody,会报错“I/O error while reading input message; nested exception is java.io.IOException: Stream closed”。有个牛人写了“SpringBoot Controller 中使用多个@RequestBody的正确姿势”,地址:https://blog.csdn.net/w605283073/article/details/82119284
总结:基于以上,即使只有一两个参数,也建议使用dto。
参数为DTO
新增所有需要的参数放入一个dto中,不包括有文件的情况。
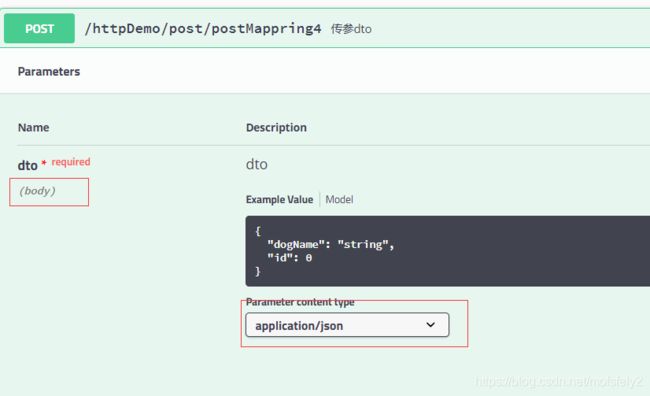
@ApiOperation("传参dto")
@PostMapping("/post/postMappring4")
public ResponseVo postMappring4(@RequestBody DogDTO dto) {
return ResponseFactory.success(dto.getDogName());
}
参数为DTO加文件
遇到上传文件时,只能使用@RequestPart注解文件,dto也必须使用@RequestPart注解。这是因为当同时存在@RequestPart和@RequestBody时。@RequestPart的优先级更高,会将contentType设置为multipart/form-data。但前面说过@RequestBody不支持multipart/form-data。
/**
* 注解一个dto和一个文件
* @param dto
* @param file
* @return
*/
@ApiOperation("RequestPart注解上传文件和DTO")
@PostMapping("/post/requestPart5")
public ResponseVo postMappring5(@RequestPart DogDTO dto,
@RequestPart MultipartFile file) {
return ResponseFactory.success(dto);
}
修改——@PutMapping
参数为基本类型
使用@RequestParam
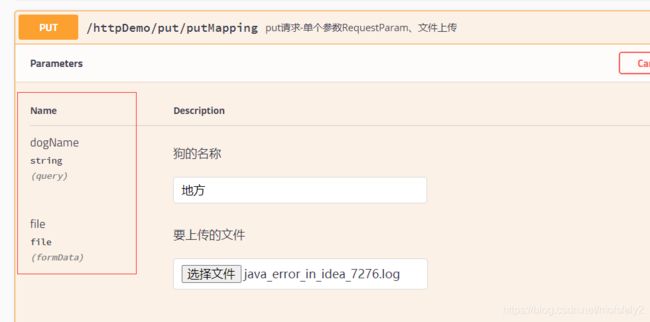
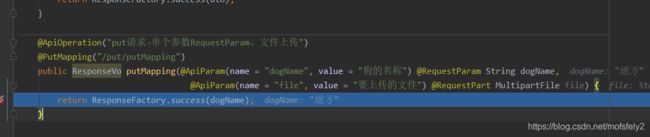
@ApiOperation("put请求-单个参数RequestParam、文件上传")
@PutMapping("/put/putMapping")
public ResponseVo putMapping(@RequestParam String dogName,
@RequestPart MultipartFile file) {
return ResponseFactory.success(dogName);
}
参数为DTO加文件
@ApiOperation("put请求-DTO加文件上传")
@PutMapping("/put/putMapping2")
public ResponseVo putMapping2(@RequestPart DogDTO dto,
@RequestPart MultipartFile file) {
return ResponseFactory.success(dto.getDogName());
}
注:与post没有区别,不作特殊说明
删除——@DeleteMapping
通过基本类型参数(少参数)
PathVariable 方式
/**
* 单个参数
* @param id
* @return
*/
@DeleteMapping("/deleteMapping/{id}")
public ResponseVo deleteMapping(
@ApiParam(required = false, value = "主键id") @PathVariable int id) {
return ResponseFactory.success(id);
}
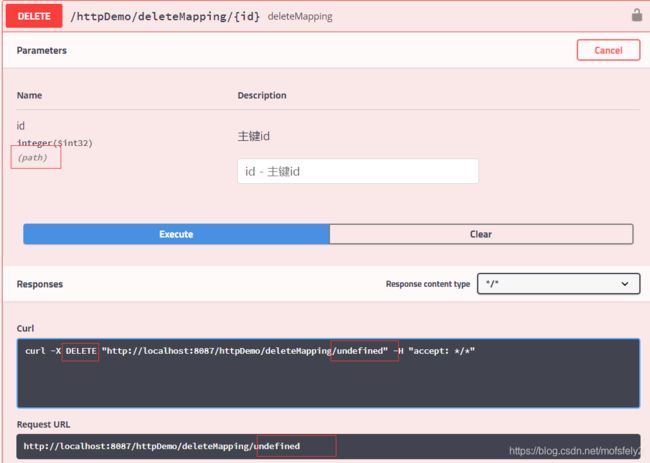
注:getMapping时PathVariable 注解的参数是可以为null的,但是@DeleteMapping时却不可以,此时它默认id是一定要有值的。所以如果确定id不存在特殊字符,且一定有值,可以使用这种方式。
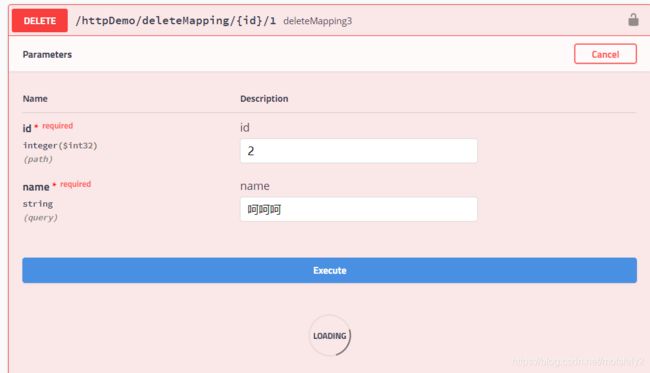
RequestParam方式
@DeleteMapping("/deleteMapping/{id}/1")
public ResponseVo deleteMapping3(@PathVariable int id,
@RequestParam String name) {
return ResponseFactory.success(id + name);
}
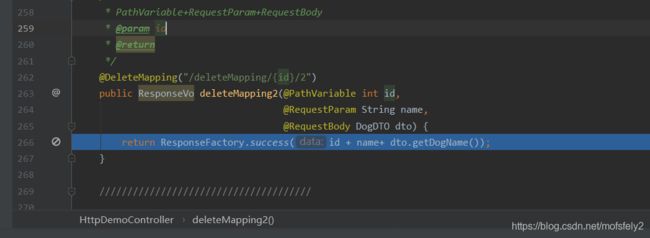
通过DTO
/**
* PathVariable+RequestParam+RequestBody
* @param id
* @return
*/
@DeleteMapping("/deleteMapping/{id}/2")
public ResponseVo deleteMapping2(@PathVariable int id,
@RequestParam String name,
@RequestBody DogDTO dto) {
return ResponseFactory.success(id + name+ dto.getDogName());
}
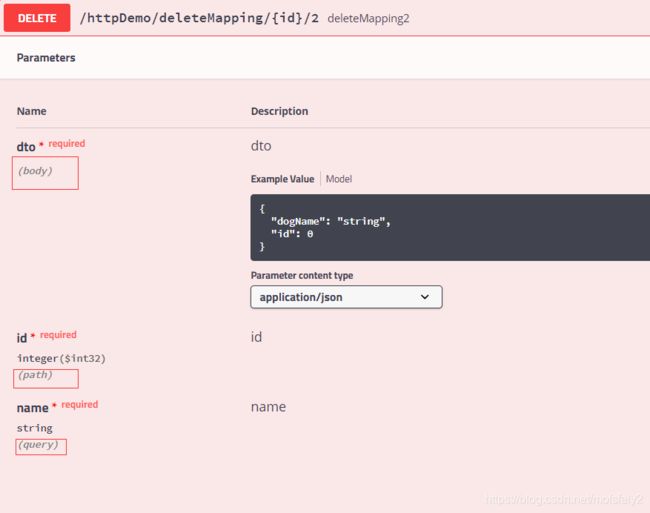
注:很奇怪,本来以为会和getMaping 一样,无法使用RequestBody。
没想到竟然可以。
总结
http既然针对增删改查的业务场景区分了4种mapping,那么自然是有它的用意的。只是网络不熟,所以不明白,百度上也几乎没有说明。不过照着用总是没有问题的。写postMapping时提到了幂等性,我猜测http可能根据请求对数据库的具体操作,进行了定制优化。